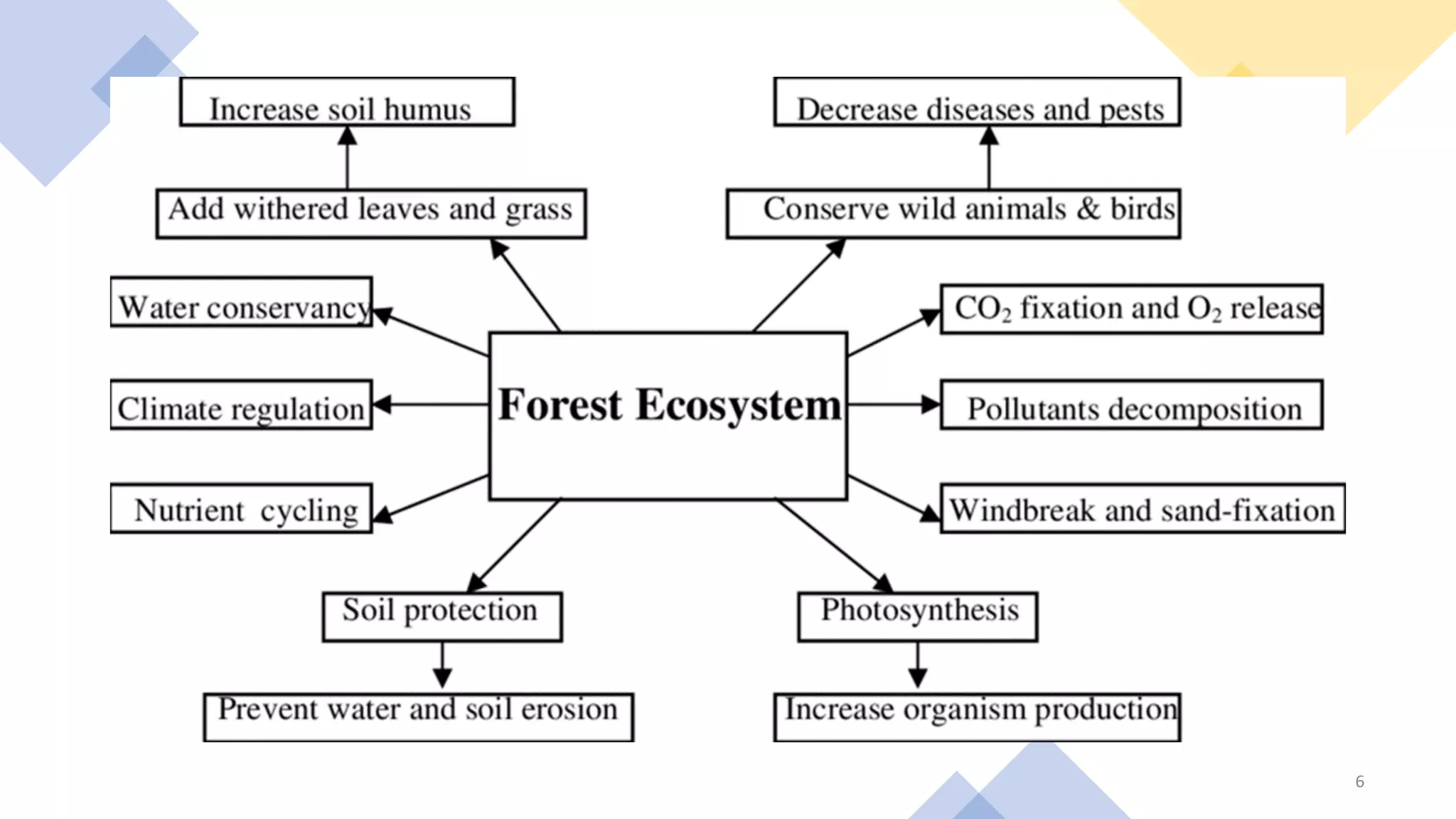
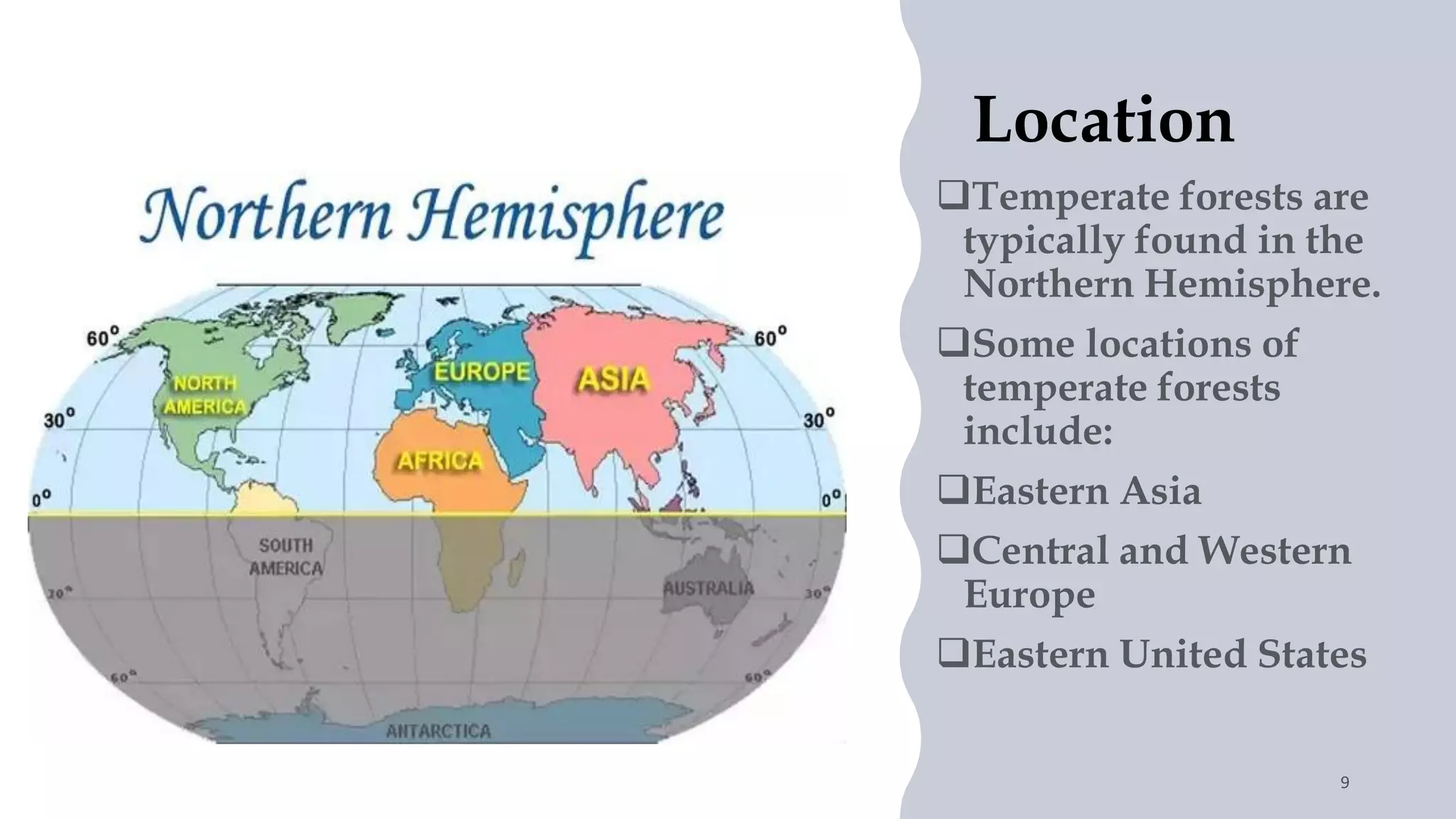
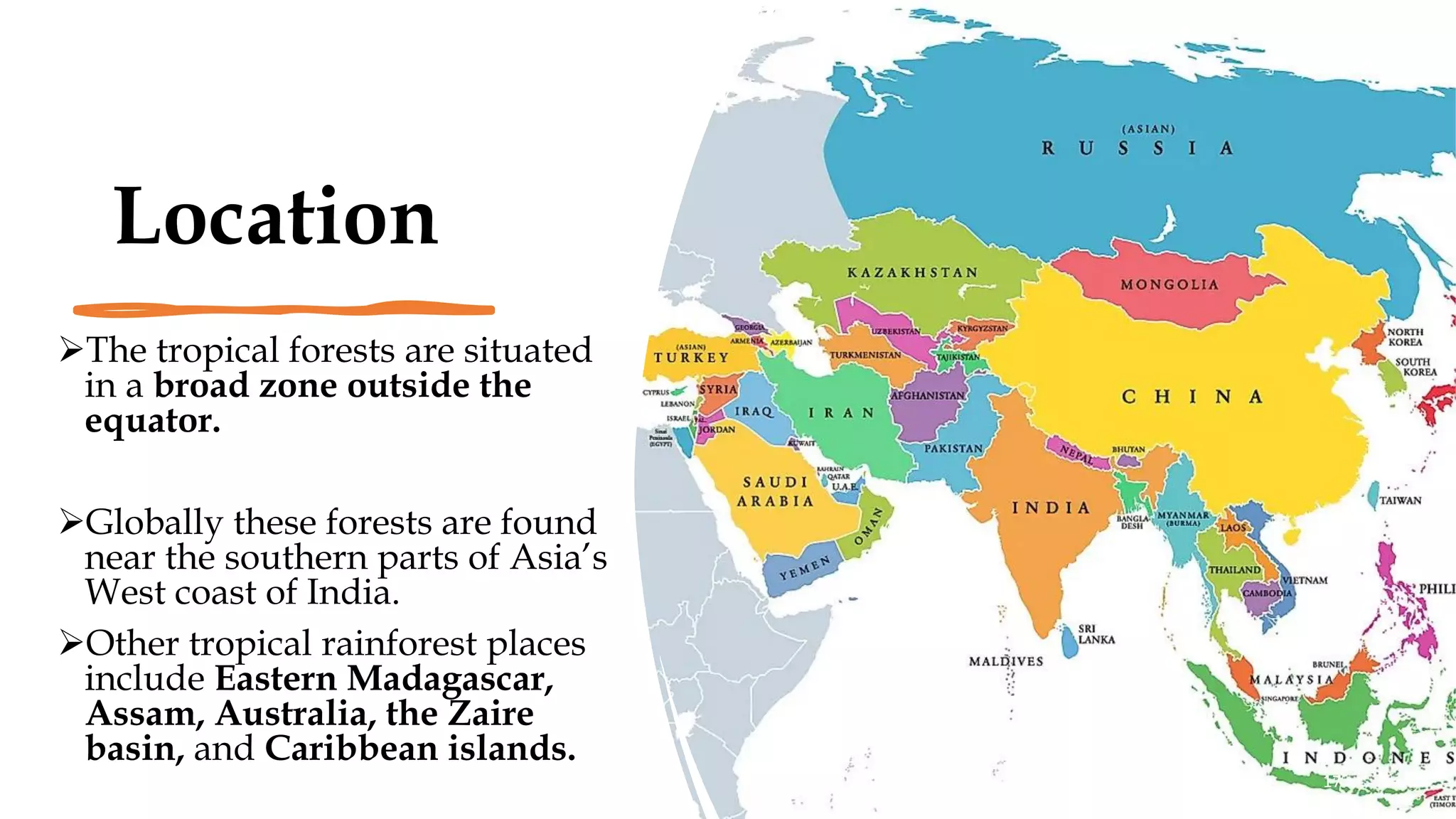
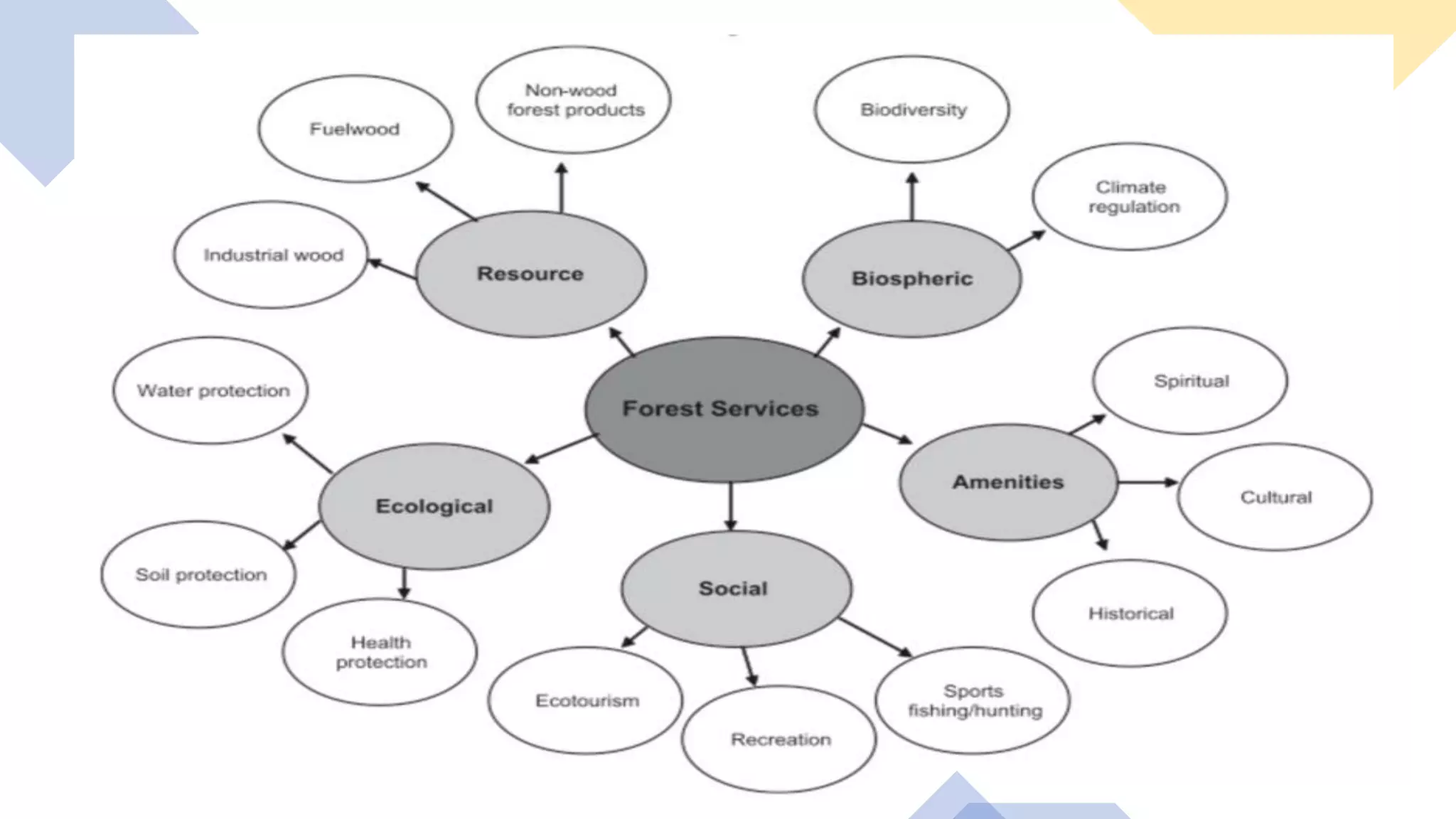
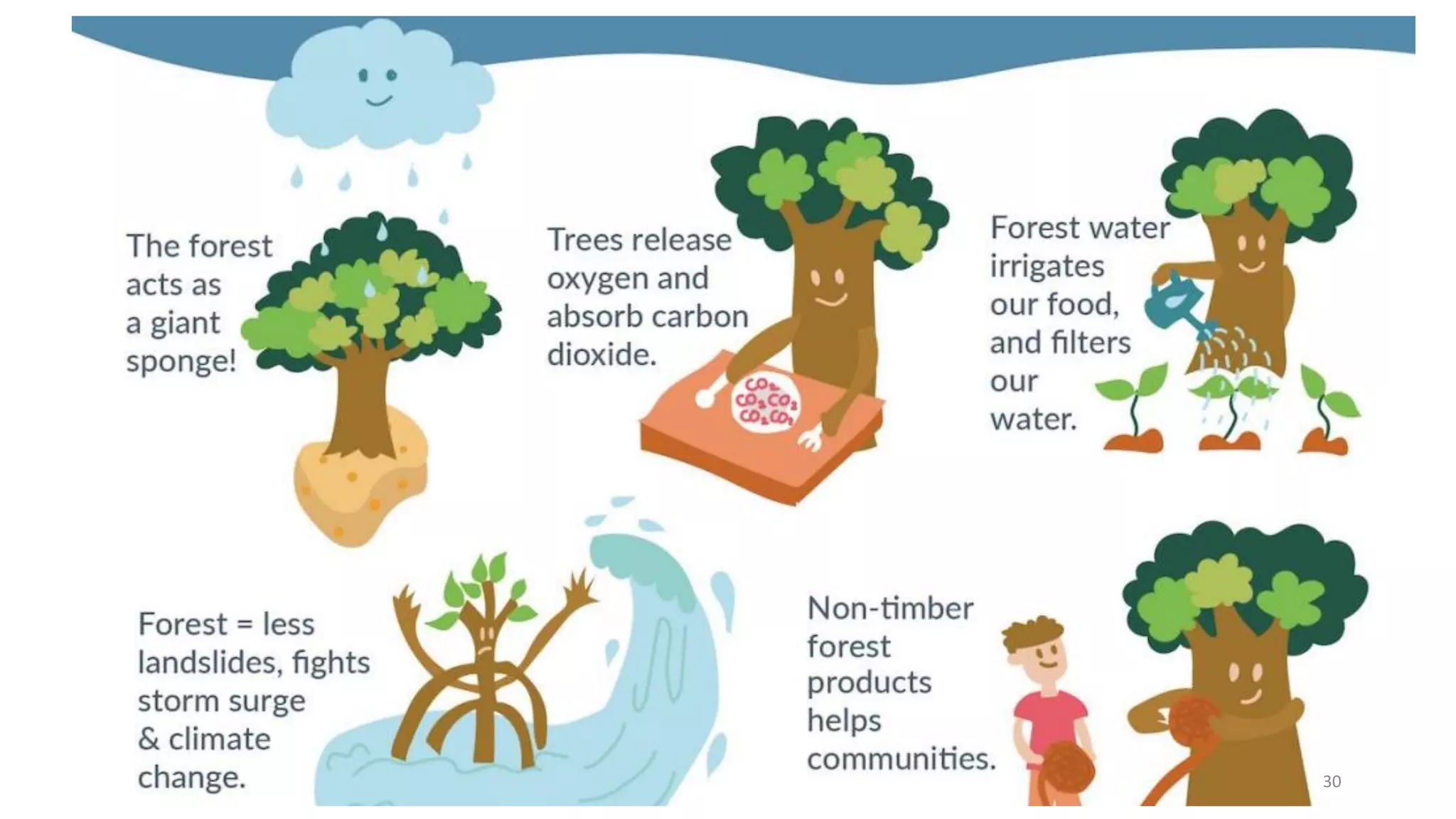
Forests, covering around 40% of the Earth's land, are ecosystems dominated by trees and diverse communities of plants, animals, and microbes. They are classified into three main types: tropical, temperate, and alpine forests, each with specific climatic conditions, flora, and fauna. Forests offer numerous ecological benefits, including clean air and water, wildlife habitat, and support in combating climate change.