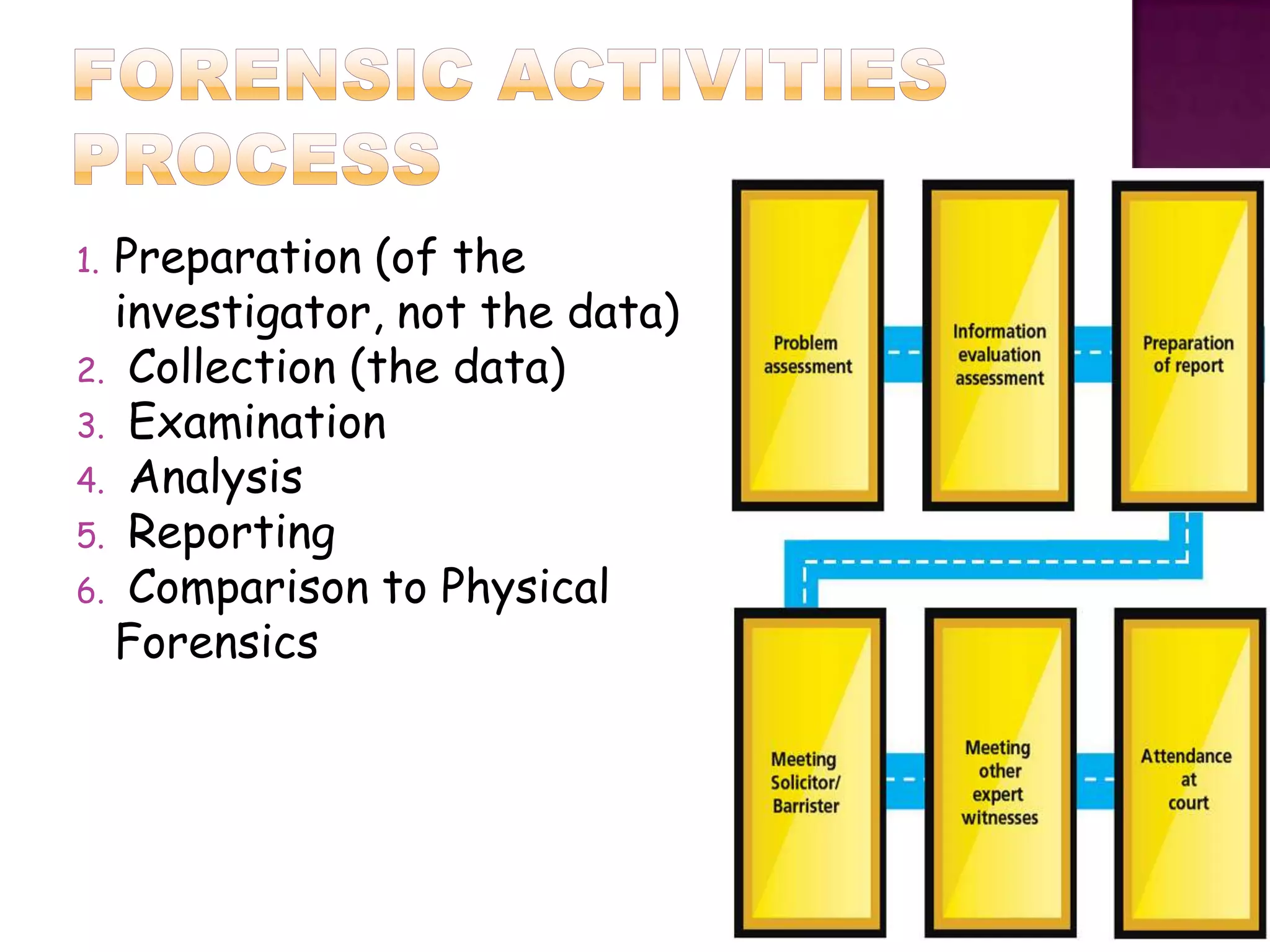
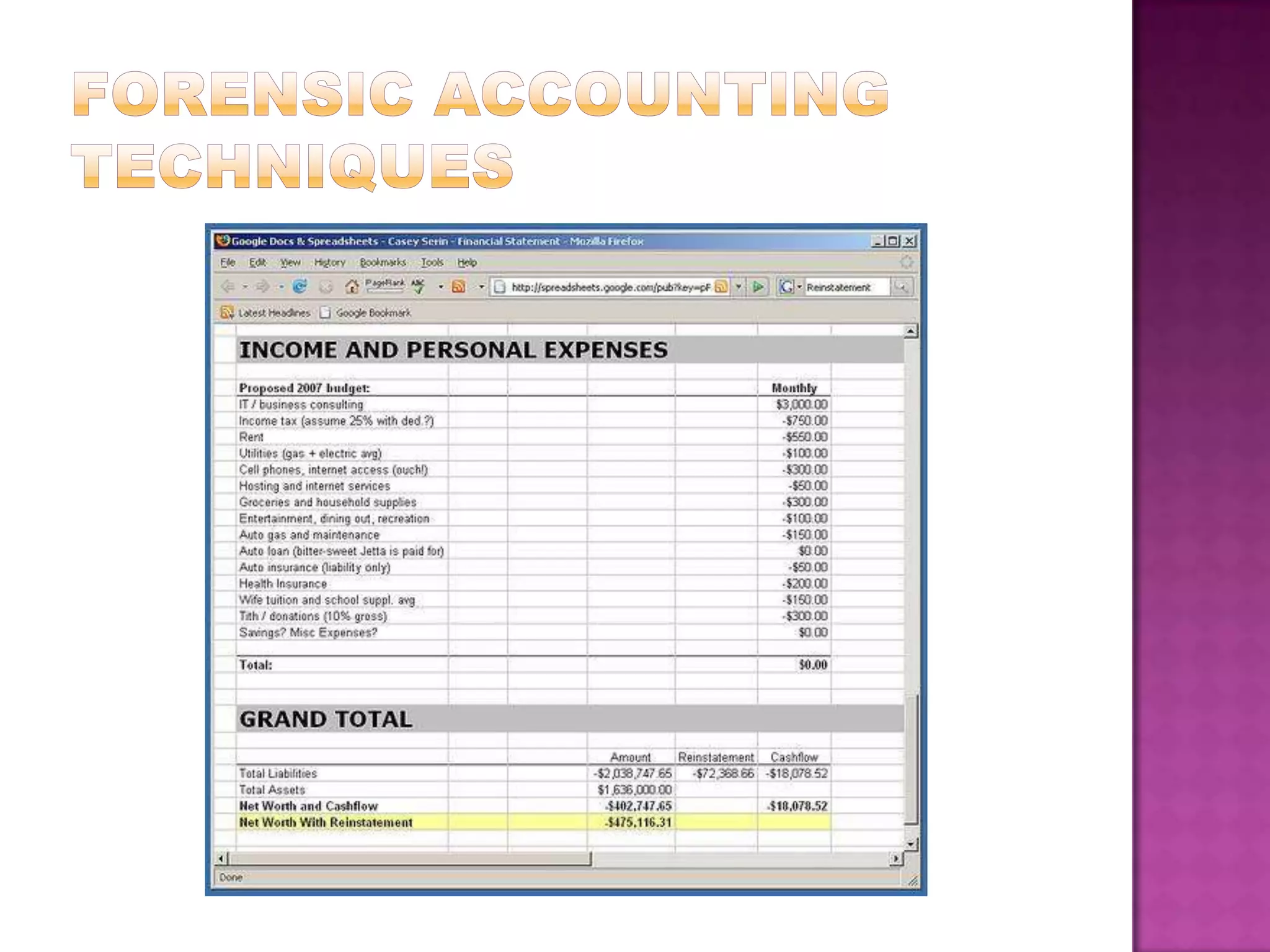
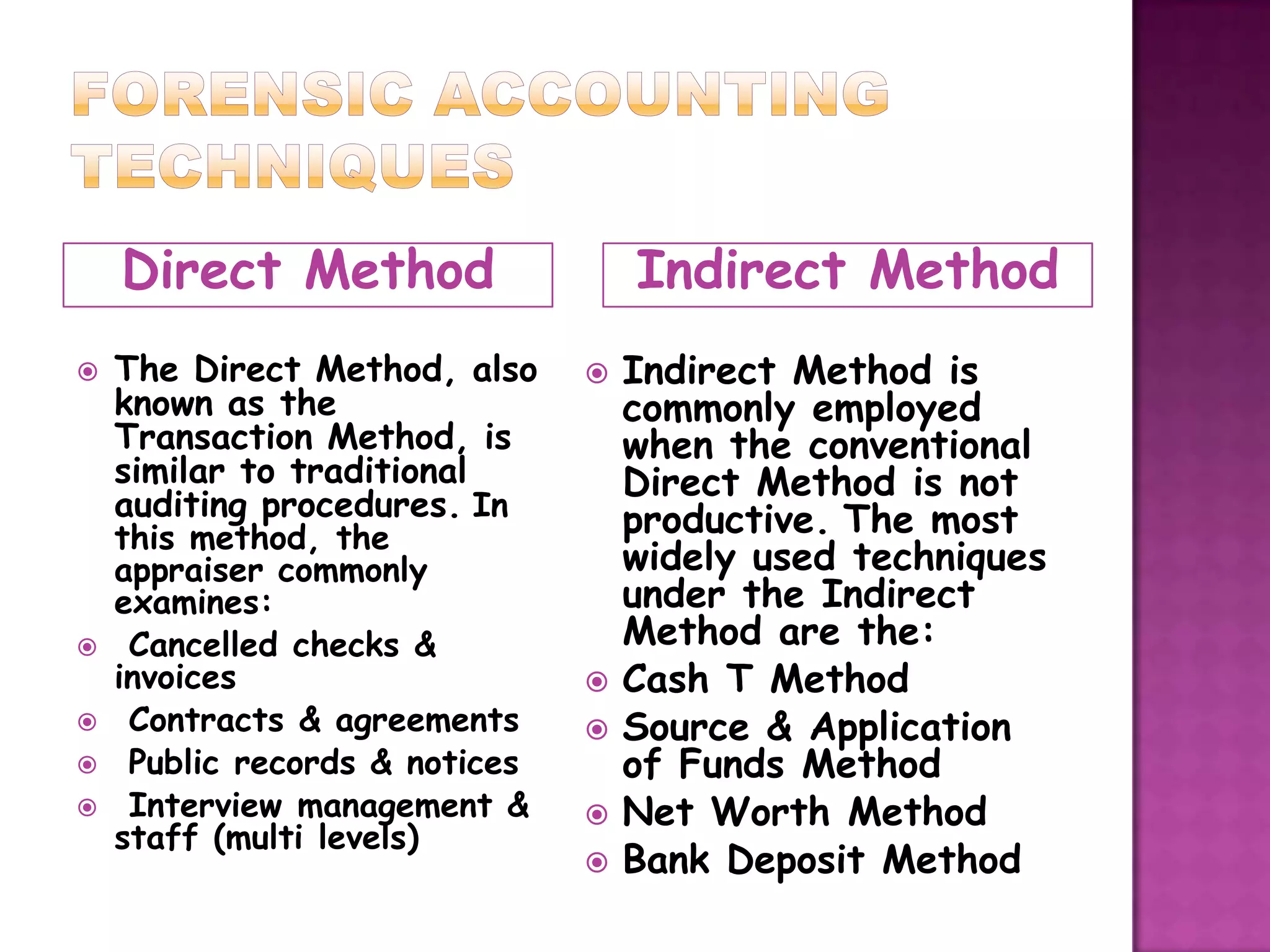
Forensic accounting is a specialized area of accounting that investigates financial fraud and white collar crimes. It has been used for nearly 200 years to assist courts and investigate matters like employee theft, securities fraud, and insurance fraud. Forensic accountants use techniques like cash flow analysis and net worth calculations to detect anomalies and trace missing funds. Their work supports litigation, investigations, and helps protect businesses, banks, and the public from financial deception and crime.