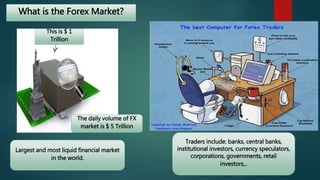
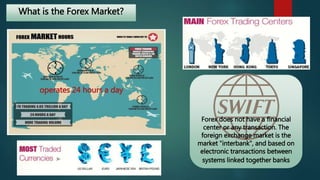
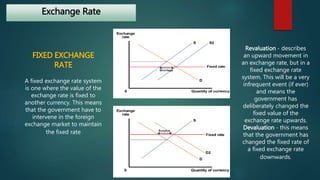
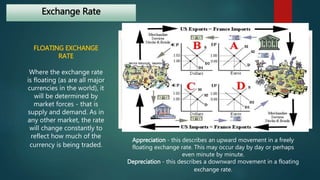
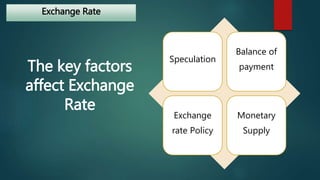
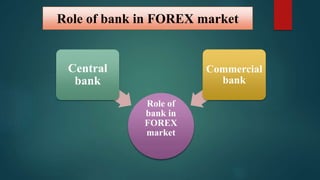
The document discusses the foreign exchange market. It begins by defining the forex market as a decentralized global market for trading currencies without a central exchange. It operates 24/7 globally with a daily trading volume of $5 trillion, making it the largest financial market in the world. Commercial banks and their clients participate in the forex market, trading currency pairs like EUR/USD. The document also discusses exchange rates, factors that influence rates like balance of payments and monetary supply, and the roles that central banks and commercial banks play in the forex market.