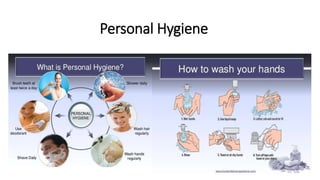
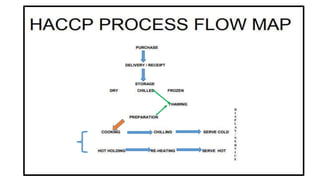
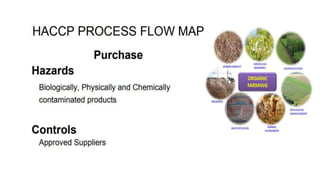
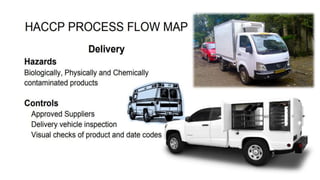
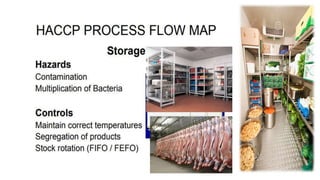
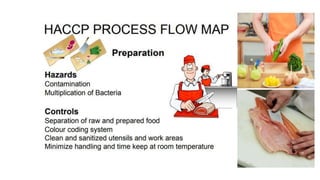
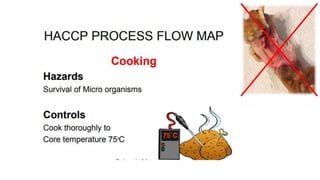
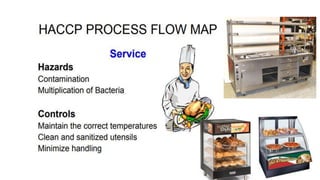
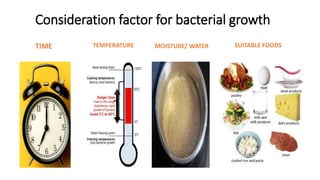
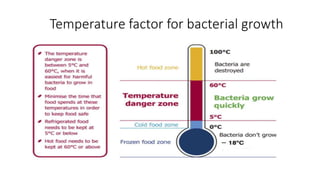
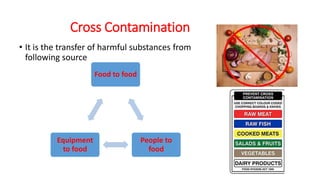
This document discusses key concepts of basic food safety. It outlines three important aspects of hygiene - food hygiene, kitchen hygiene, and personal hygiene. Food hygiene involves using safe water/raw materials, properly cooking and cooling foods, and preventing contamination. Kitchen hygiene requires properly cleaning and sanitizing surfaces and equipment. Personal hygiene refers to practicing good hygiene habits while handling food. The document also discusses food safety principles like preventing cross-contamination and properly storing foods.