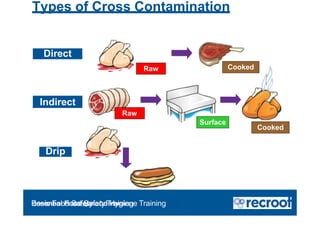
The document outlines the importance of food safety and hygiene in the food industry, emphasizing the responsibilities of food handlers to prevent contamination and foodborne illnesses. It details various types of hazards (physical, chemical, biological) that can affect food safety, proper food storage, cooking temperatures, and personal hygiene practices. Key measures to prevent cross-contamination and maintain hygiene standards are also discussed, along with the legal responsibilities of food businesses to protect consumer health.