Embed presentation
Download to read offline


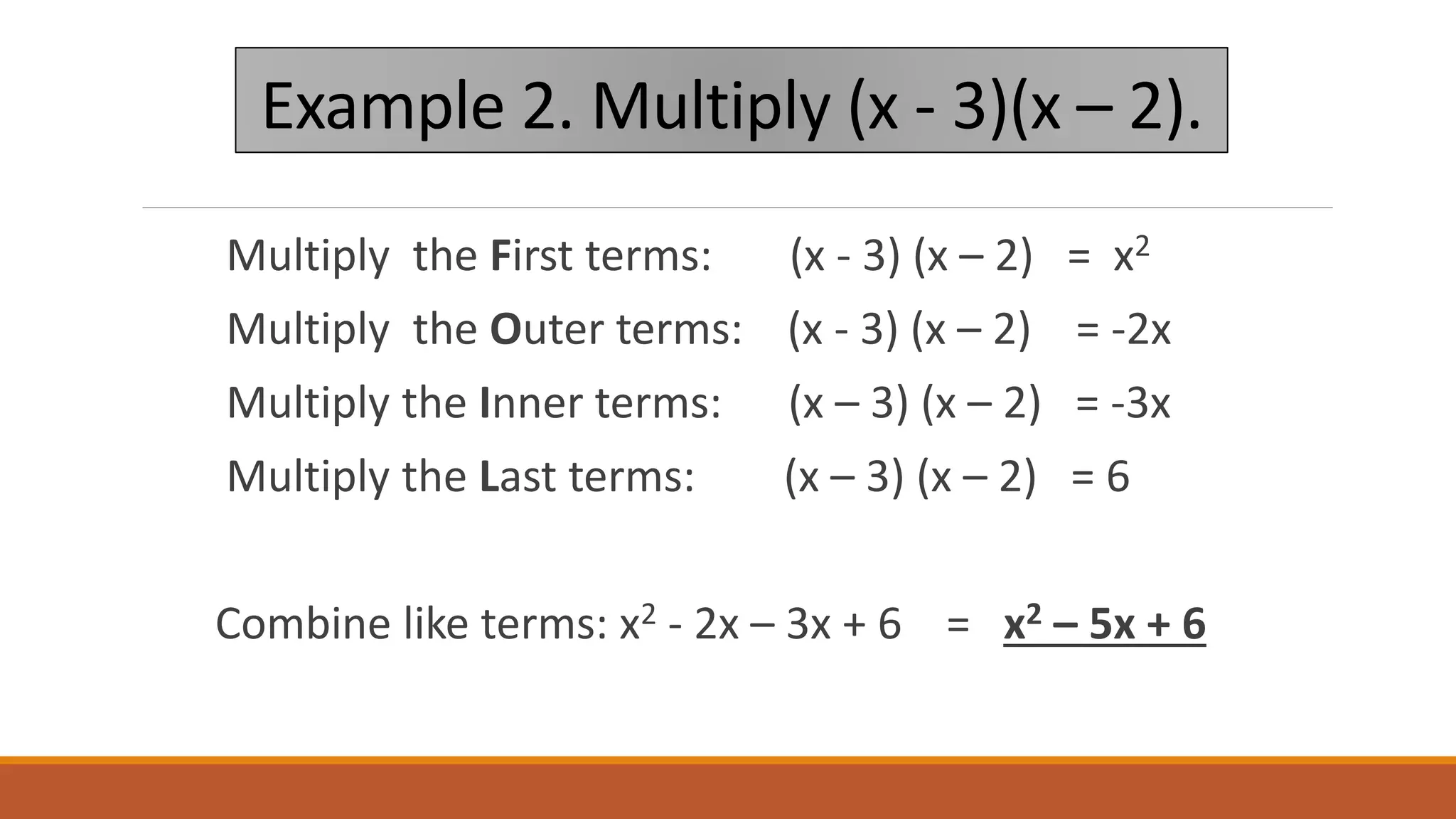
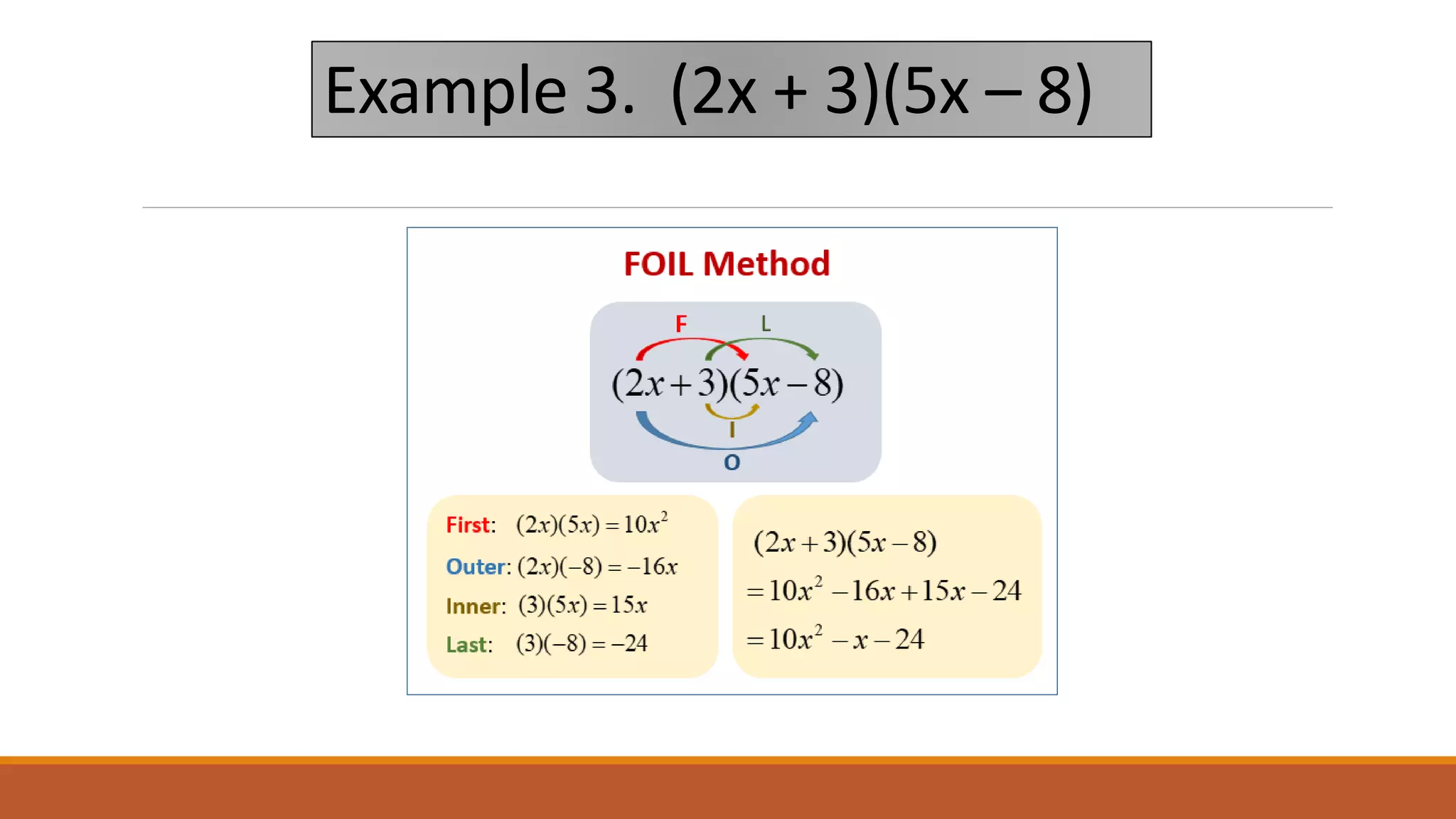
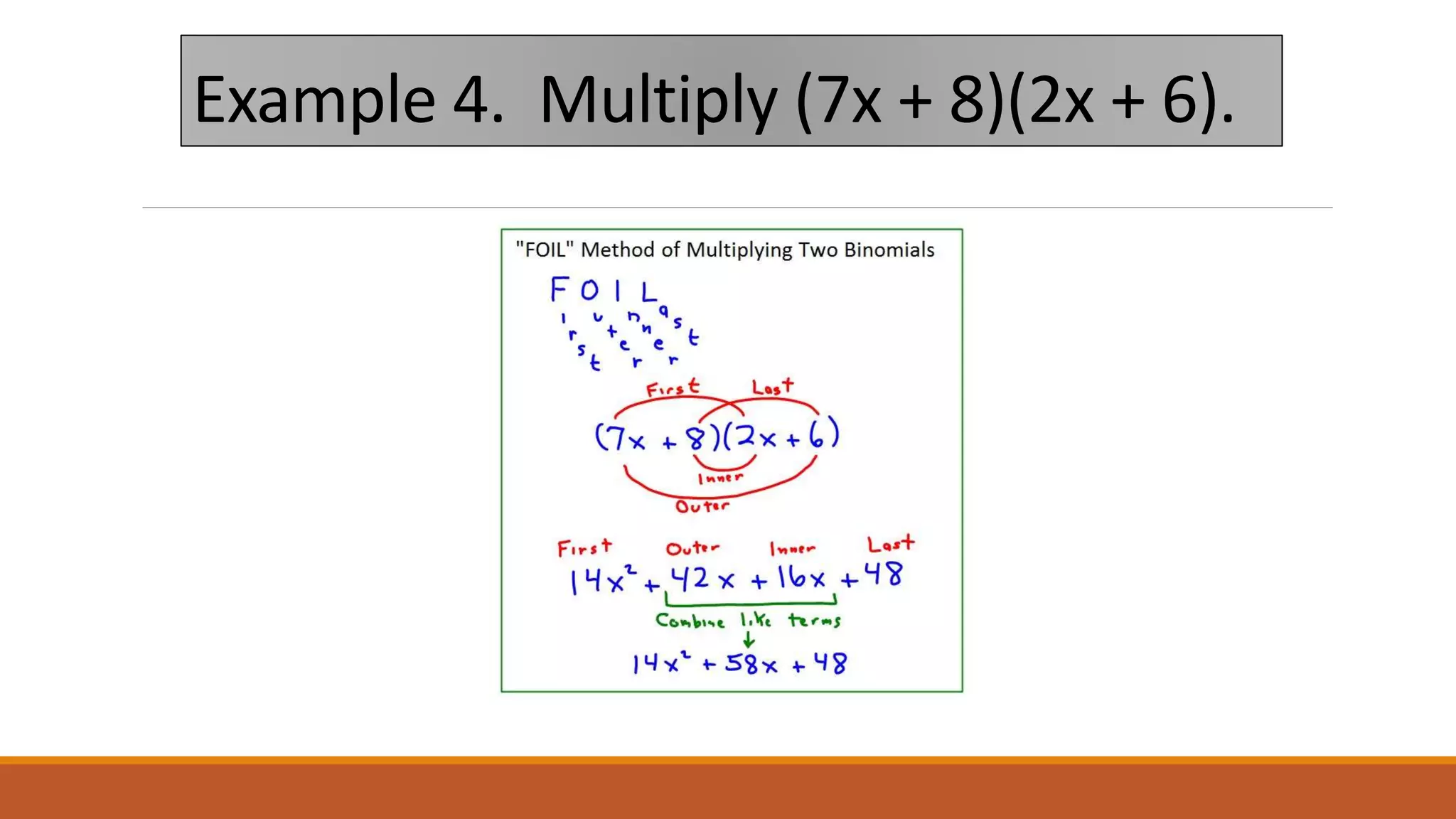
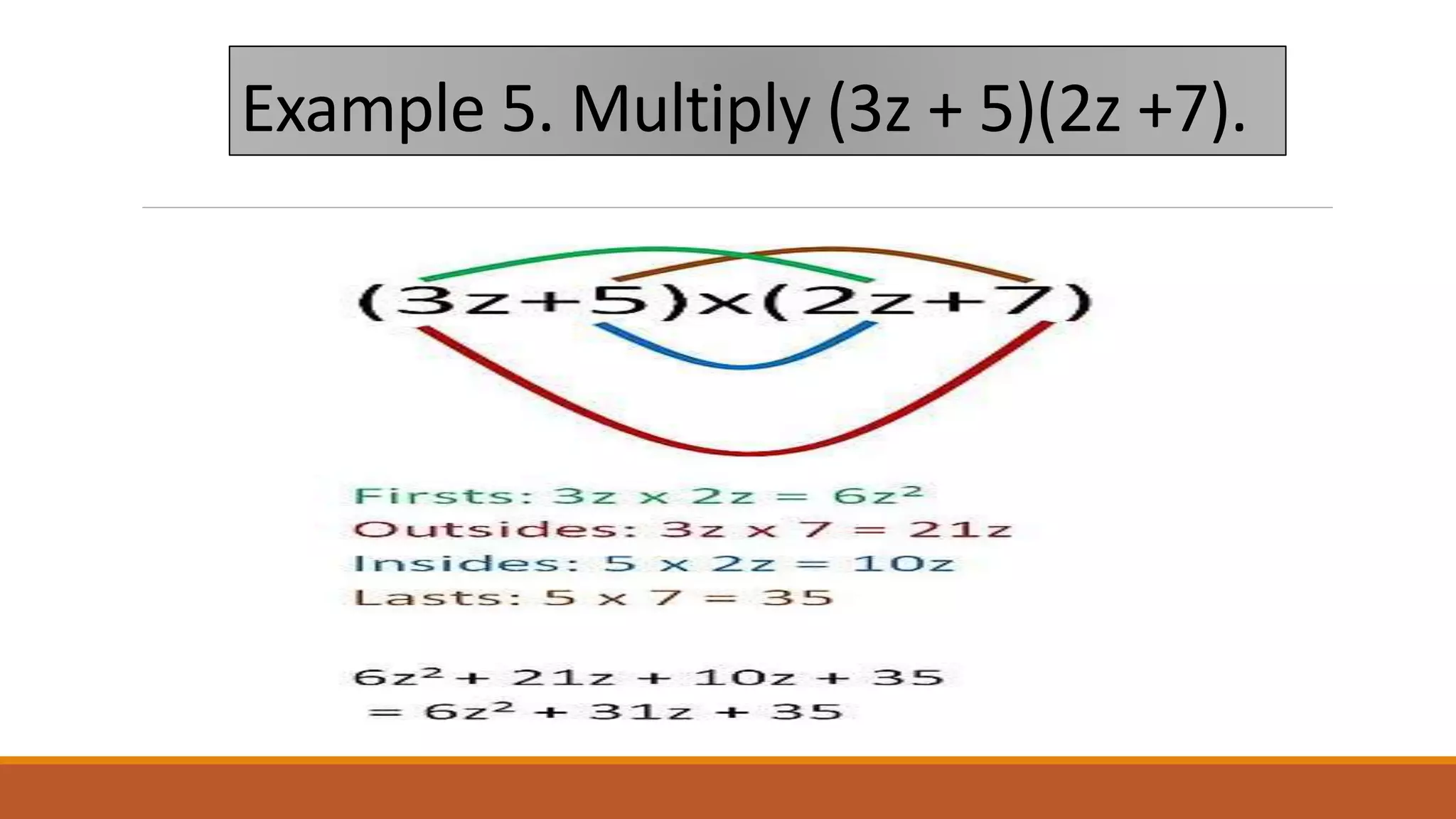
The document provides examples of using the FOIL (First, Outer, Inner, Last) method to multiply binomial expressions. It shows step-by-step work for multiplying (x + 2)(x - 4) and (x - 3)(x - 2) using FOIL. It then lists three additional practice problems for multiplying binomial expressions using FOIL without showing the steps.





