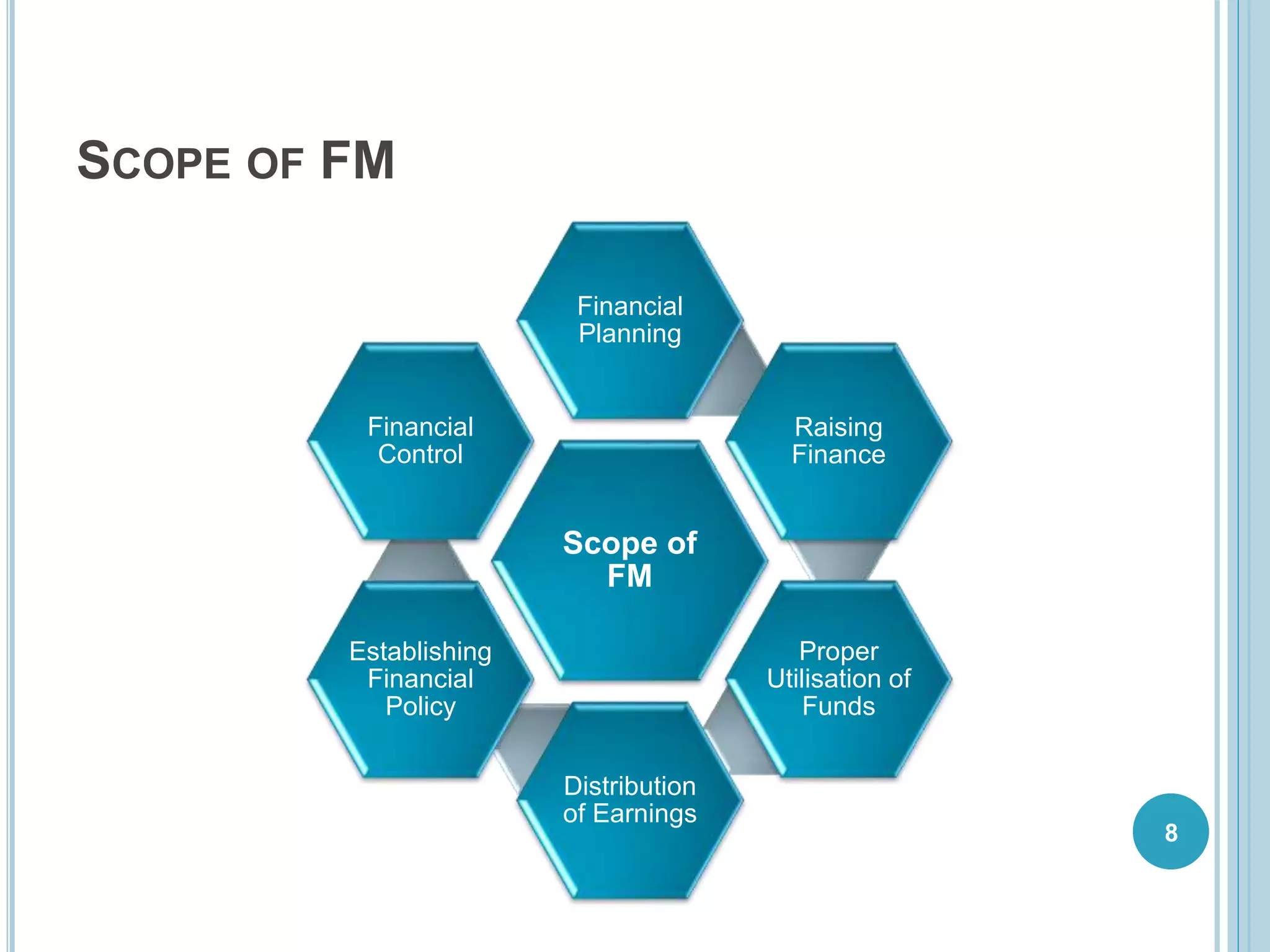
The document provides an introduction to financial management, outlining its meaning, nature, scope, and key functions such as finance, investment, dividend, and liquidity decisions. It discusses the goals of financial management, including profit and wealth maximization, along with the roles and responsibilities of a finance manager. Additionally, it contrasts traditional and modern approaches to financial management, emphasizing the importance of thorough financial planning and effective fund utilization across all business functions.