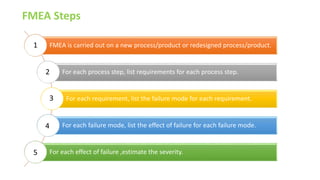
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic team approach to identify and evaluate potential failures and their effects, as well as to develop actions to mitigate risks. It is used to prevent failures in processes or products, particularly where failures could have serious consequences. The FMEA process involves several steps including listing requirements, identifying failure modes, estimating severity and occurrence, and recommending actions based on calculated risk priority numbers.