This document provides an analysis of the FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods) sector in India through SWOT, PEST, Porter's Five Forces, and market type analyses. Some key points:
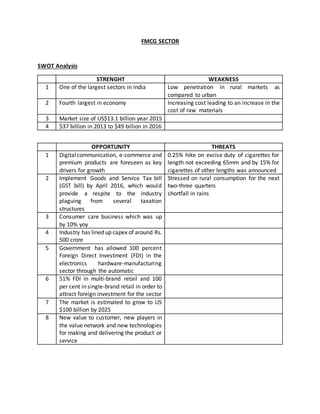
1) The FMCG sector in India has strengths such as its large market size and role in the economy, but weaknesses include low rural market penetration and increasing costs.
2) Opportunities for growth include digital/e-commerce expansion and policy changes like GST, while threats include increased taxation and weather issues impacting consumption.
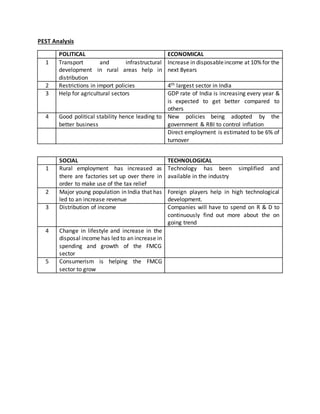
3) Political, economic, social and technological factors are analyzed in the PEST framework.
4) Porter's Five Forces analysis examines high competition and bargaining power of consumers