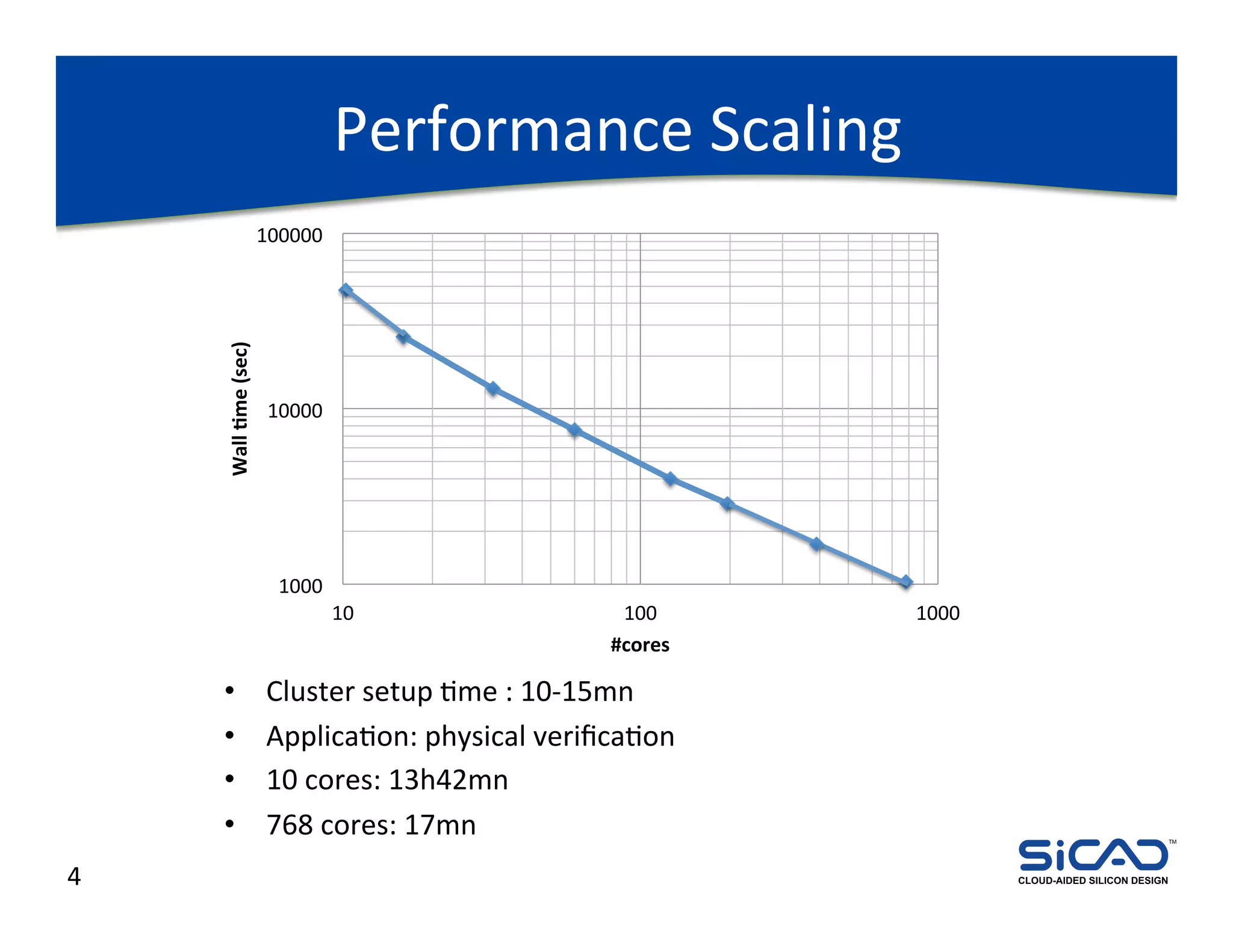
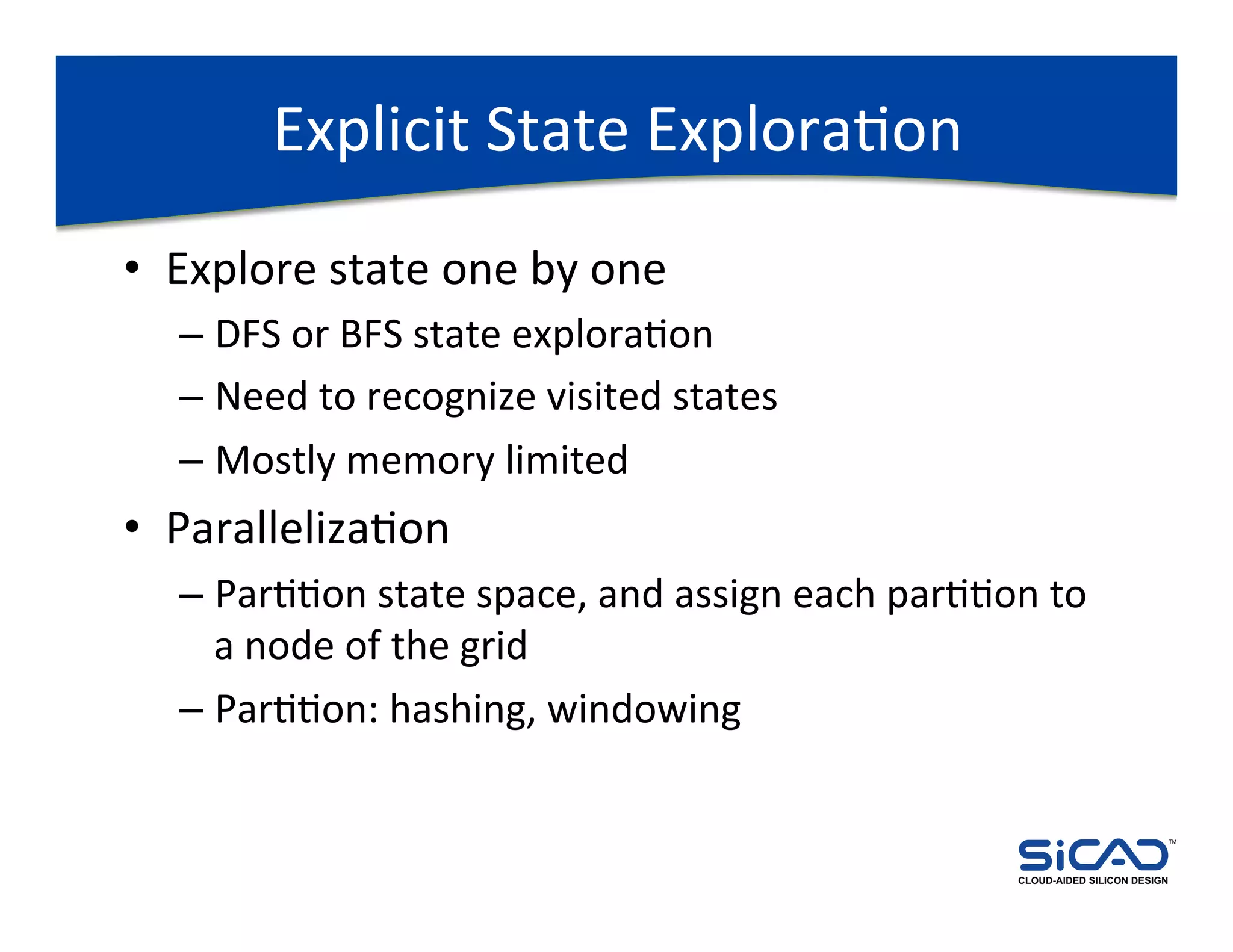
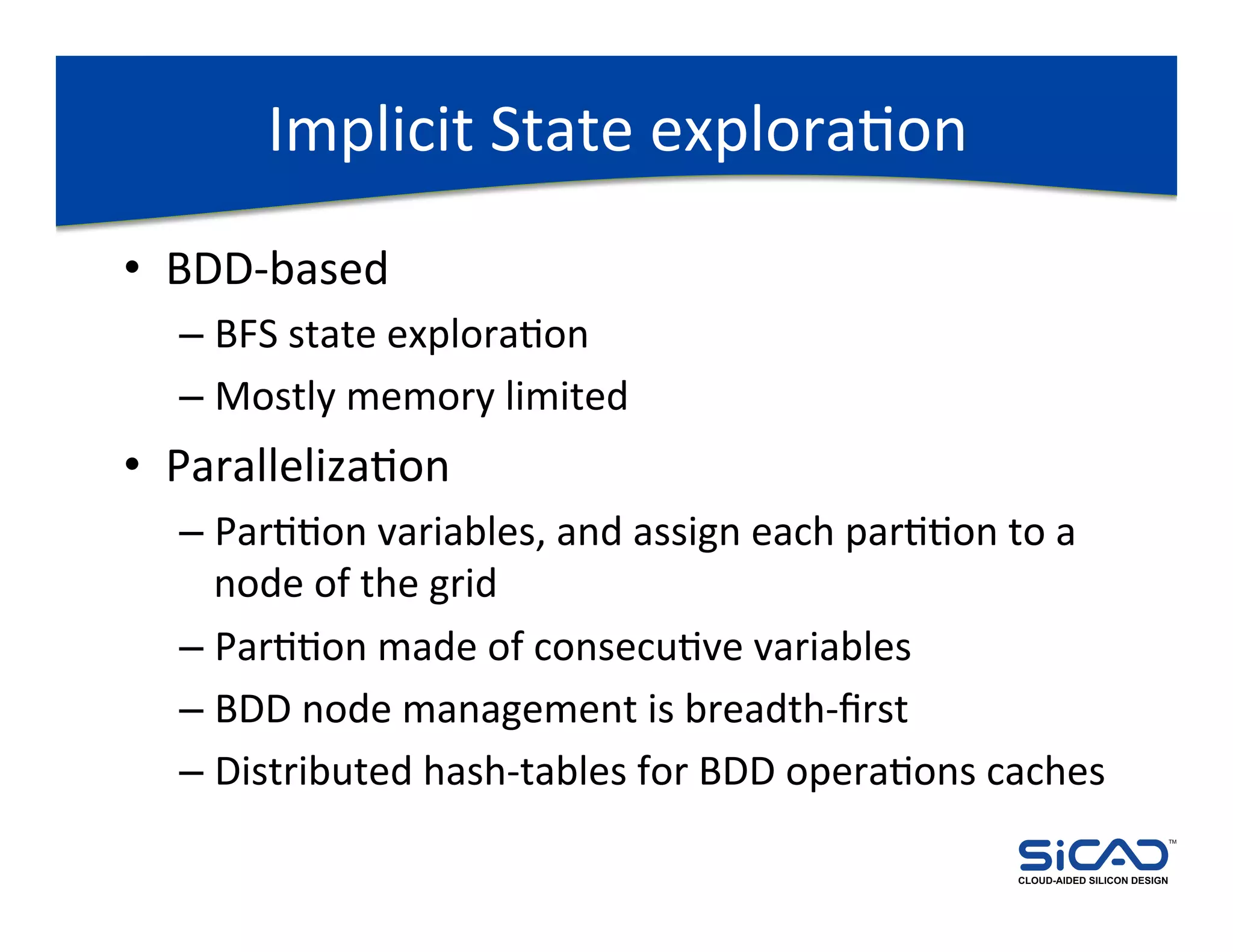
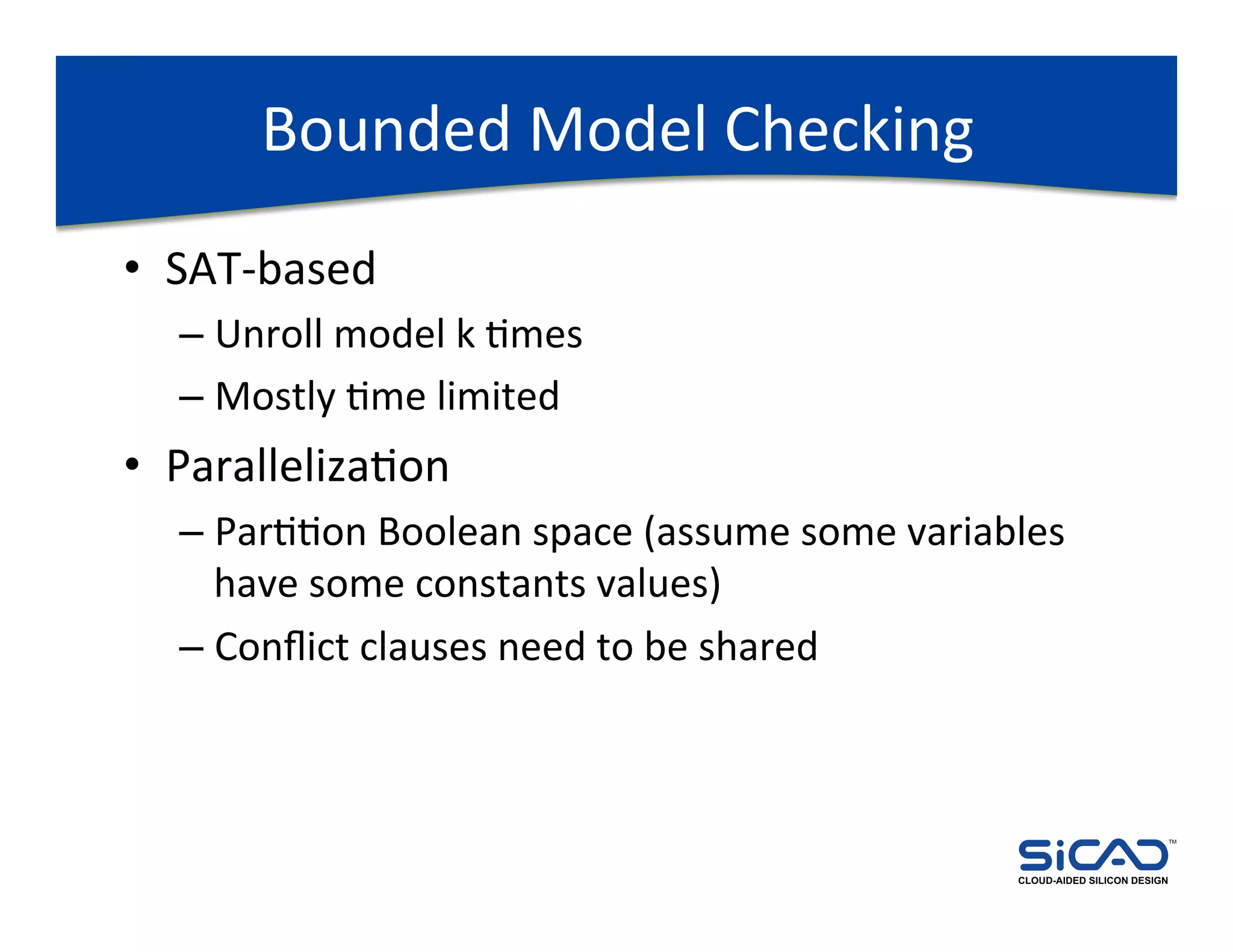
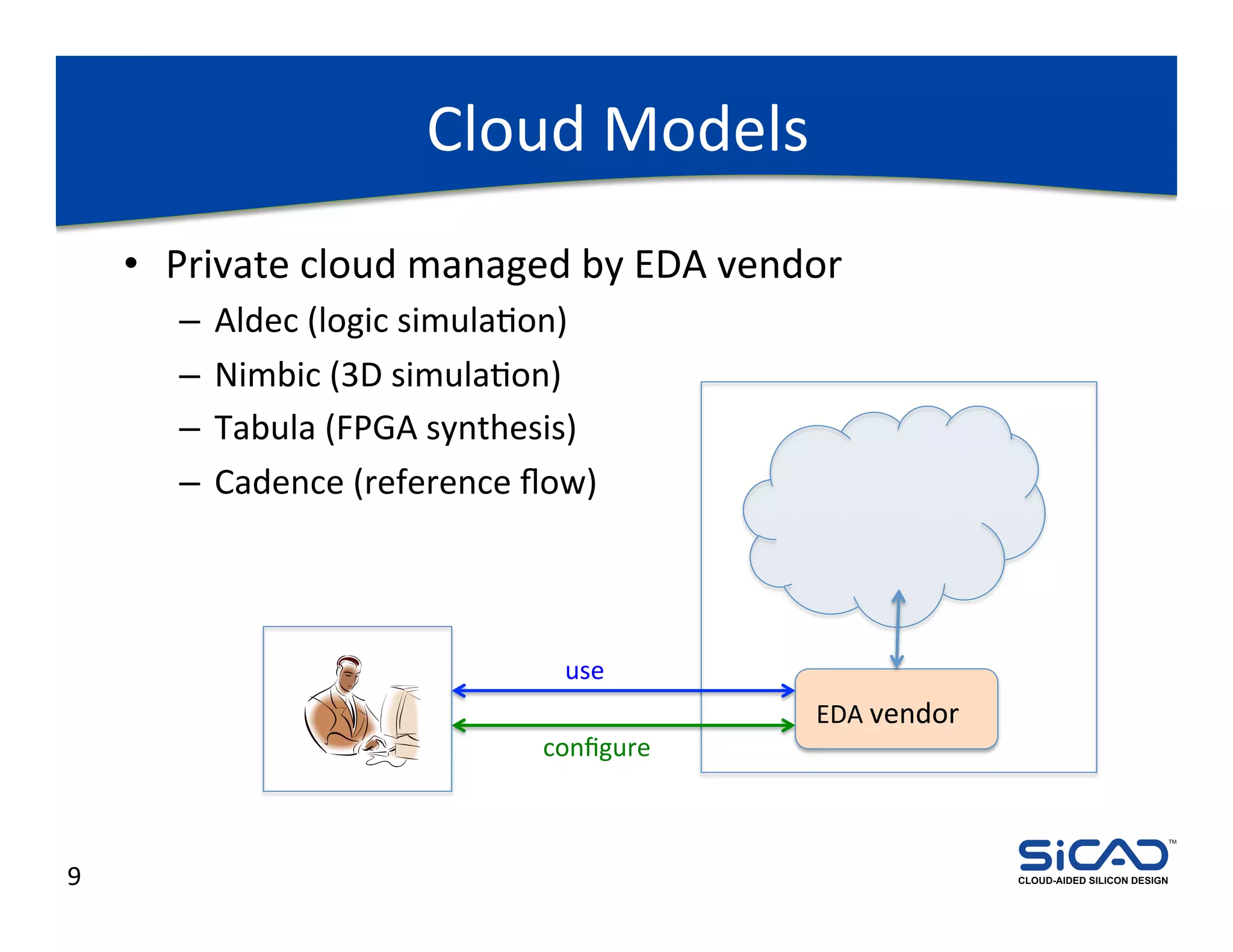
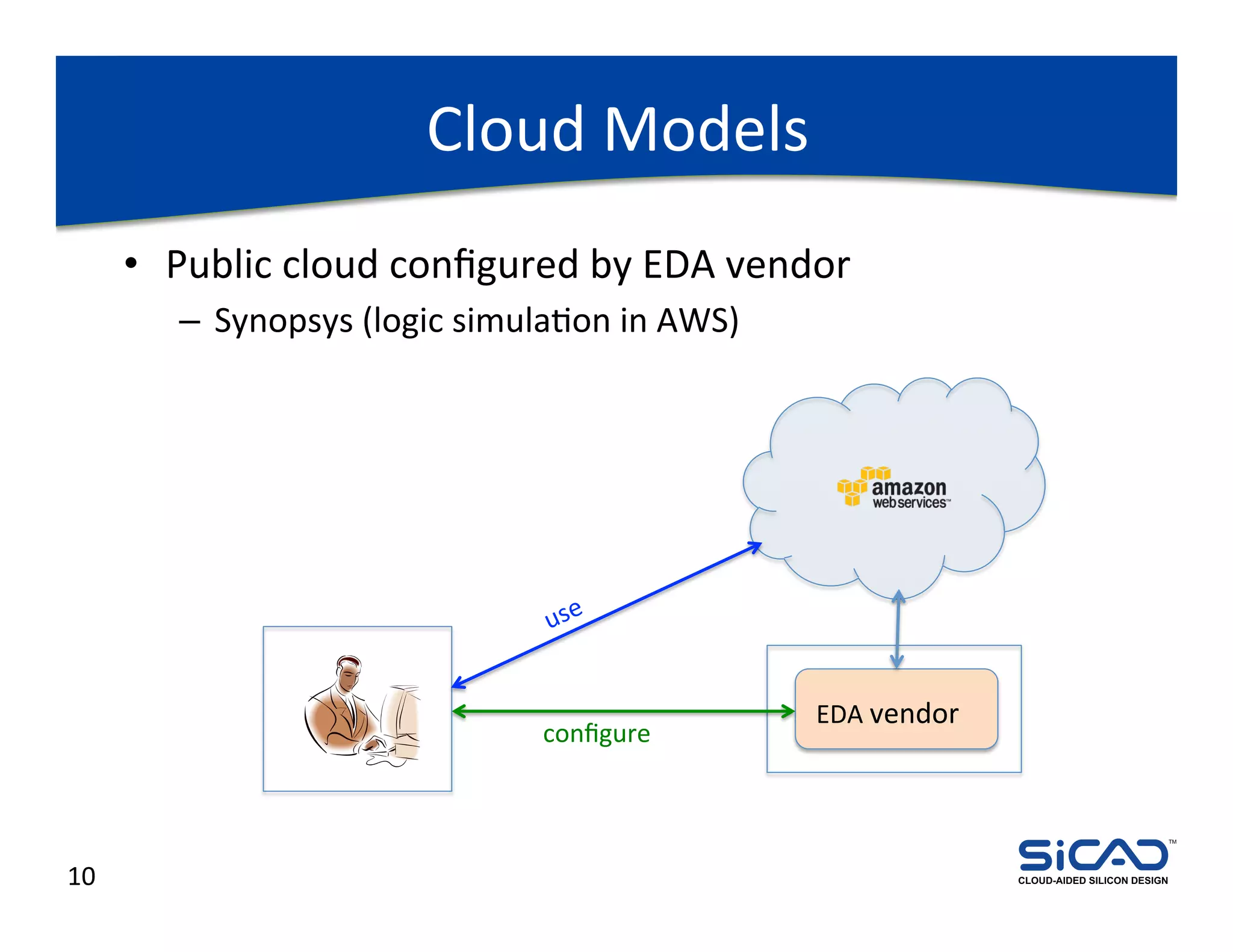
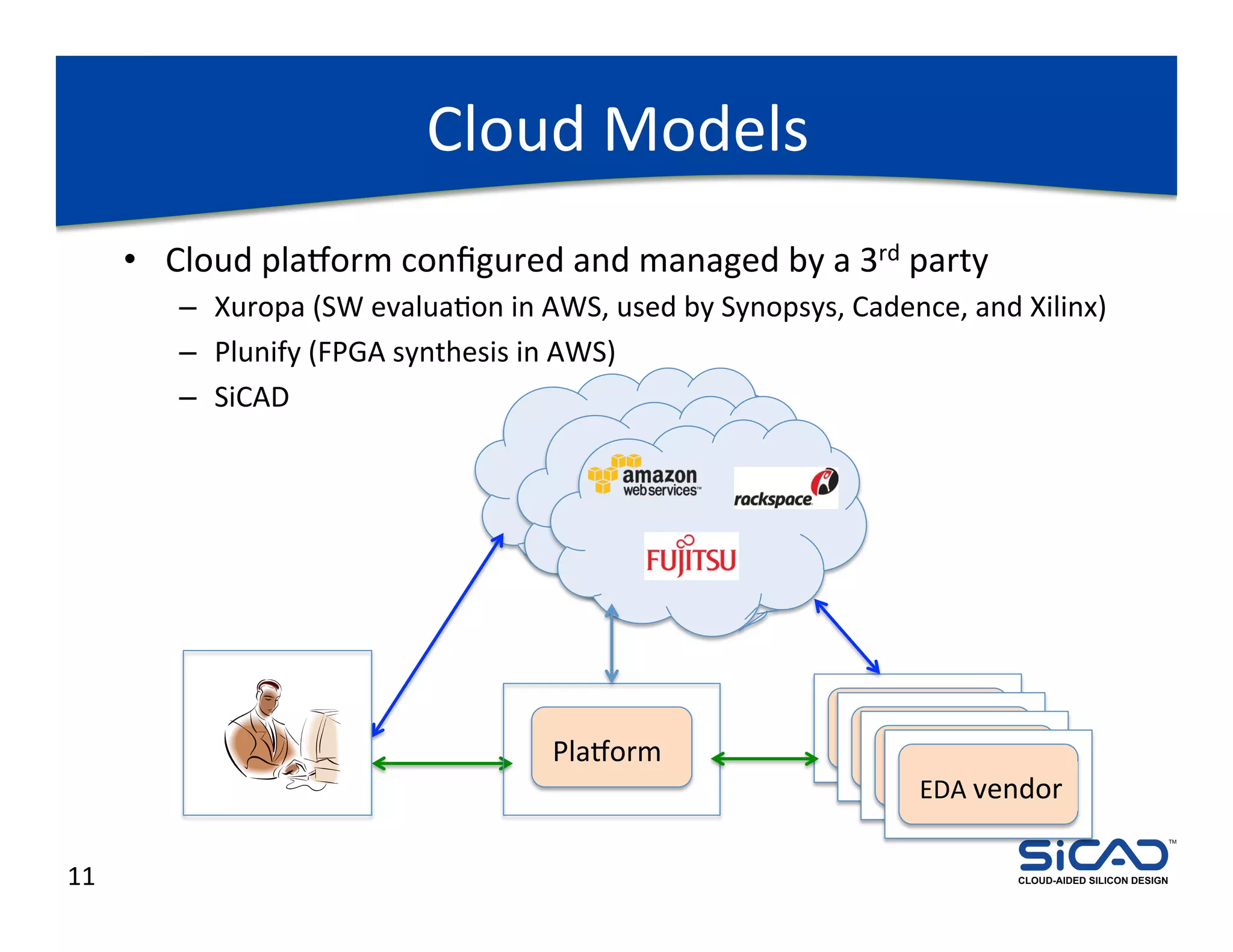
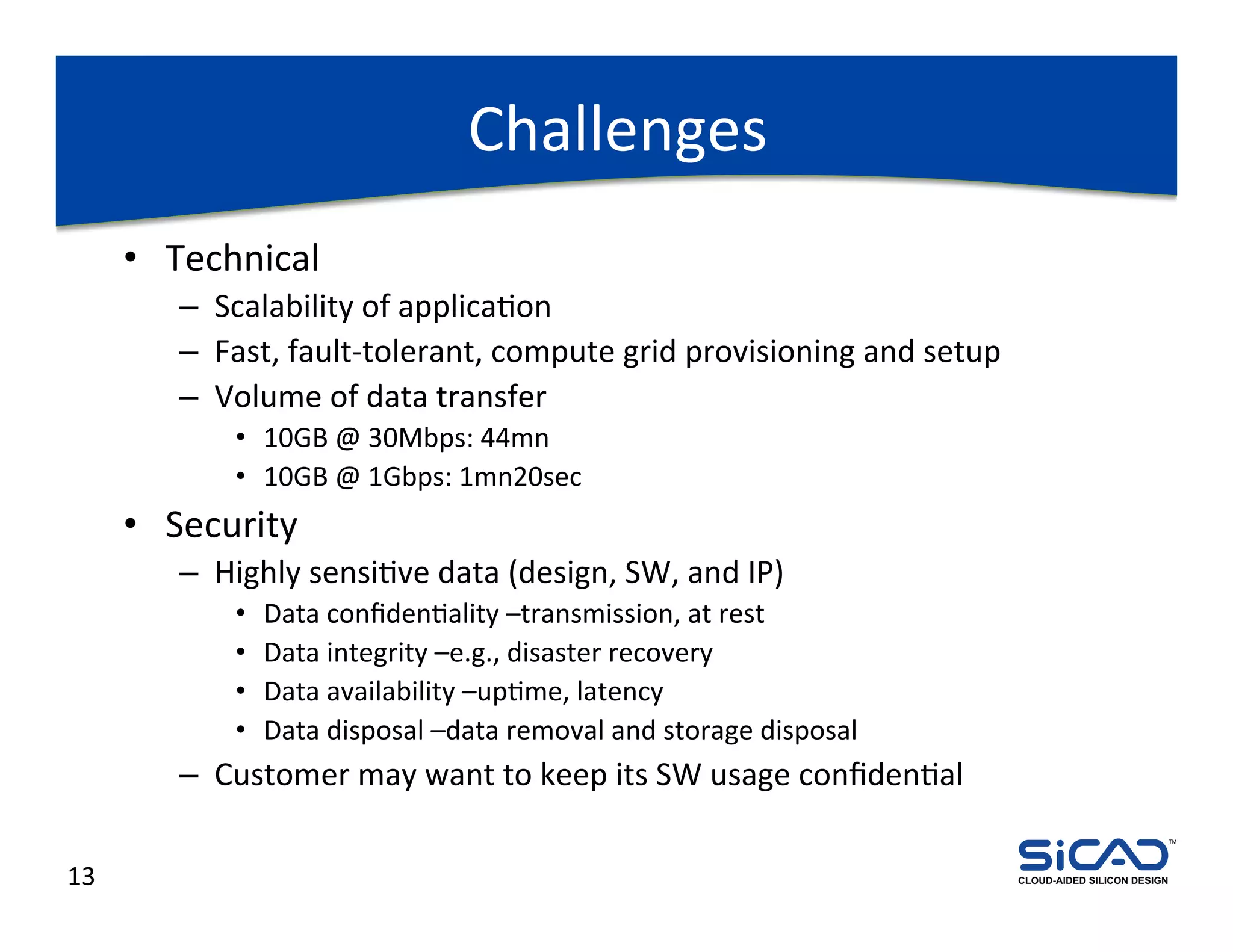
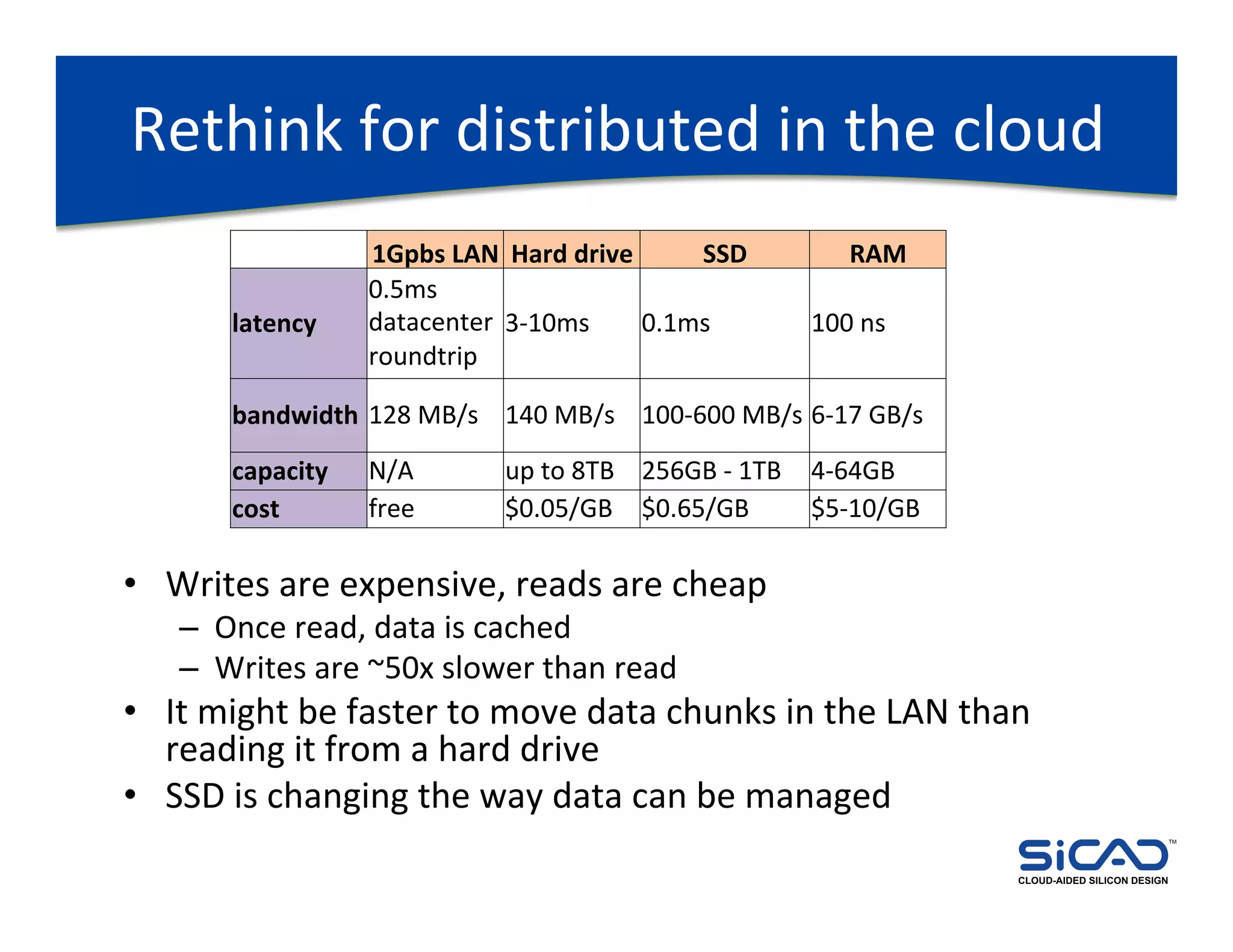
The document discusses cloud-aided silicon design and model checking, highlighting the benefits of cloud computing such as scalability and on-demand resources. It addresses various types of model checking like explicit and implicit state exploration, bounded model checking, and the configuration of cloud models by EDA vendors. Additionally, it outlines challenges related to legal, technical, and business models, emphasizing the importance of security and efficient data transfer in distributed computing environments.