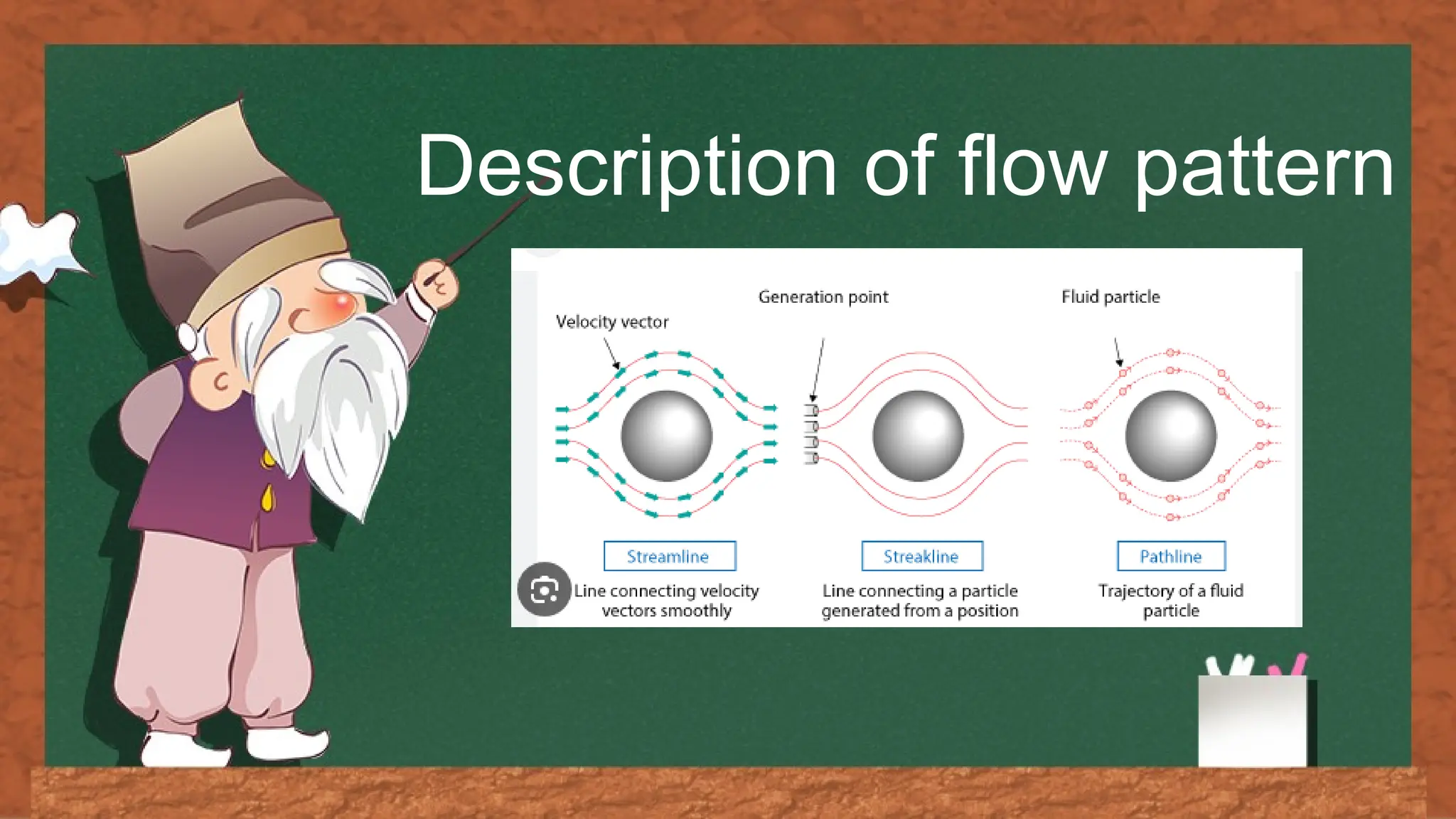
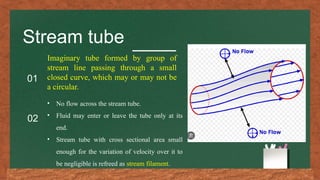
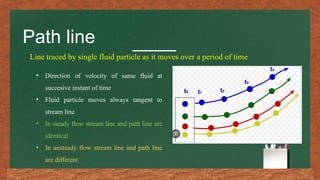
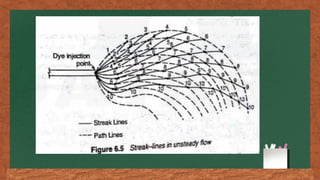
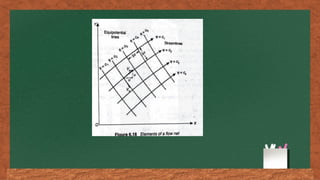
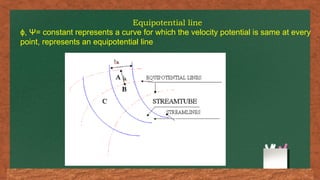
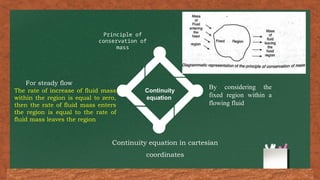
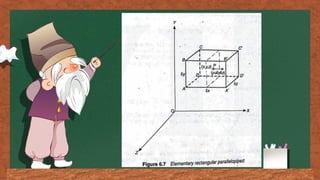
The document discusses fluid flow patterns, defining key concepts like streamlines, pathlines, and streaklines, which illustrate the direction of fluid velocity at various points. It explains the differences between steady and unsteady flow, as well as introduces concepts like stream tubes, flow nets, equipotential lines, and the continuity equation. It emphasizes the fundamental principles governing fluid dynamics including conservation of mass, energy, and momentum.