The document presents a research study on online shopping on Flipkart.com in India. It includes:
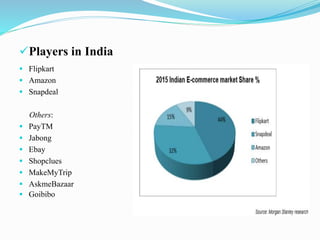
1) An introduction to online shopping and its history globally and in India. Major online shopping players in India are discussed including Flipkart.
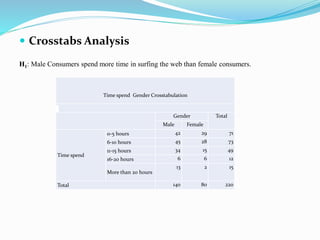
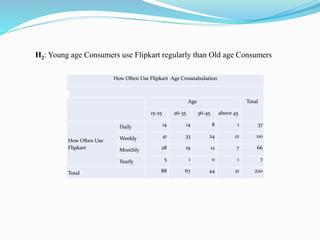
2) The objectives of the study which are to analyze the impact of gender, age and other factors on online shopping experience on Flipkart.
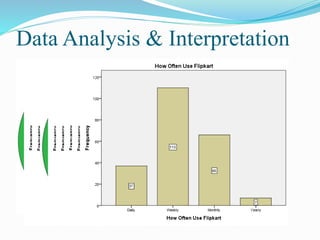
3) The research methodology which uses a questionnaire survey with 220 respondents in Ahmedabad, India. Statistical analysis methods like frequency distribution, chi-square tests, t-tests and factor analysis are to be used.