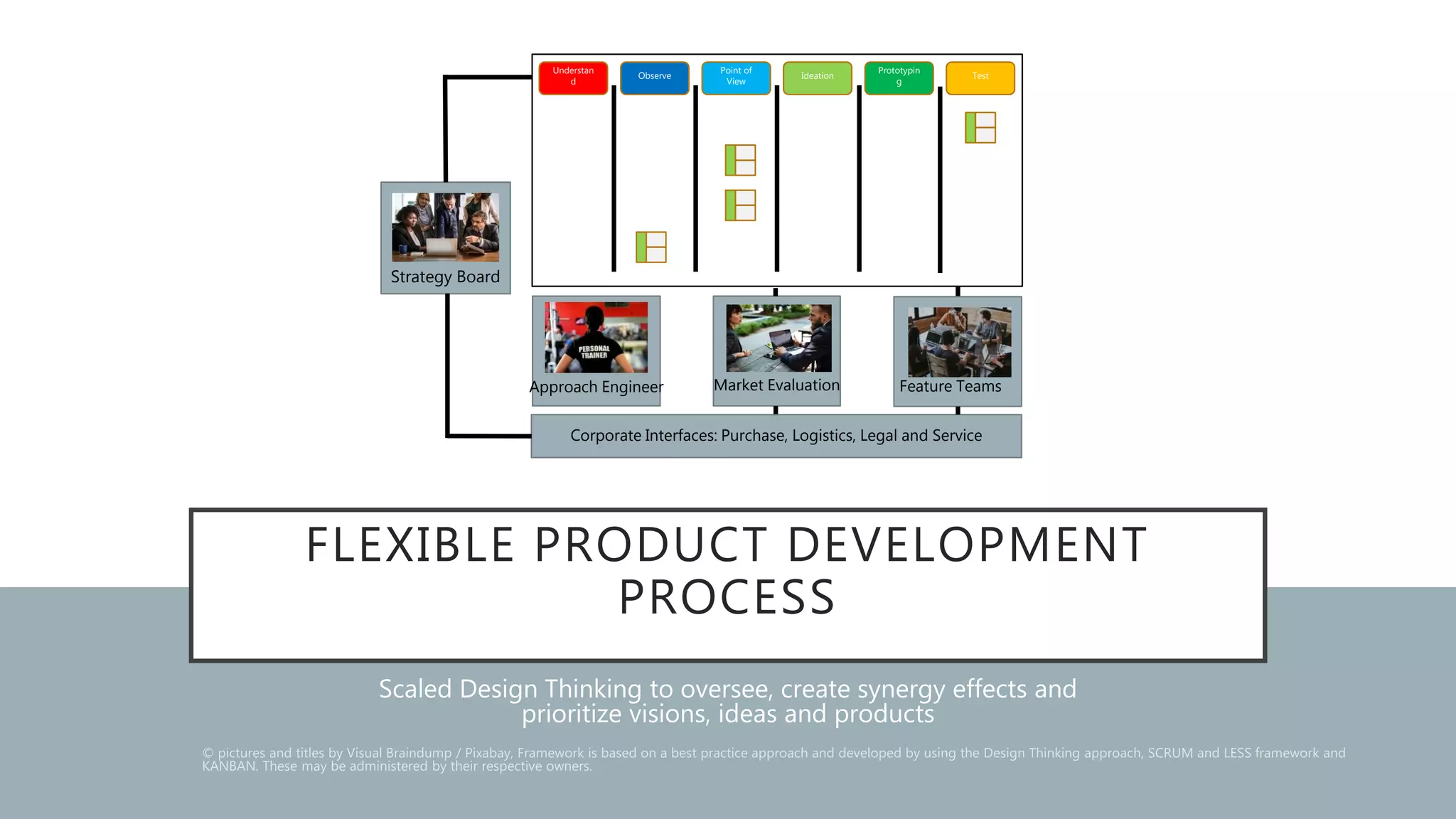
The document describes a Flexible Product Development Process (FPDP) that scales design thinking to oversee multiple design thinking teams and challenges within an organization. The FPDP uses a Kanban board to track design thinking challenges from understanding to testing. Key roles like a Strategy Board, Market Evaluation team, and Approach Engineer help oversee teams, prioritize ideas, and ensure alignment with corporate goals and metrics. The FPDP aims to balance autonomy for teams with oversight of ideas and coordination across teams to optimize investments and create synergy.