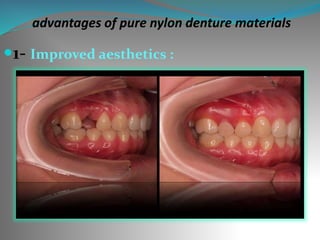
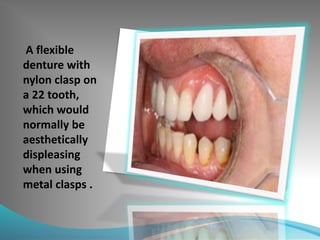
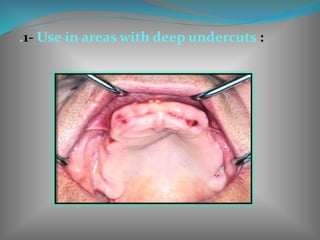
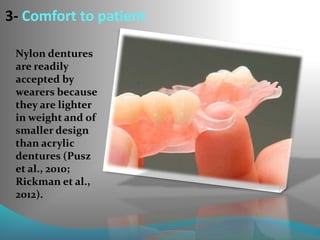
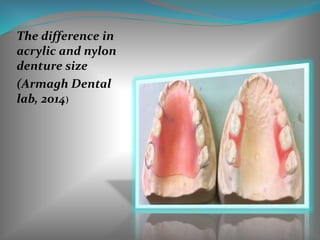
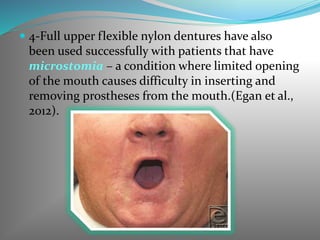
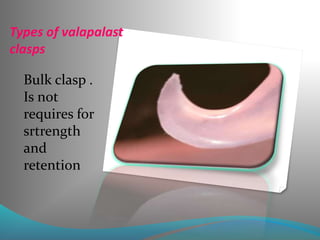
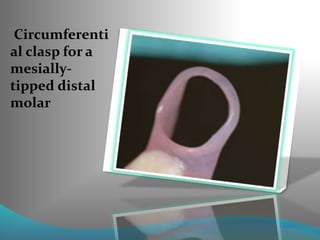
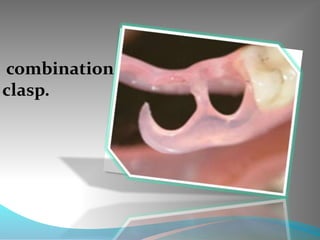
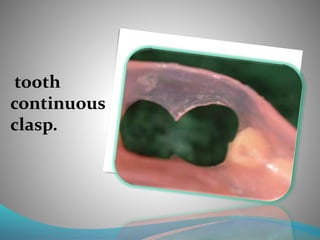
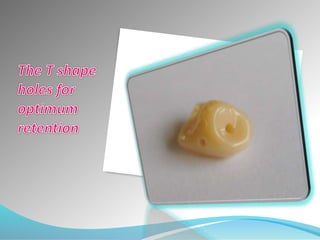
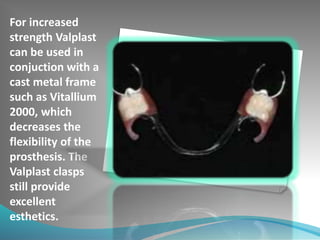
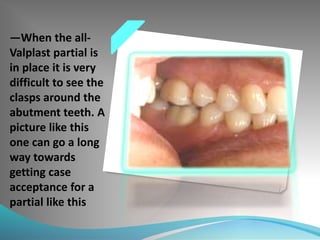
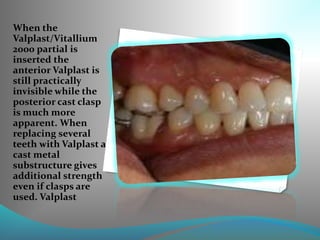
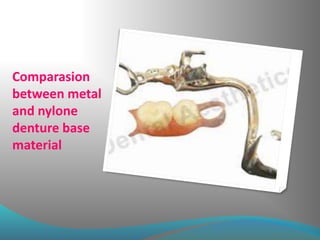
This document discusses the requirements and advantages of flexible nylon denture base materials. It provides background on nylon and describes how Valplast was the first nylon denture base material developed in 1953. The document outlines 10 advantages of Valplast like flexibility, aesthetics, comfort, and affordability. It also compares the physical properties of nylon and polymethyl methacrylate denture bases and discusses factors that could cause mechanical retention failure between acrylic teeth and pure nylon bases.