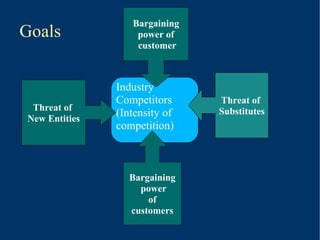
According to Michael Porter, the competitiveness of an industry is determined by five forces: the threat of new entrants, the power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Porter identified these five forces that shape every industry and market. A company's corporate strategy should aim to modify these competitive forces to improve the company's position within the industry.