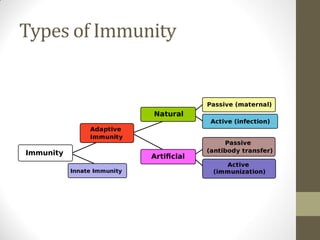
The document discusses immunity, defining it as the body's ability to resist pathogenic agents with two types: innate and acquired immunity. Innate immunity is the natural defense against pathogens, while acquired immunity is developed through exposure to specific pathogens and involves T and B lymphocytes. The document also covers cellular immunity, humoral immunity, and allergic reactions, including their mechanisms and common examples.