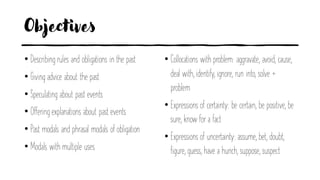
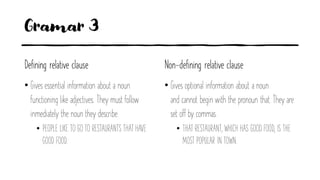
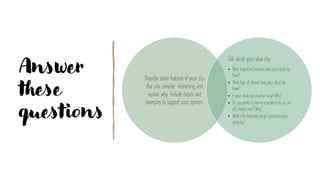
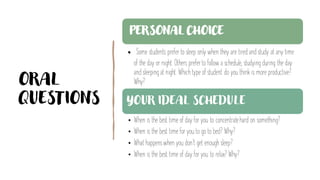
This document outlines the objectives and grammar points covered in 6 units of an English speaking course on topics related to friends, family, cities, schedules, communication and news/storytelling. The objectives describe language functions like describing personalities, preferences, past events and advice. Grammar topics include gerunds, relative clauses, reported speech, tense choice and time clauses. Sample questions are provided to elicit student speaking on personal topics related to the unit themes.