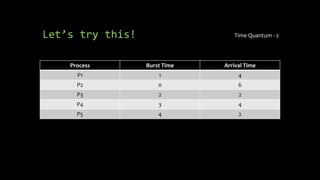
The document discusses CPU scheduling, particularly focusing on the round-robin algorithm, which is a preemptive scheduling method that allows each process to use the CPU for a fixed amount of time in a cyclic manner. It highlights how the round-robin algorithm operates by comparing process burst times to a designated time quantum and offers examples of problem-solving using Gantt charts and calculations for CPU efficiency and turnaround times. Additionally, a sample case with processes and their respective times is presented for clarification.