The document discusses finite automata and provides an example of using a finite state machine to model the scoring system in tennis. Key points:
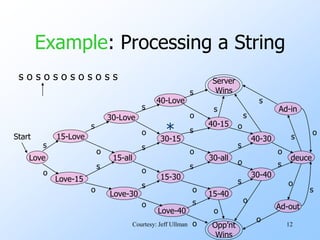
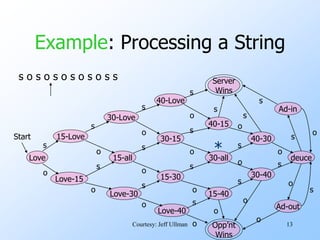
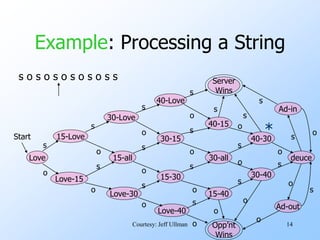
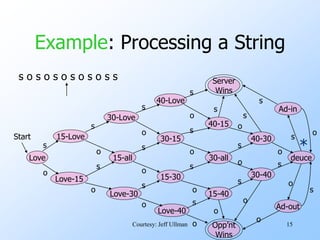
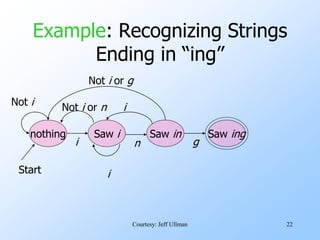
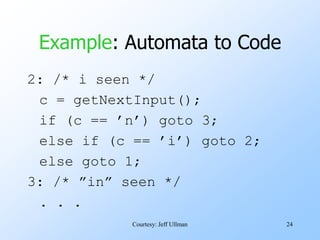
- Finite automata are formal systems that can have a finite number of states and transition between states based on inputs. They are commonly represented as graphs.
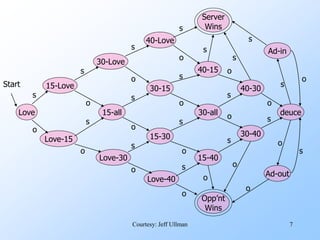
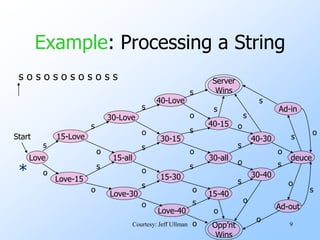
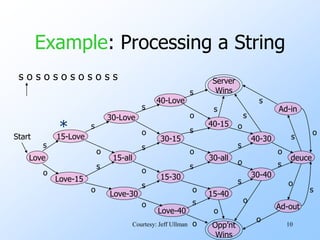
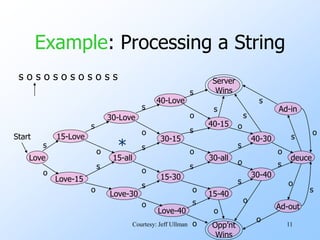
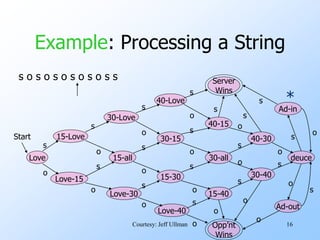
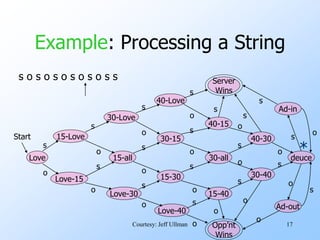
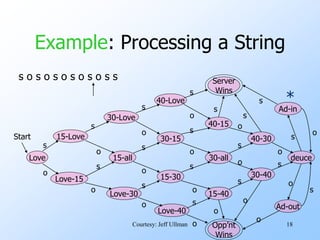
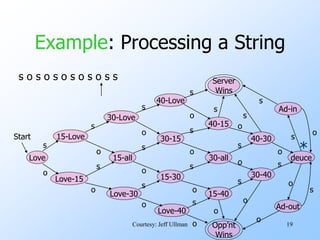
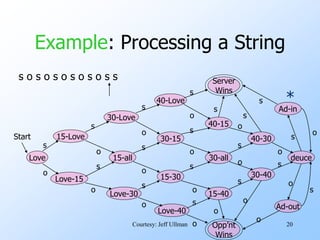
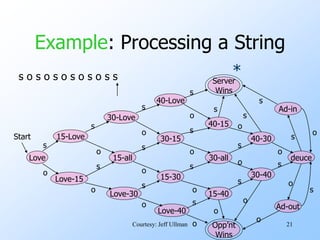
- An example finite automata is presented to model the scoring in a tennis game, with states like "Love-15" and transitions labeled with "s" for server point or "o" for opponent point.
- Strings of points can be processed by starting in the start state and following the transitions between states for each point in the string. If the final state is reached, the input string is accepted.