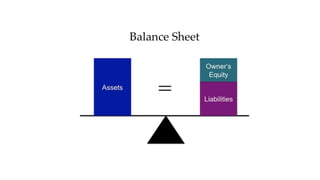
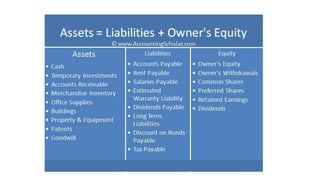
Financial statements include the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. The balance sheet summarizes a company's financial position at a point in time by listing assets, liabilities, and equity. It uses the accounting equation that assets equal liabilities plus equity. The income statement summarizes revenues and expenses over a period of time to determine profit or loss. The statement of cash flows explains the changes in a company's cash balance due to operating, investing, and financing activities during a period.

![Financial Statement [Introduction]
• There are three types of financial statements which are frequently used.
• It is used to address the needs of external stakeholders i.e. suppliers, investors,
and other people who are interested in the performance of the company but don’t
work for the company.
• Balance sheet – summarizes firm’s financial position at a specific point in time.
• Income statement – summarizes financial performance over a given period of time.
• Statement of Cash Flows – explains how cash is acquired or spent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialstatements-170413184803/85/Financial-Statements-Presentation-2-320.jpg)