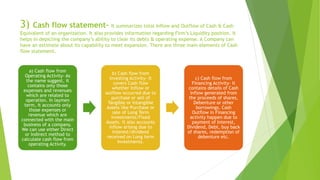
Financial statements include an income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and notes to accounts. The income statement shows revenue, expenses and profit/loss. The balance sheet outlines assets, equity, and liabilities to depict the company's financial position. The cash flow statement summarizes cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing and financing activities. Notes to accounts provide additional details and breakdowns to fully explain the information in the financial statements.