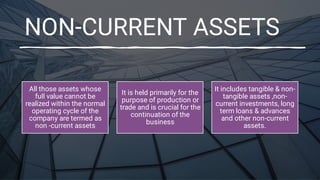
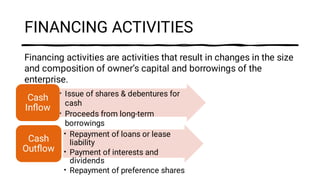
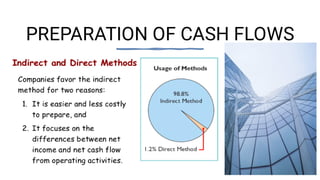
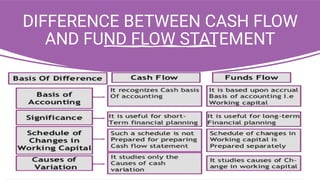
The document discusses major classifications of cash flows according to accounting standard AS-3 and the importance of disclosing non-cash transactions. It covers cash flows from operating, investing and financing activities, and how non-cash transactions that significantly impact a company's financial position should be disclosed, either in a separate schedule or note. Key financial statements including the balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statement are also explained, along with their objectives, components and limitations.