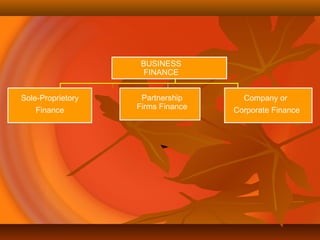
Finance is the lifeblood of business. It is needed to start, operate, and grow a business. Without adequate financing, a business cannot be established, assets cannot be acquired, products cannot be developed, or management encouraged to progress. The finance function involves planning, raising, and managing the funds required by a business to accomplish its objectives in an efficient manner.