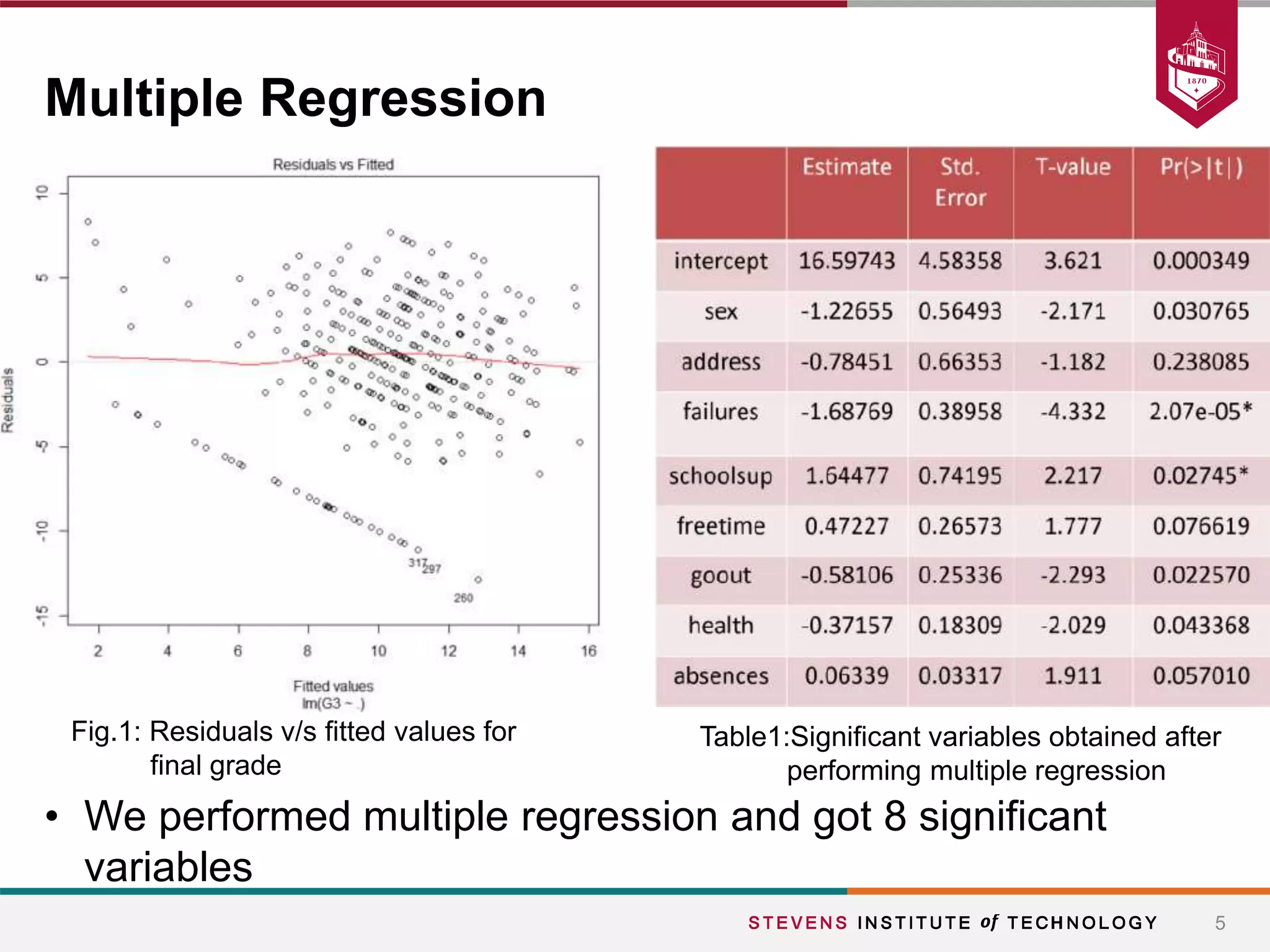
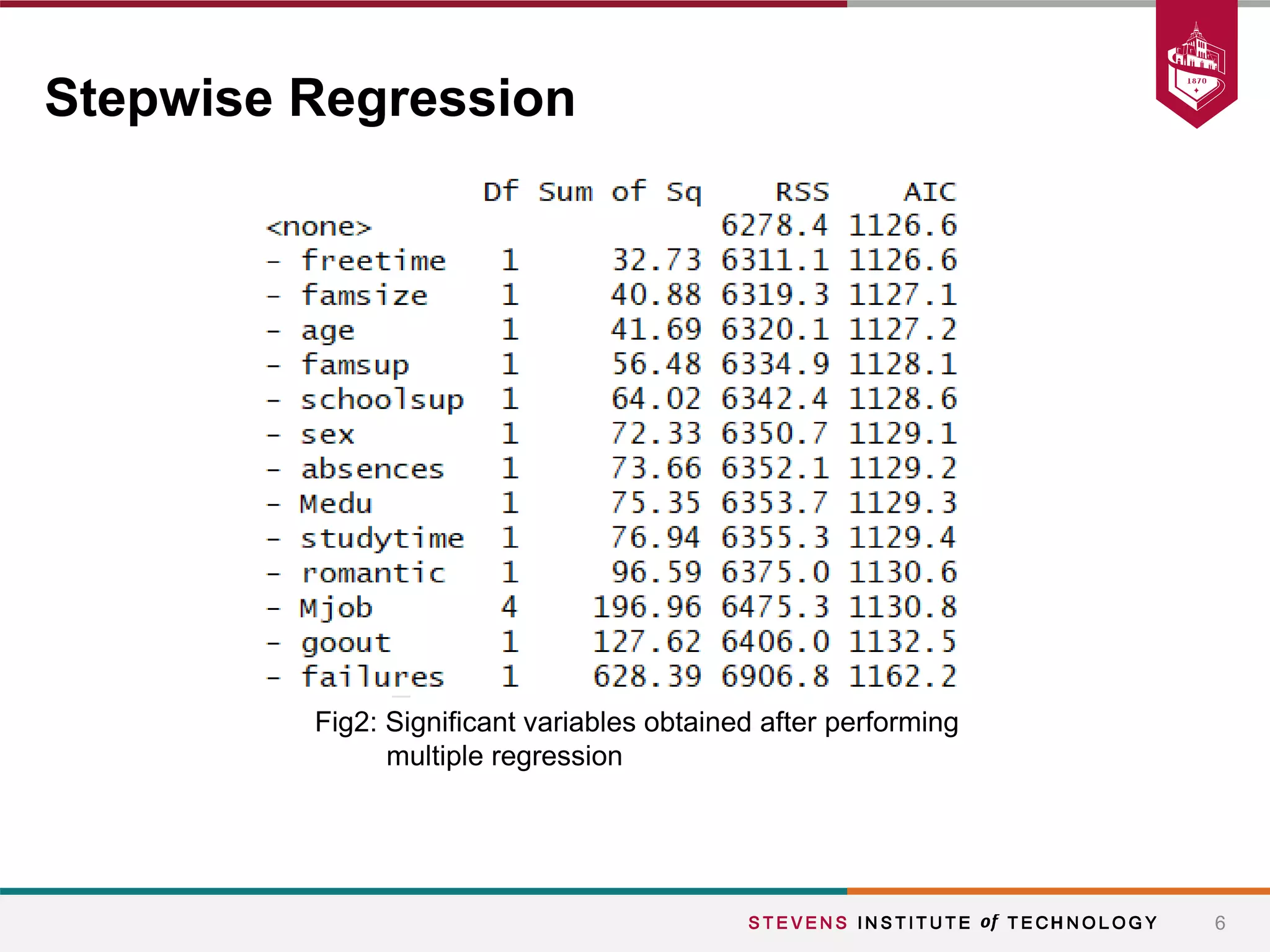
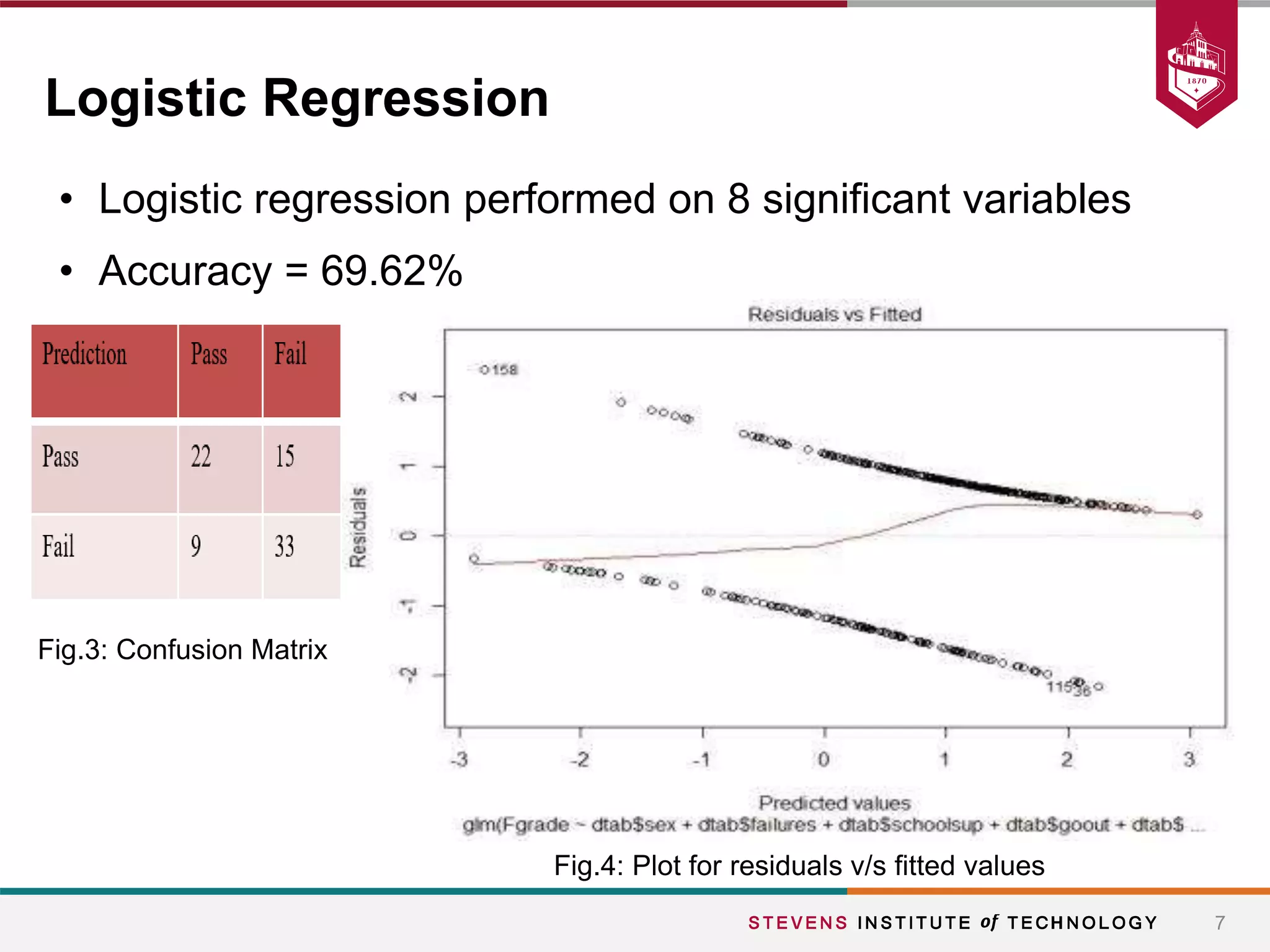
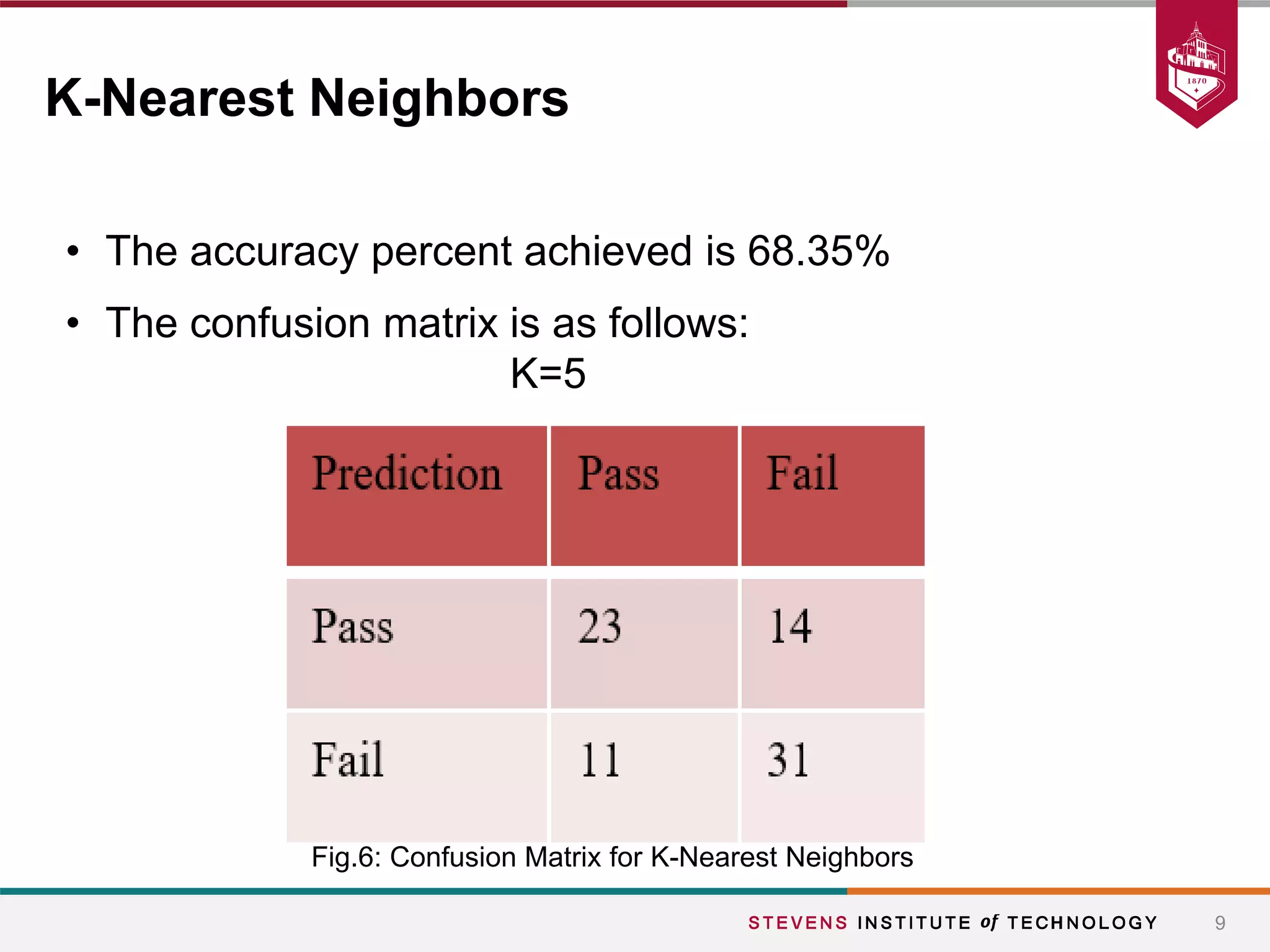
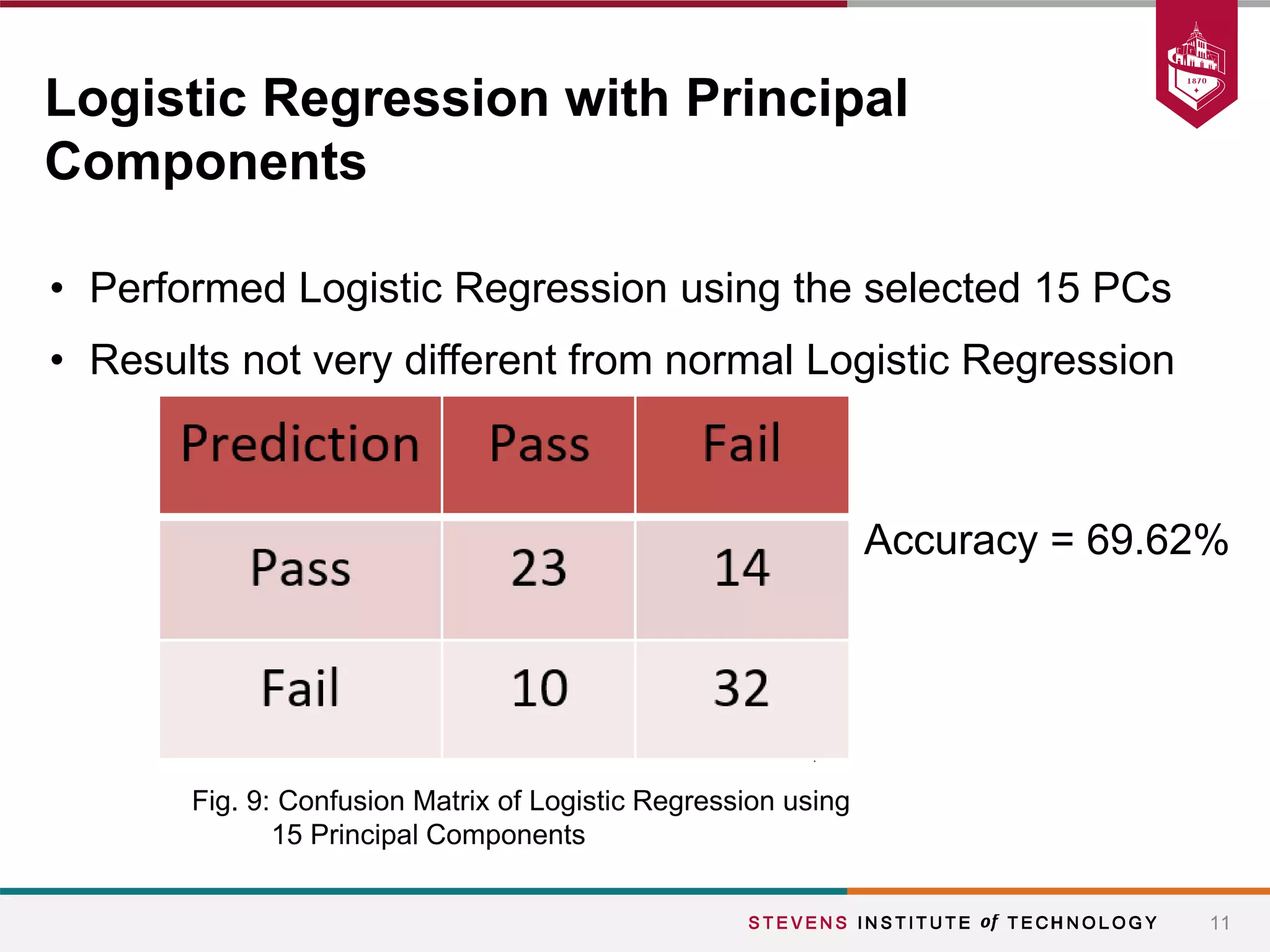
This document summarizes a student project that aimed to predict students' final grades based on various demographic and social factors. The students analyzed a dataset of 396 student observations with 33 attributes and used classification algorithms like logistic regression, naive bayes, and k-nearest neighbors. Their key findings were that variables like alcohol consumption did not significantly impact grades, while factors like failures, sex, age, extracurricular activities were statistically significant. The various models tested achieved similar accuracy between 65-70% in predicting student grades.