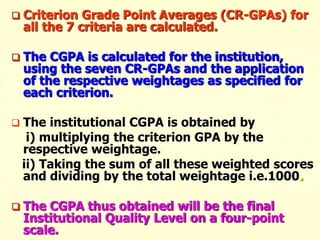
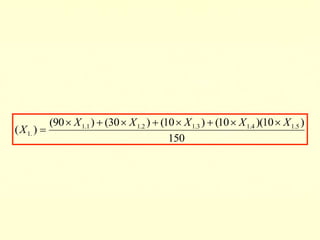
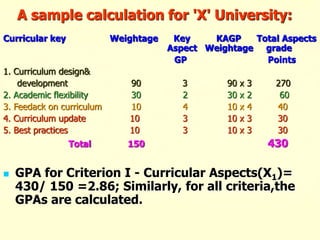
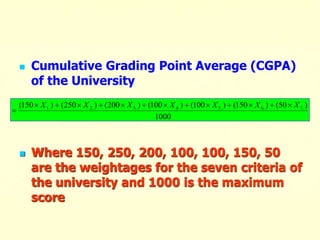
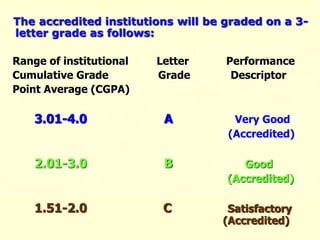
The document outlines the criteria and process for quality assurance and accreditation of higher education institutions in India by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC). It discusses the 7 criteria that are assessed, including curricular aspects, teaching-learning and evaluation, research, infrastructure, student support, governance, and innovative practices. Institutions are given an institutional cumulative grade point average (CGPA) on a scale of 1 to 4 based on their performance across the 7 criteria to determine their accreditation level.