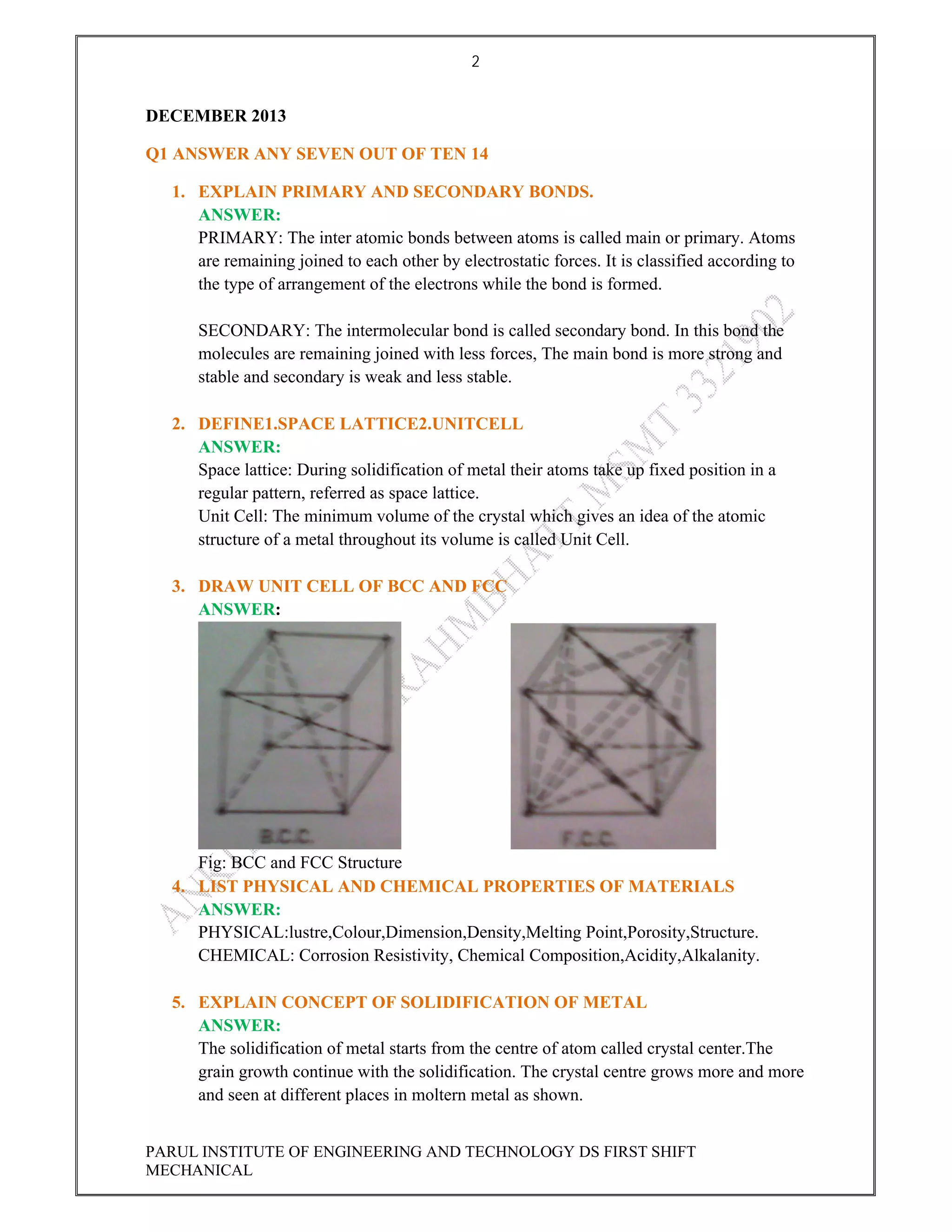
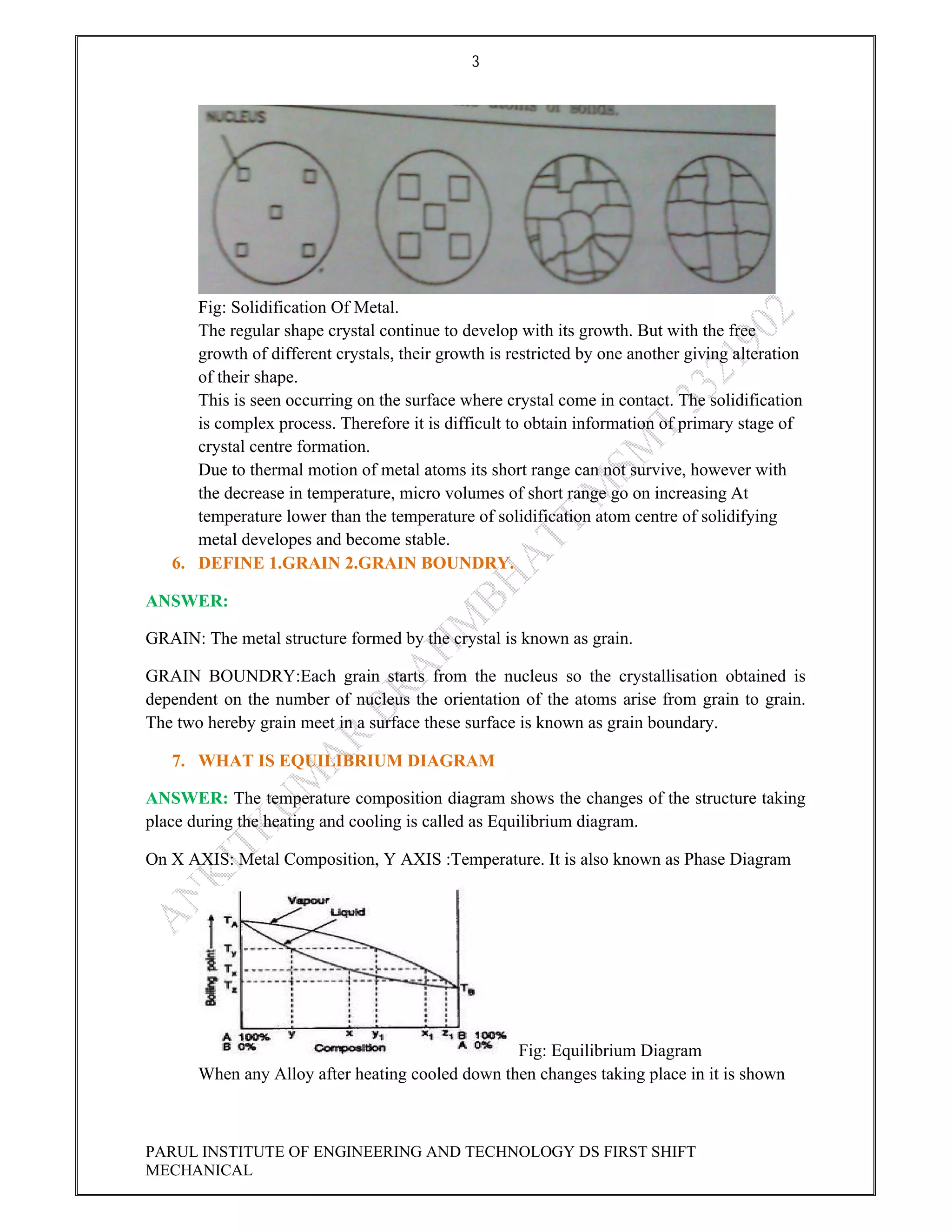
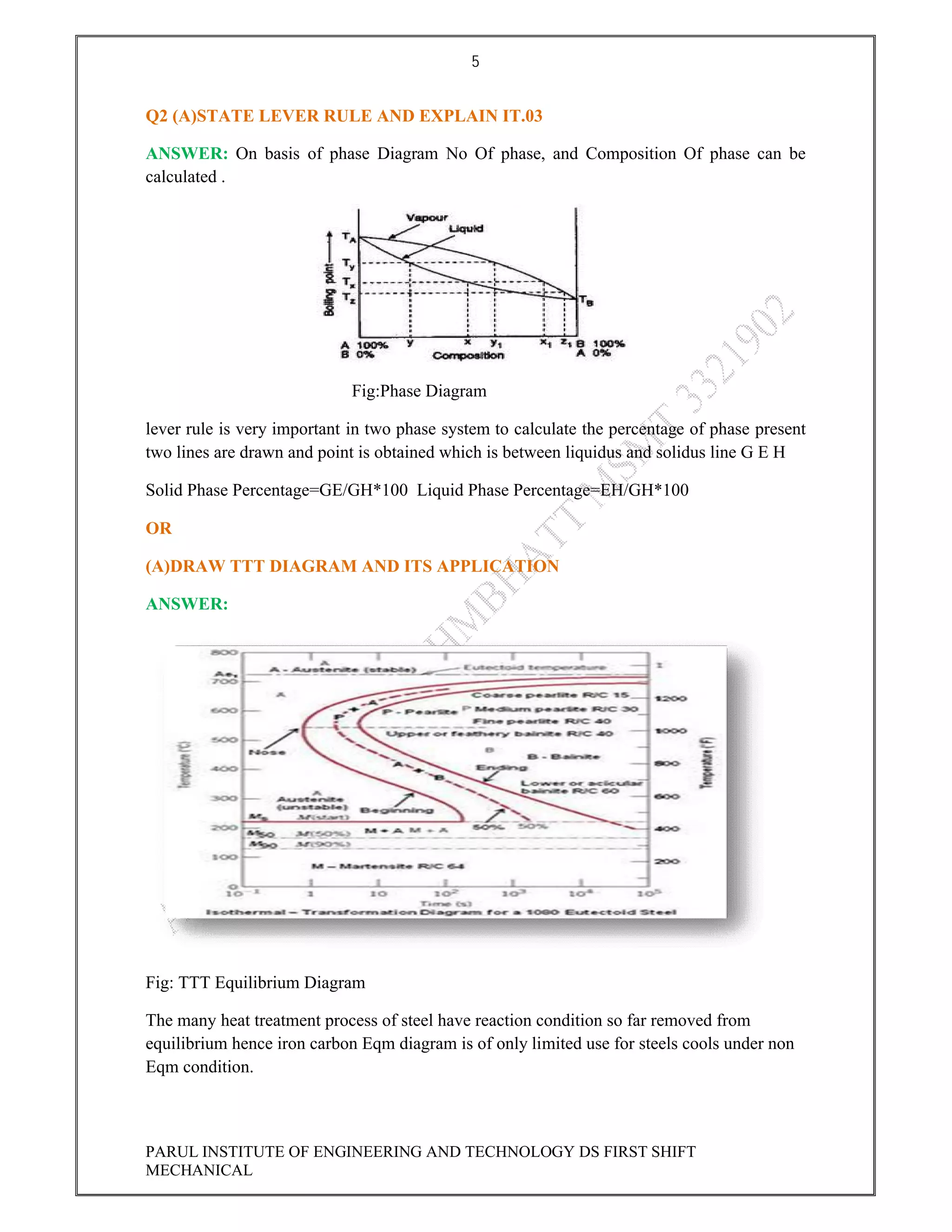
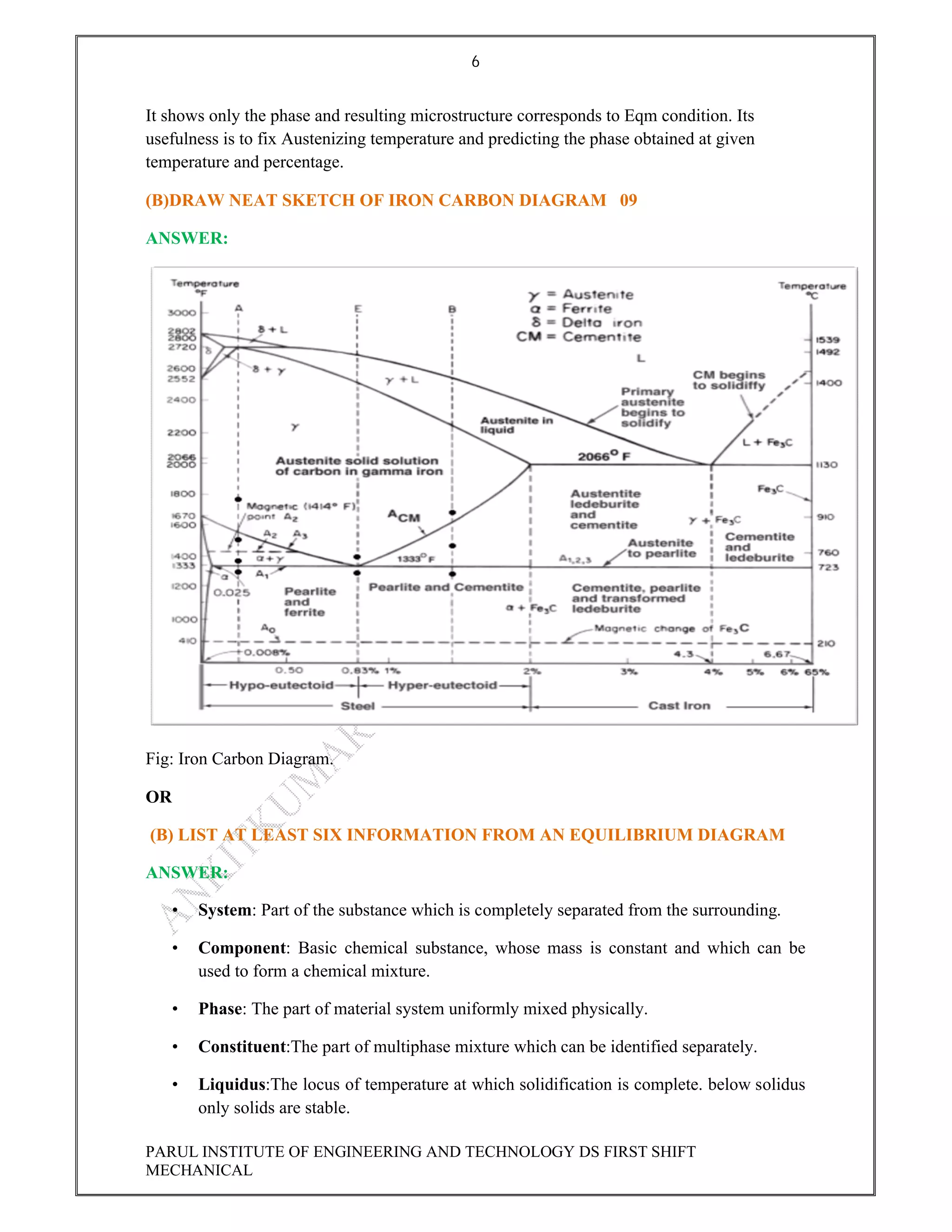
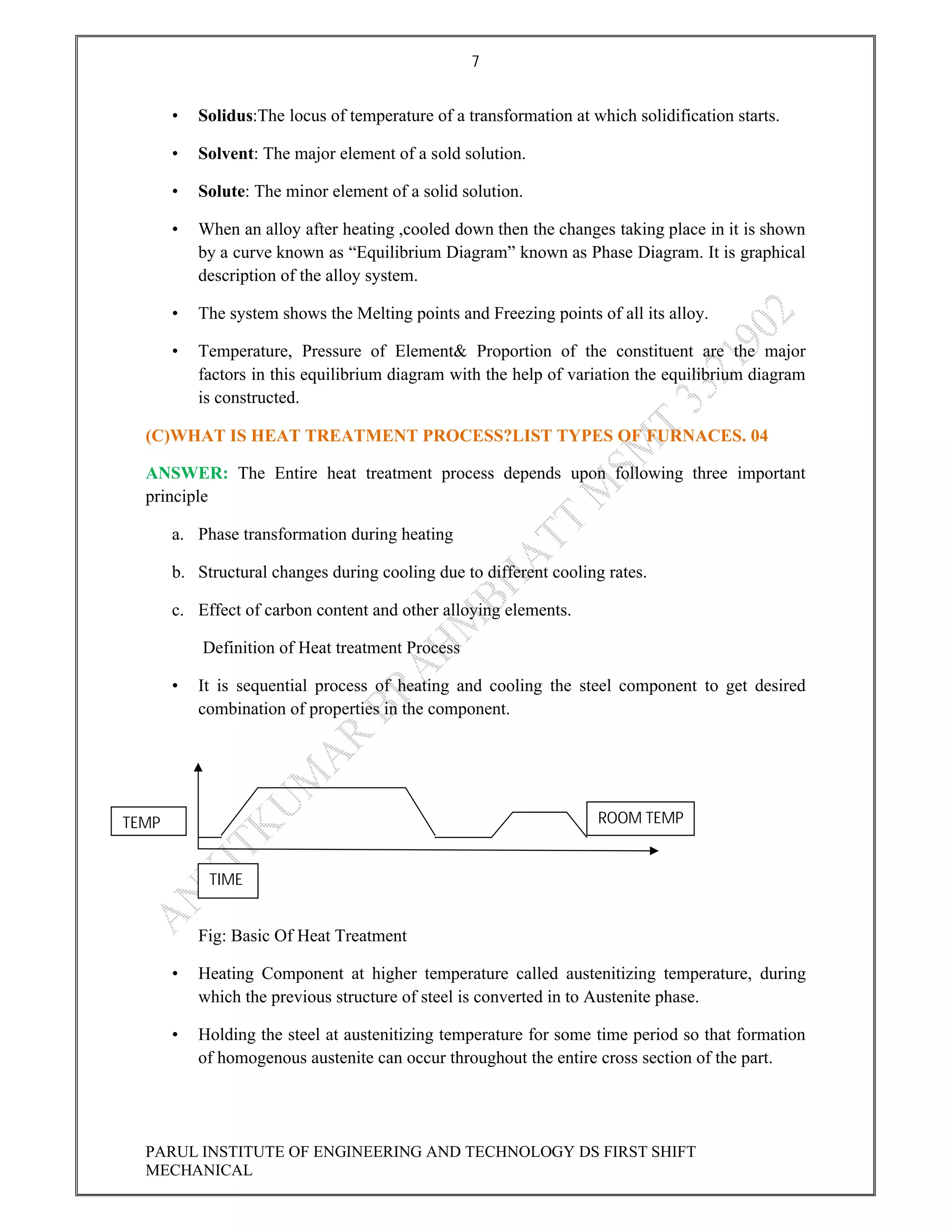
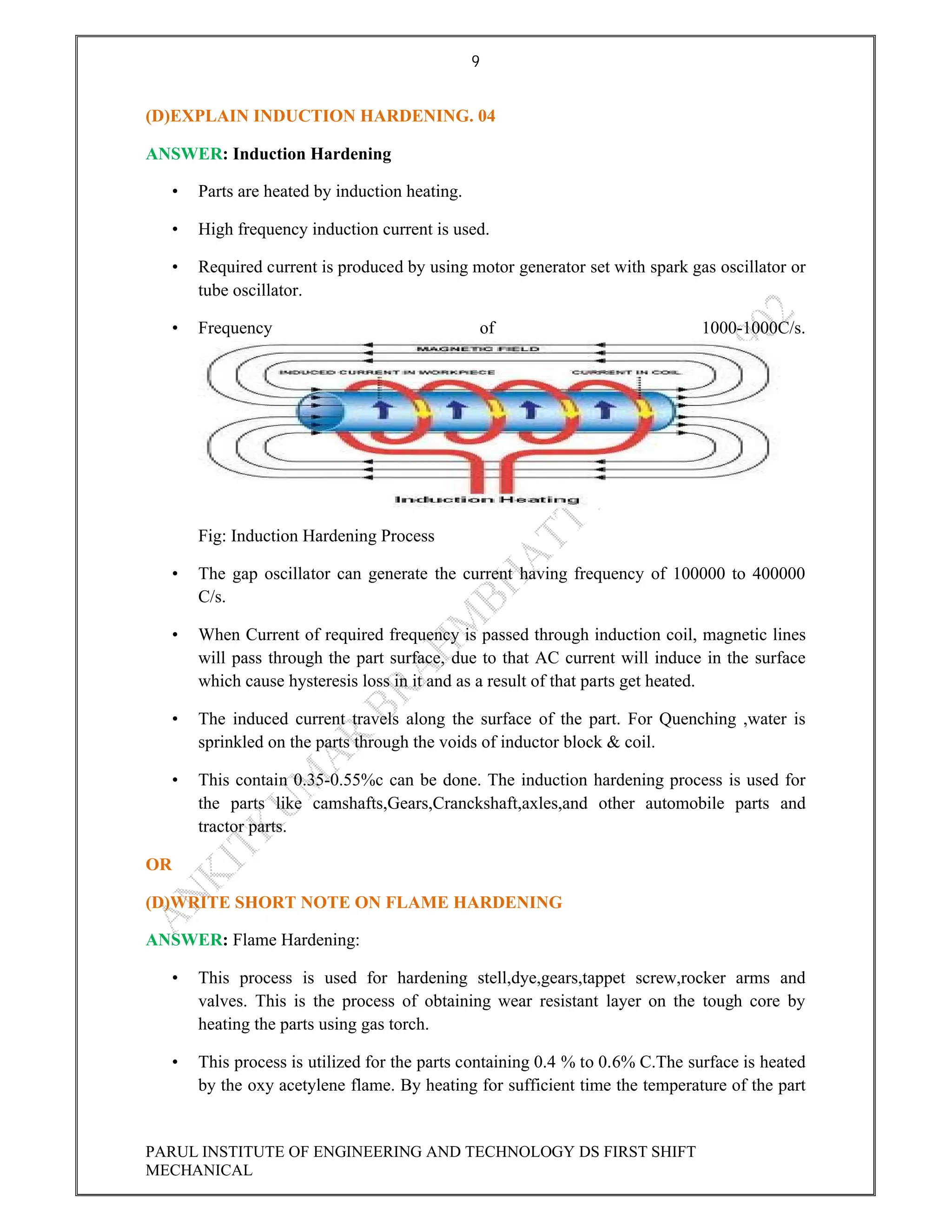
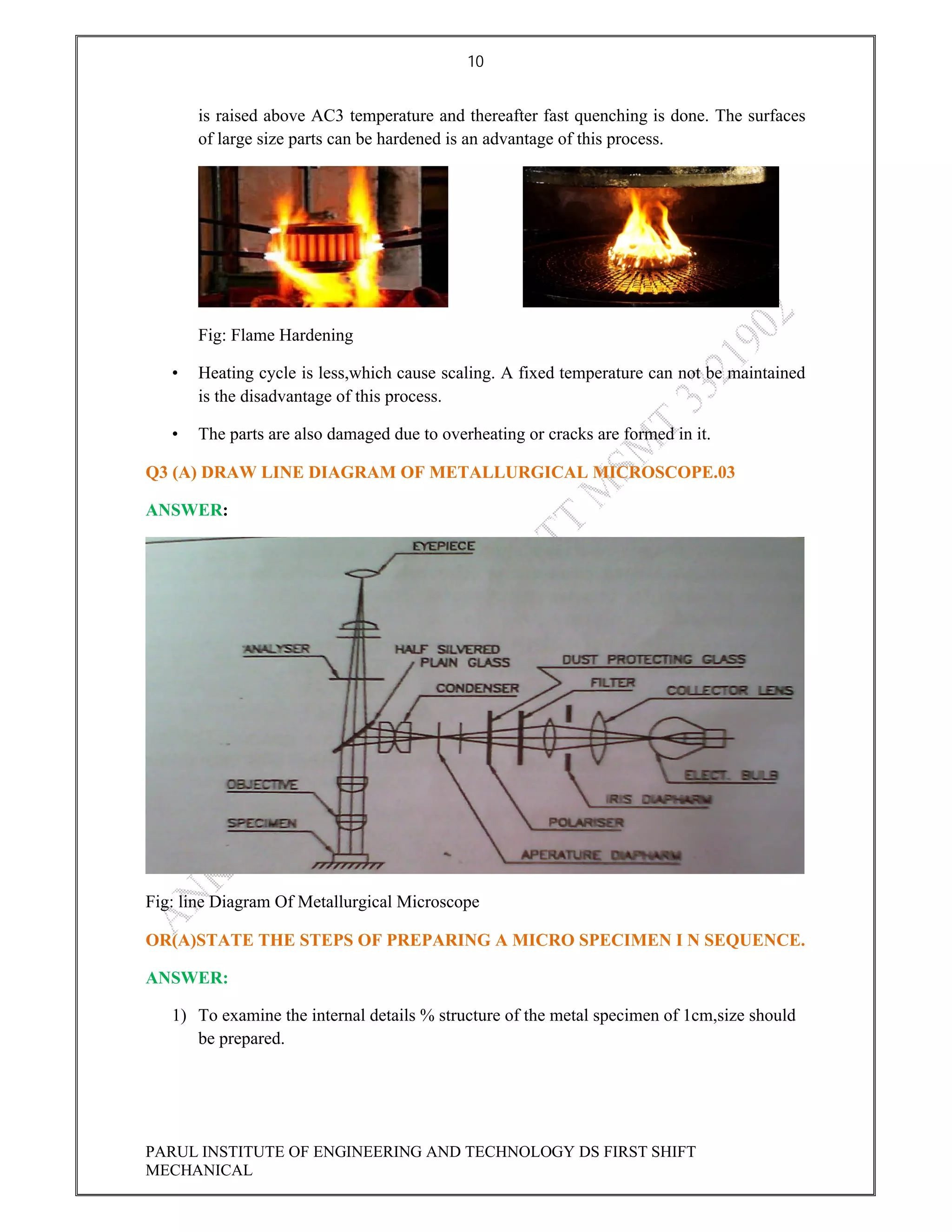
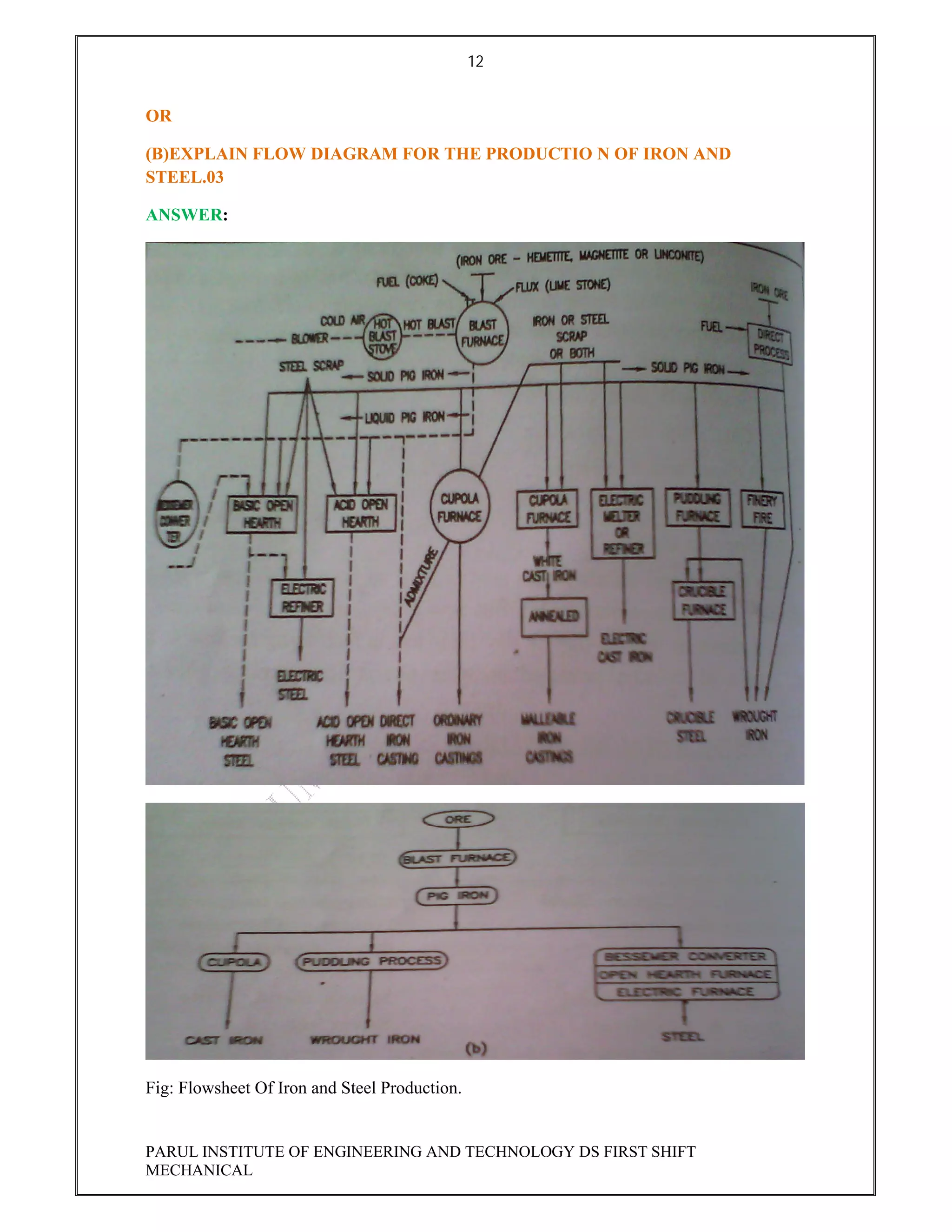
This document contains the solved question paper from December 2013 for Parul Institute of Engineering and Technology's Mechanical Engineering program. It includes answers to 7 out of 10 questions on topics like primary and secondary bonds, unit cells, solidification of metals, phase diagrams, heat treatment processes and furnaces. Diagrams are included to illustrate concepts like the BCC and FCC unit cell structures, lever rule on a phase diagram, TTT diagram, iron-carbon phase diagram and the induction hardening process.