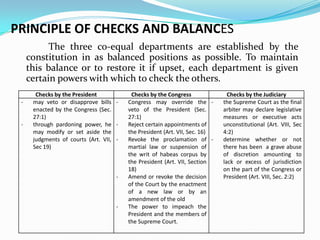
The document summarizes the three branches of the Philippine government according to the 1987 Constitution: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. It describes the principle of separation of powers and checks and balances between the branches. Specifically regarding the legislative and executive branches:
The legislative branch is bicameral, consisting of the Senate and House of Representatives. The executive branch is headed by the President, who is both head of state and head of government, and assisted by the Vice President. Qualifications, terms of office, powers, and impeachment processes are outlined for the President, Vice President, and members of Congress.