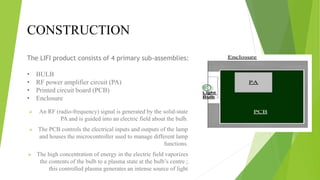
Li-Fi, or "light fidelity," is a wireless communication technology that utilizes LED light to transmit data through varying light intensities, aiming to alleviate congestion in the radio spectrum as demand for wireless data grows. Originating in the 1990s, Li-Fi can achieve rapid data transmission rates and has various applications, including transforming streetlights into data hotspots and enabling underwater communication. However, the technology faces limitations such as high installation costs, the need for line-of-sight for transmission, and challenges in two-way communication.