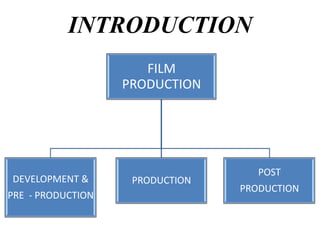
This document outlines the major stages of film production:
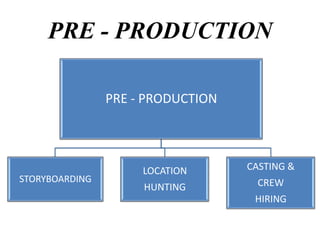
1) Development and pre-production which includes developing the script, securing financing, location scouting, casting, and storyboarding.
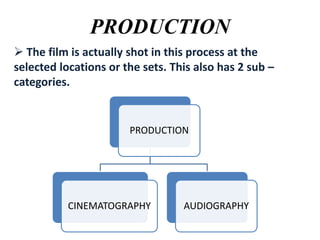
2) Production which involves principal photography through cinematography and recording audio.
3) Post-production including editing, adding visual effects, sound mixing, scoring music, and finalizing the film for distribution, promotion, and release.