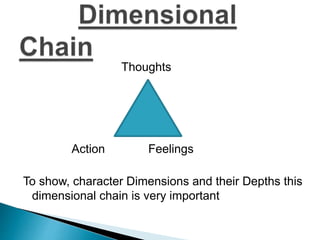
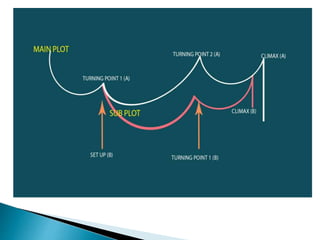
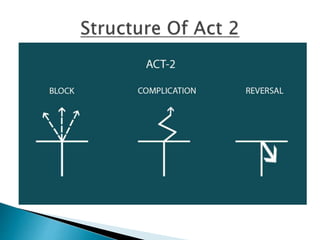
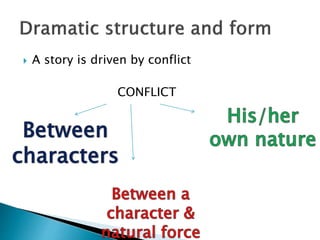
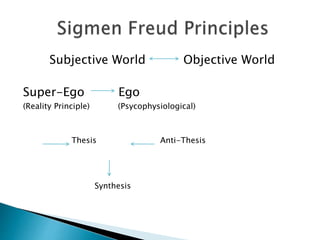
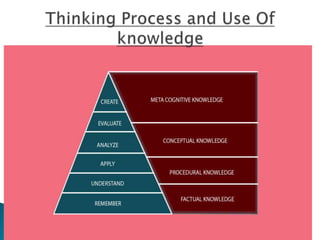
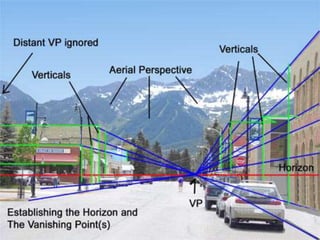
The seminar by J.K. Anubhav presents an in-depth exploration of narrative techniques in filmmaking, emphasizing the thematic and structural elements that contribute to character development and storytelling. Key concepts include characterization, point of view, the use of voice-over, and the importance of subplots, while also discussing historical context in screenwriting practices. The document concludes with a call to foster a more reflective film viewing culture, encouraging a deeper understanding of film narratives.