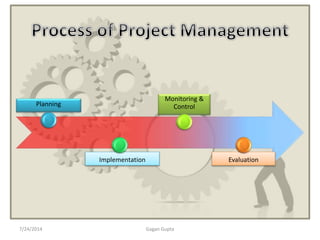
The document discusses various challenges that can occur in project management and provides recommendations to address them. It notes that project failure can result from going over budget and schedule, lower quality than expected, and stress on the team. Issues like scope creep, poor communication, inadequate resources, unclear requirements, unrealistic timelines, unplanned risks, undefined deliverables, and lack of formal project processes are identified as common causes of problems. The document recommends establishing clear plans, documentation, and controls for scope, schedule, communication, resources, risks, and deliverables to help manage projects successfully. Formal project management training is suggested for those who feel their projects are out of control.