1) The document discusses biochar, its history and production methods. Various feedstocks can be used to produce different types of biochar.
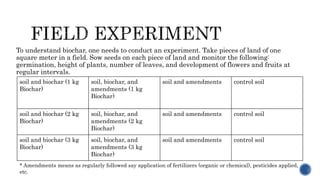
2) Communities and local production of biochar using locally available materials is more sustainable than industrial approaches. Testing of biochar's effects on soil, plants and the environment is important.
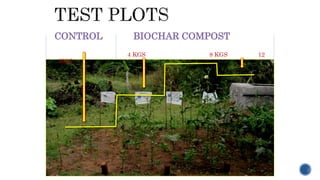
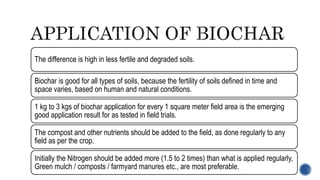
3) Initial application of 1-3 kg of biochar per square meter shows benefits like increased soil quality, crop yields and carbon storage. Combining biochar with other amendments like compost maximizes these effects.