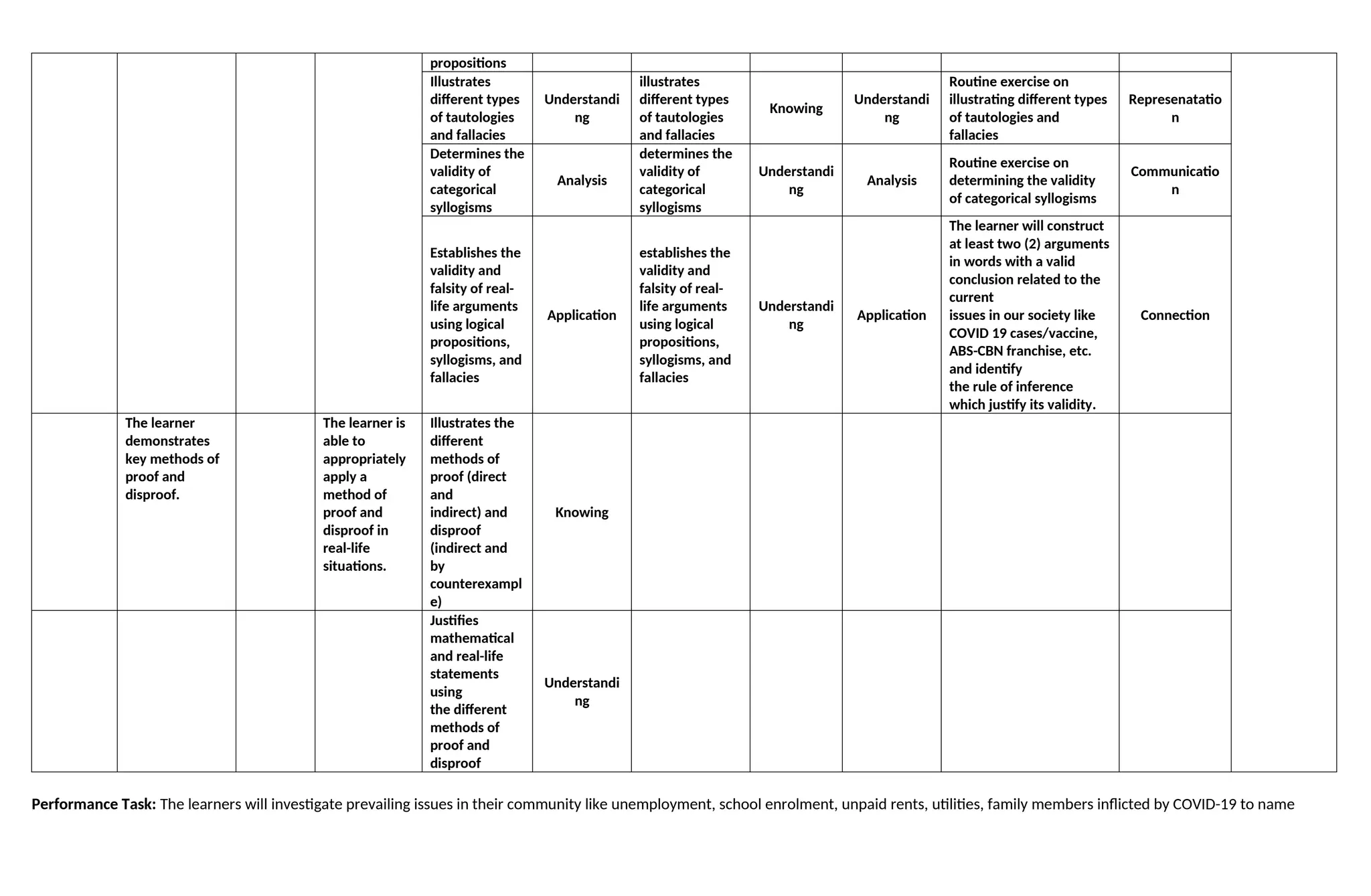
The document outlines the Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan for Grade 11 General Mathematics at Saint Martin Academy for the 2023-2024 academic year, emphasizing key learning areas such as functions, rational functions, inverse functions, and business mathematics. Students will develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills through structured learning activities and projects, culminating in a performance task that involves investigating community issues and presenting financial solutions. Assessments are designed to evaluate mathematical content, persuasive delivery, creativity, and teamwork.