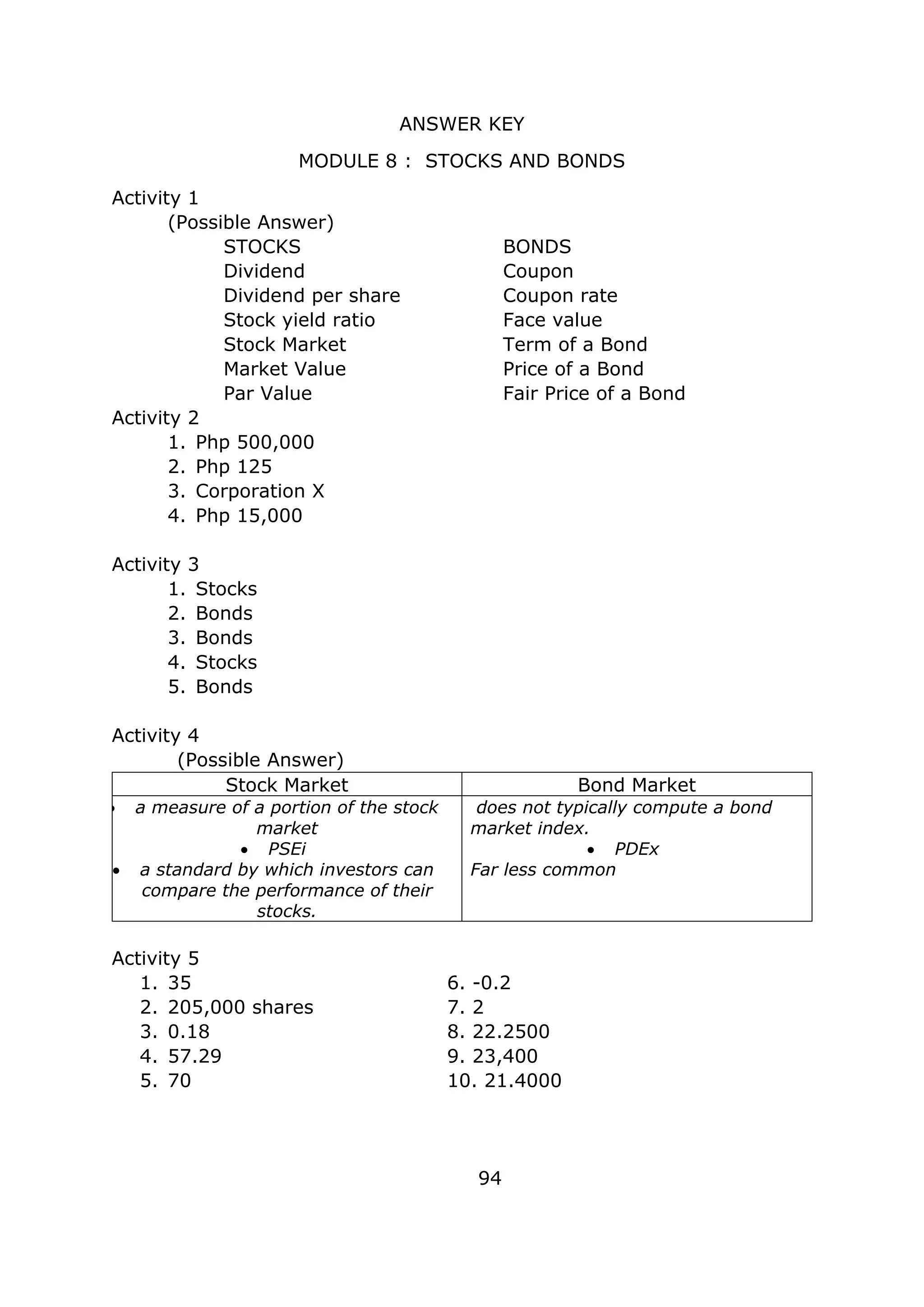
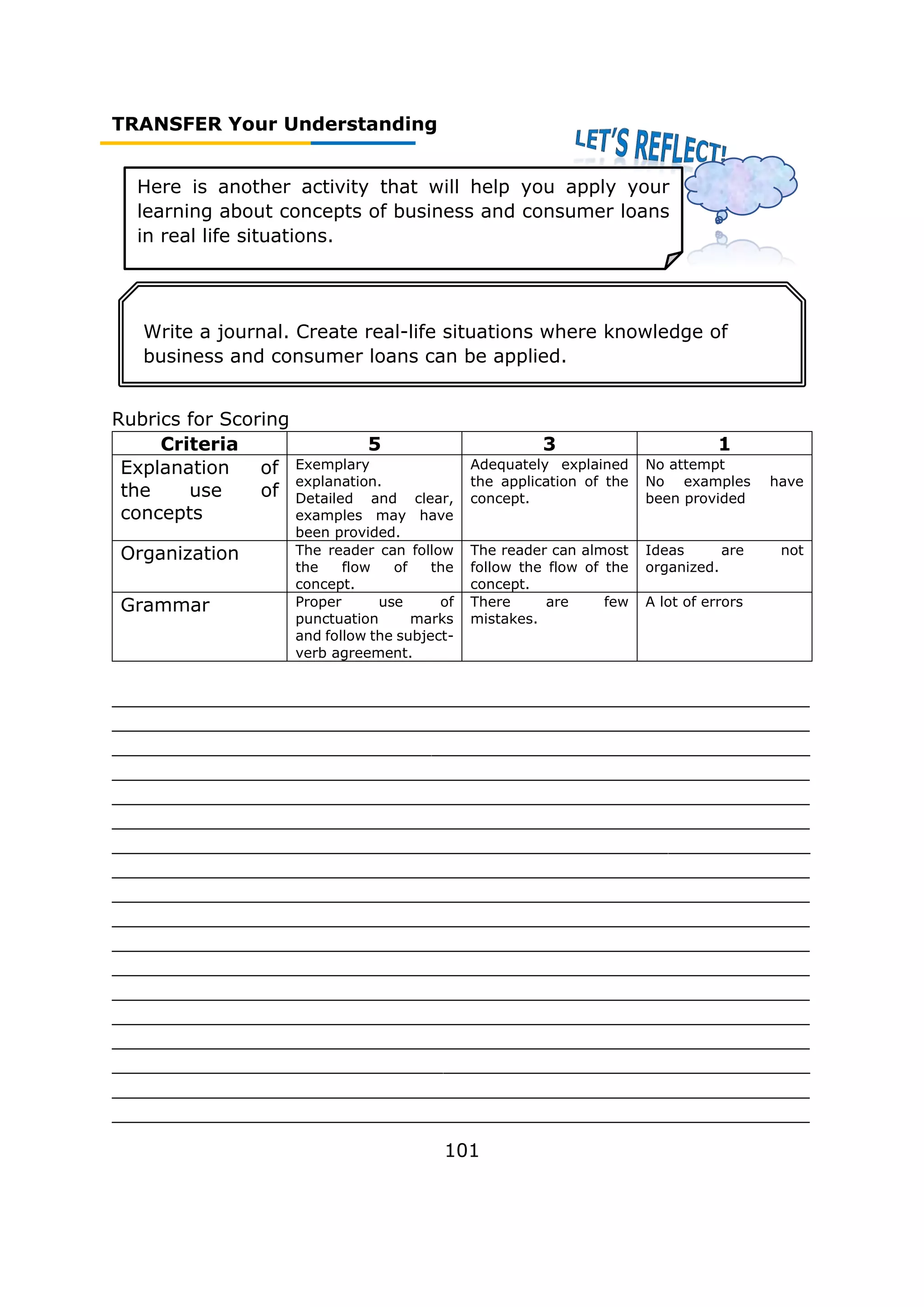
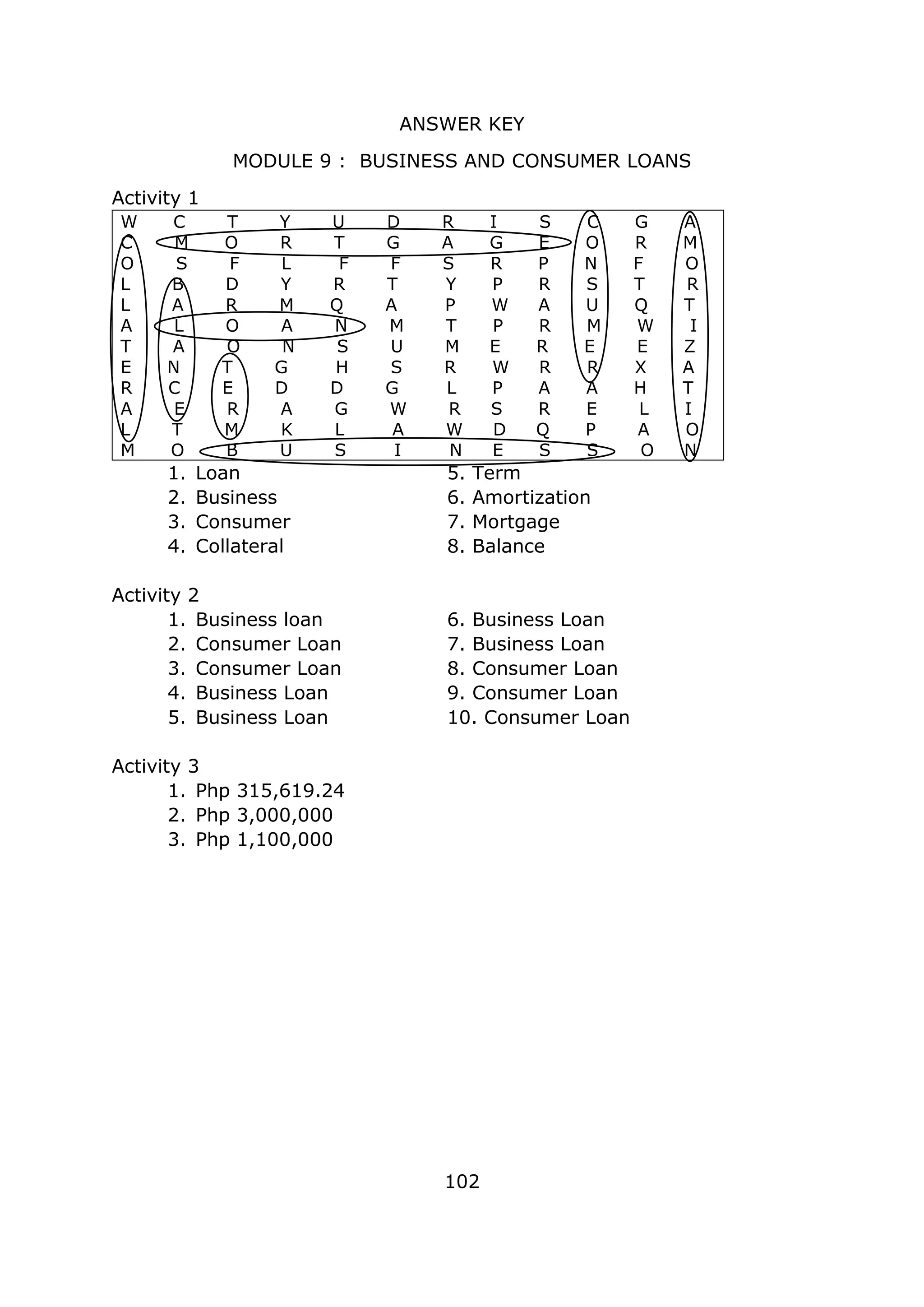
This document is a self-learning kit on general mathematics developed by the Department of Education Region VII - Central Visayas for Mandaue City public schools. It contains 11 modules covering key topics in functions, rational functions, inverse functions, exponential functions, logarithmic functions, simple and compound interest, annuities, stocks and bonds, loans, propositions, and validity of arguments. The developers encourage teachers and stakeholders to provide feedback and recommendations to improve the learning resource.











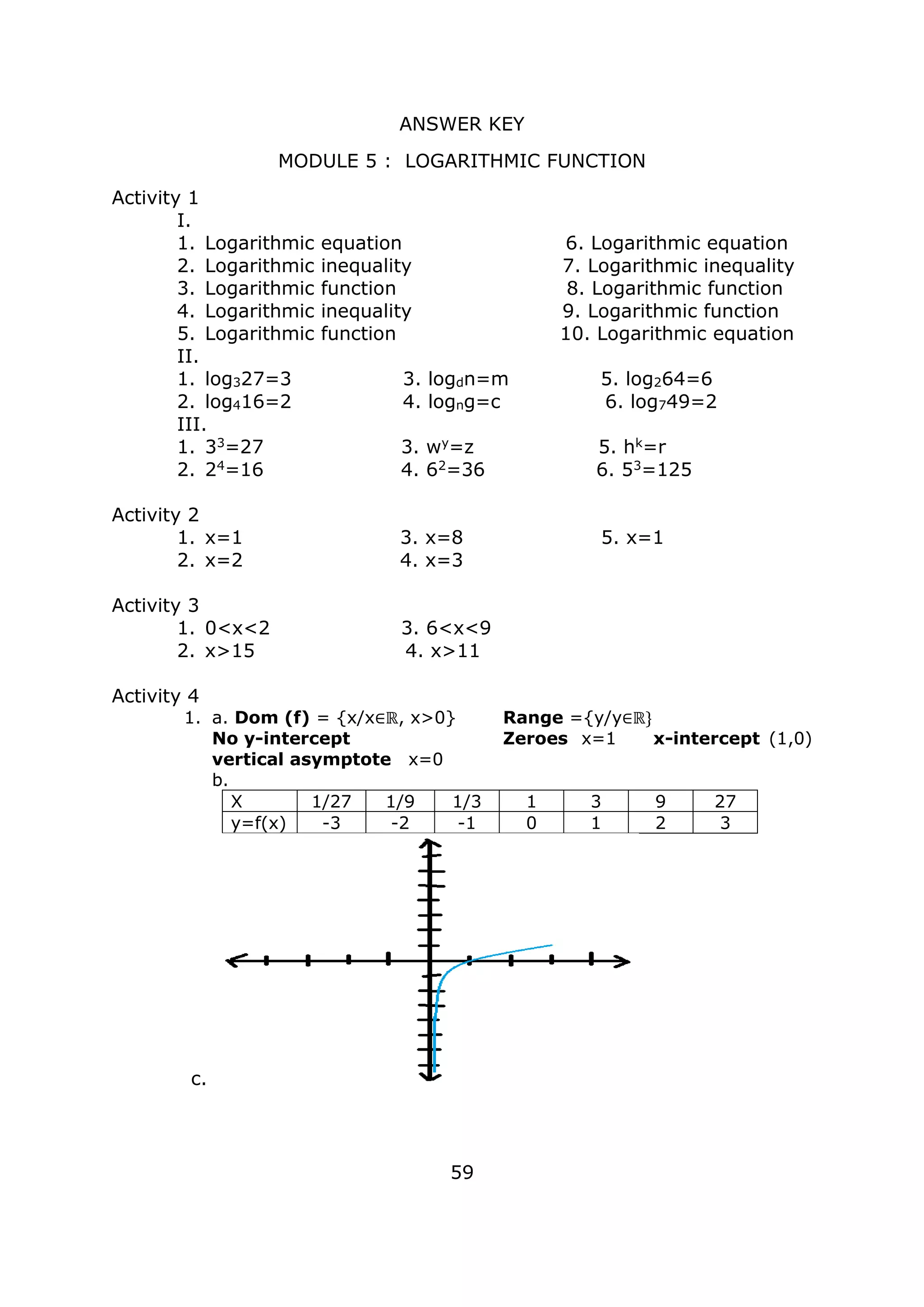
![Activity 5
7
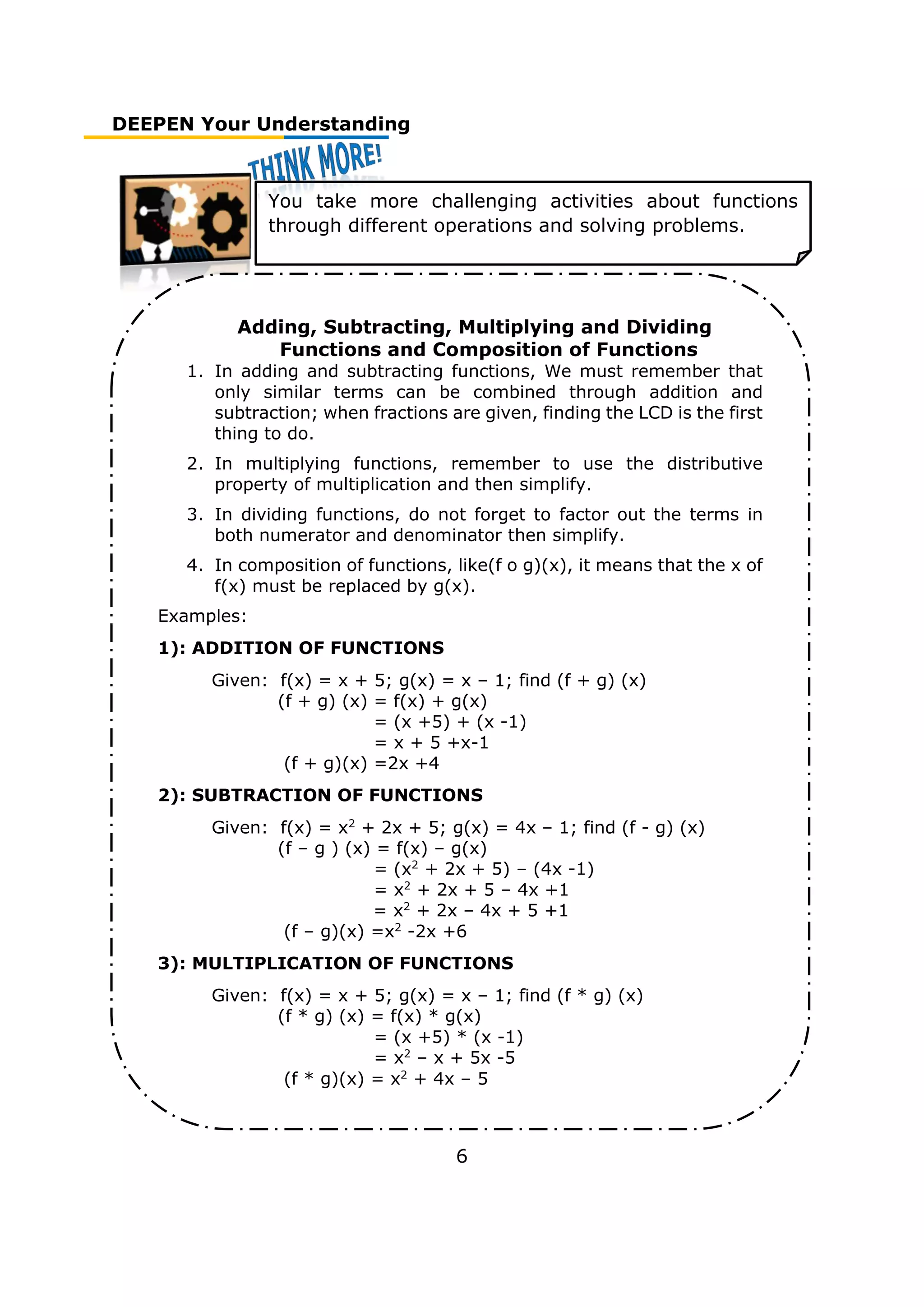
Examples:
4): DIVISION OF FUNCTIONS
Given: f(x) = x2
+ 6x + 5; g(x) = x2
– 1 ; find (f / g) (x)
(f / g) (x) = f(x) / g(x)
= (x2
+ 6x + 5) / (x2
-1)
= [(x+1)(x+5)] / [(x+1)(x-1)]
(f / g)(x) =
𝒙+ 𝟓
𝒙−𝟏
5): COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS
Given: f(x) = x2
+ 2x – 3 ; g(x) = x – 1; find (f o g) (x)
(f o g) (x) = f(g(x))
= (x – 1)2
+ 2 (x – 1) – 3
= (x2
– x – x + 1) + (2x – 2) – 3
= x2
– 2x + 2x + 1 – 2 – 3
(f o g)(x) = x2
– 4
Given: f(x) = x2
+ 2x – 3 ; g(x) = x – 1; find (g o f) (x)
(g o f) (x) = g(f(x))
= (x2
+ 2x – 3) – 1
= x2
+ 2x – 3 – 1
(g o f)(x) = x2
+ 2x – 4
Given that f(x) = x2
– 2x – 8 and g(x) = x – 4, do the indicated task.
1. ( f + g ) (x) 5. ( f o g ) (x)
Answer:___________________ Answer:___________________
2. ( f – g ) (x) 6. ( g – f ) (x)
Answer:___________________ Answer:___________________
3. ( g * f ) (x) 7. ( g o f ) (x)
Answer: __________________ Answer:___________________
4. ( f / g ) (x) 8. (g / f ) (x)
Answer:__________________ Answer:___________________](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-14-2048.jpg)













































![FIRM UP Your Understanding
73
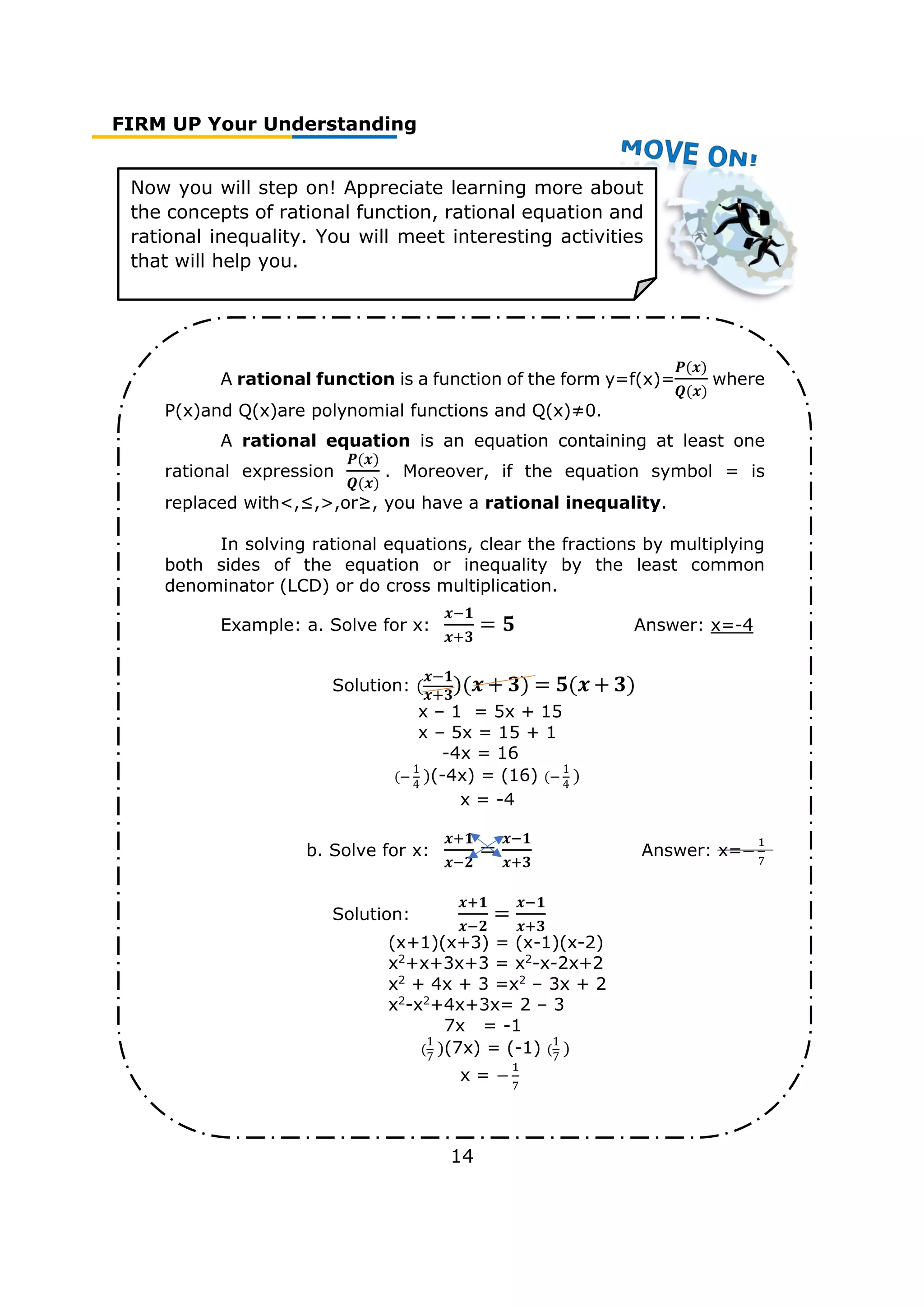
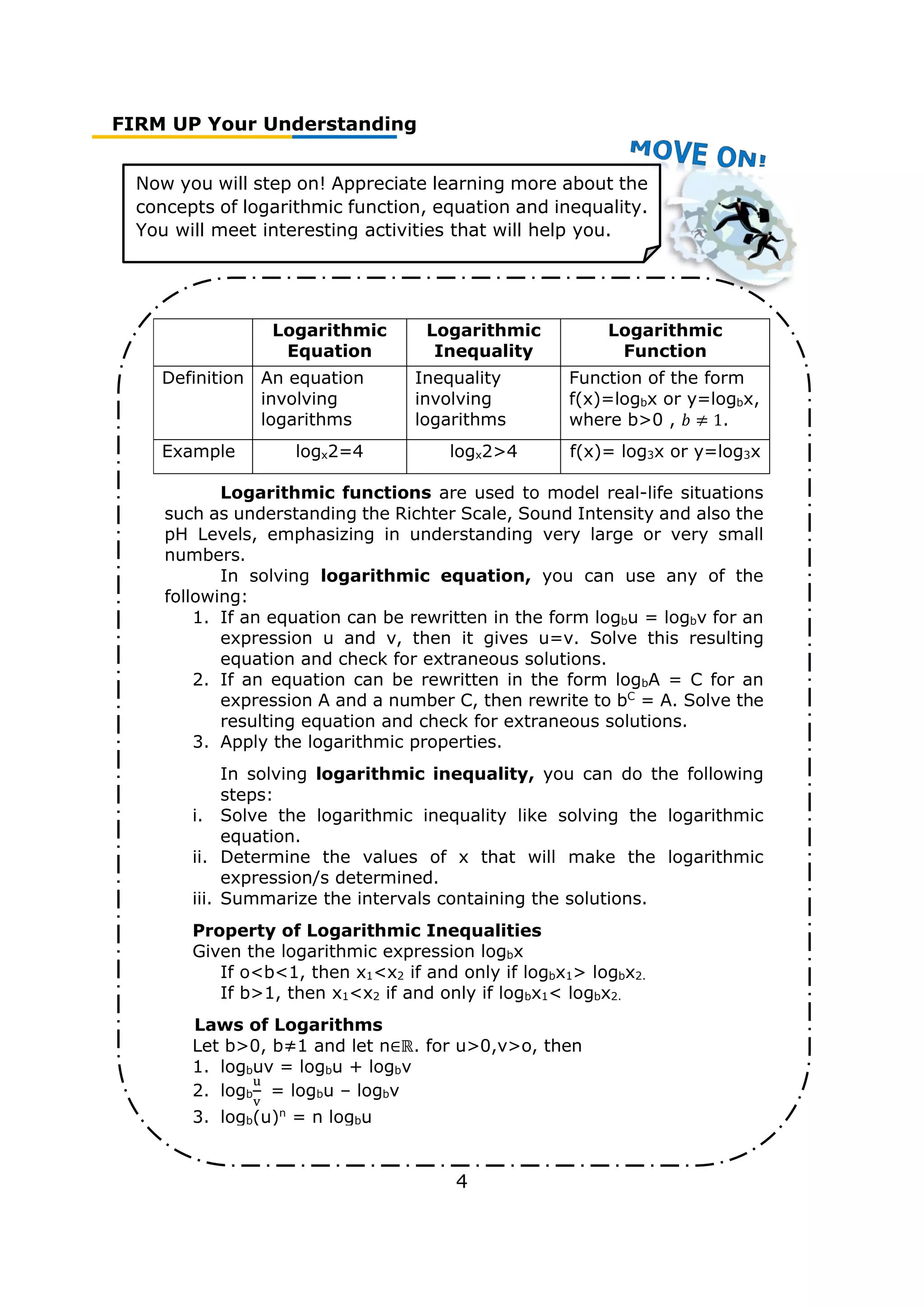
Now you will step on! Appreciate learning more about
the concepts of simple and general annuities. You will
meet interesting activities that will help you.
Annuity is a sequence of payments made at equal(fixed) intervals
or periods of time.
Simple Annuity General Annuity
According to
payment interval
and interest
period
It is an annuity where
the payment interval is
the same as the
interest period.
It is an annuity where
the payment interval is
not the same as the
interest period
Ordinary Annuity Annuity Due
According to
time of payment
It is an annuity in
which the payments
are made at the end of
each payment interval.
It is an annuity in which
the payments are made
at the beginning of each
payment interval.
Simple Ordinary Annuity is a simple annuity in which the payments
are made at the end of each payment interval.
Simple Annuity Due is a simple annuity in which the payments are
made at the beginning of each payment period.
Future Value of an annuity, F – sum of future values of all the
payments to be made during the entire term of the annuity.
Present value of an annuity, P – sum of present values of all the
payments to be made during the entire term of the annuity.
Formula of the Future Value of Formula of the Present Value
Simple Ordinary Annuity of Simple Ordinary Annuity
FV=R[
(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)𝑚𝑡−1
𝑟
𝑚
] PV=R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−𝑚𝑡
𝑟
𝑚
]
Formula of the Future Value of Formula of the Present Value
Simple Annuity Due of Simple Annuity Due
FV=R[
(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)𝑚𝑡−1
𝑟
𝑚
][1+
𝑟
𝑚
] PV=R+R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−(𝑚𝑡−1)
𝑟
𝑚
]
General Ordinary Annuity is general annuity in which the payments
are made at the end of each payment period.
Formula of the Future Value of Formula of the Present Value
General Ordinary Annuity of General Ordinary Annuity
FV=R[
(1+𝑗)𝑛𝑡−1
𝑗
] PV=R[
1−(1+𝑗)−𝑛𝑡
𝑗
]
where j=(1 +
𝑟
𝑚
)
𝑚
𝑛 − 1 where j=(1 +
𝑟
𝑚
)
𝑚
𝑛 − 1
where R=periodic payment, r=rate, m=frequency of conversion,
t= number of years j=equivalent interest rate per payment interval
converted from the interest rate per period, n= frequency of
payment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-80-2048.jpg)
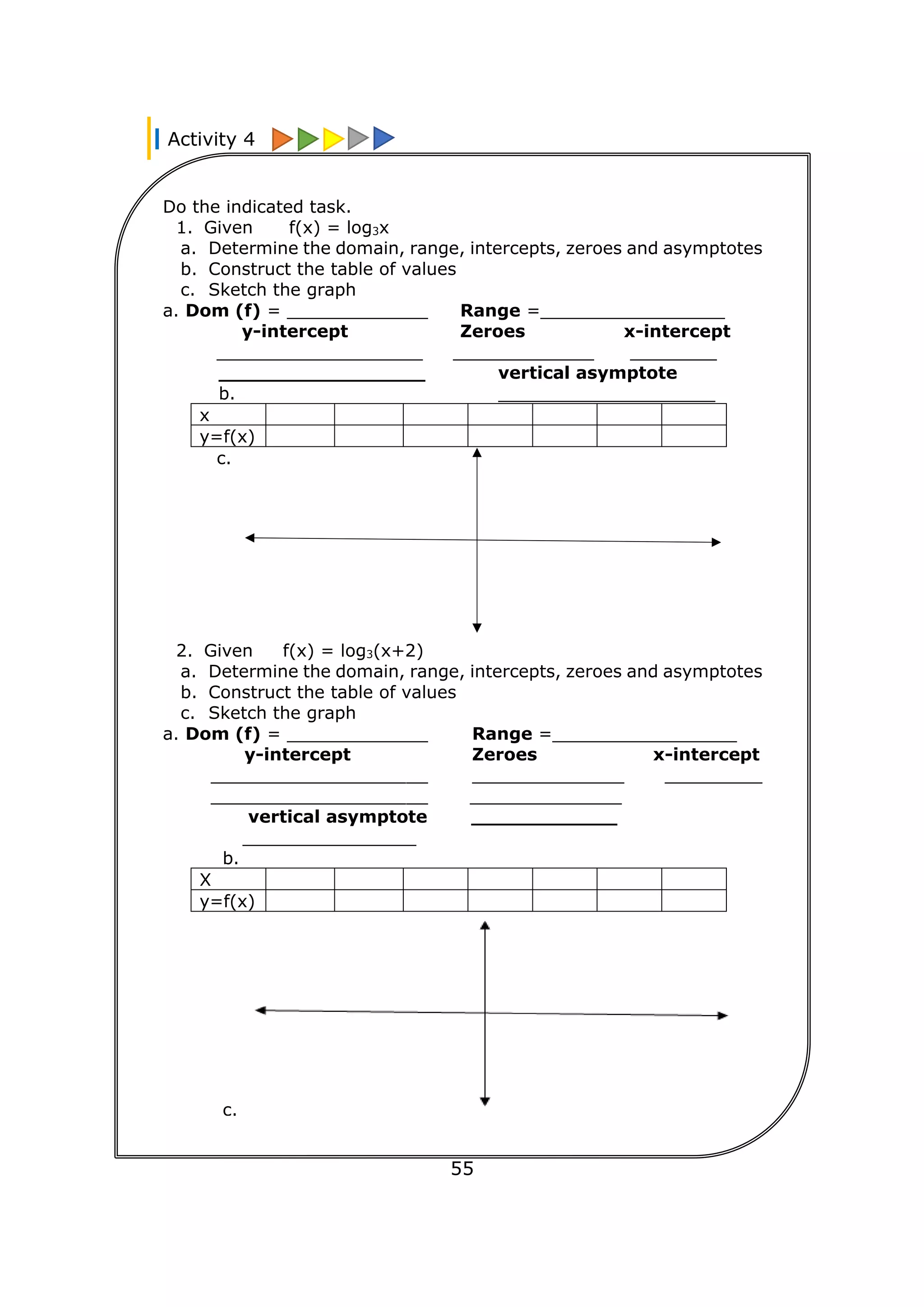
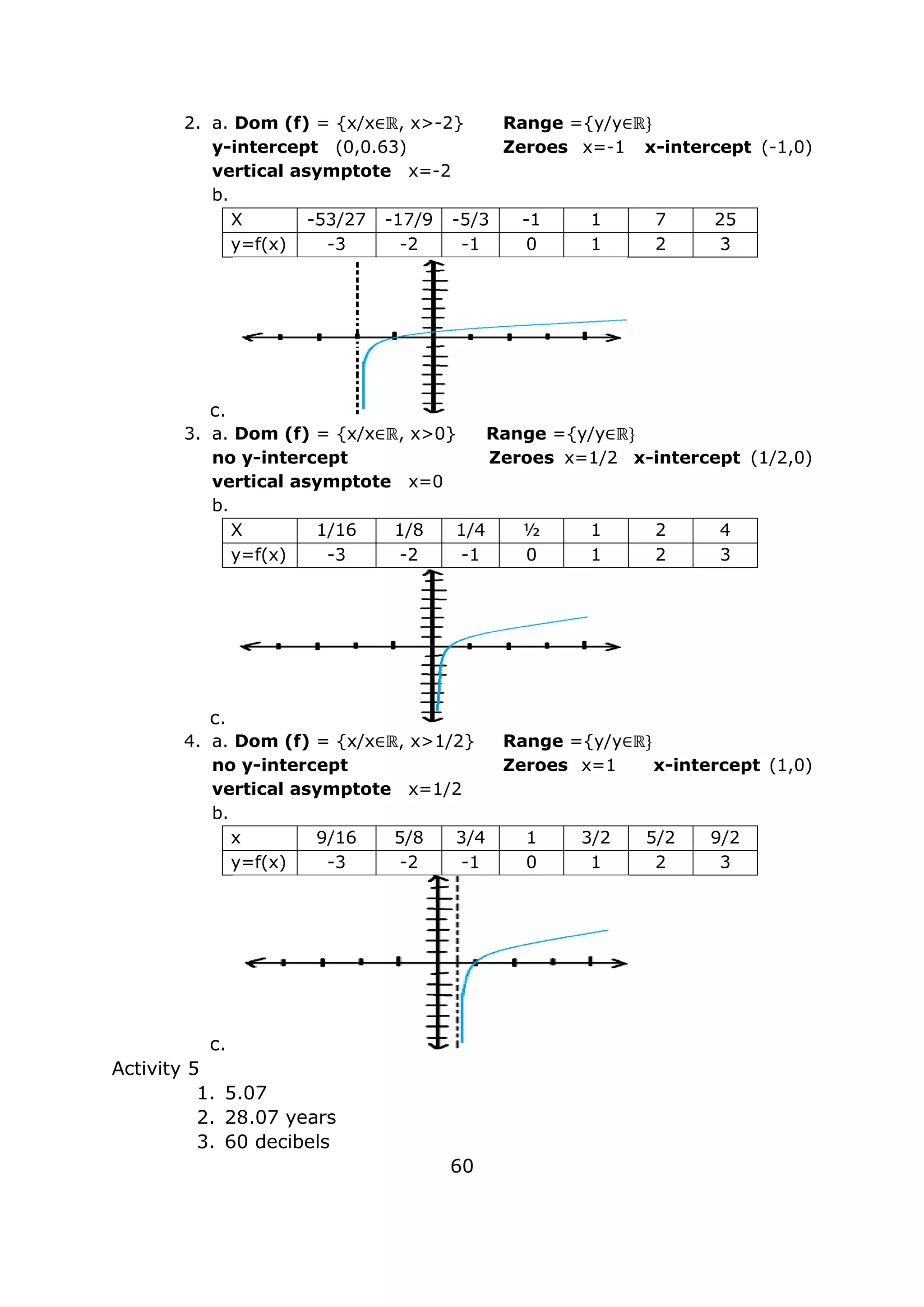
![74
Examples:
Simple Annuity General Annuity
Pirena started paying Php 1,000
quarterly in a fund that pays 6%
compounded quarterly.
Monthly payments of Php 3,000
for 6 years with interest of 4%
compounded monthly.
Danaya started paying Php 1,000
monthly in a fund that pays 6%
compounded quarterly.
Quarterly payment of Php 5,000 for 3
years with interest of 3% compounded
semi-annually.
a. Jude started paying Php 2,000 every end of the quarter in a
bank that pays 2.5% coompounded quarterly that is good for
5 years. Determine the present value and future value.
Analyse the situation: This situation shows a simple ordinary annuity
since the payment interval and interest period are the same (both
quarterly) and the payment is always at the end of the period.
Given: R=2,000 m=4 r=0.025 t=5
Required: Present Value
Formula to be used: PV=R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−𝑚𝑡
𝑟
𝑚
]
Solution: PV=(2,000)[
1−(1+
0.025
4
)−(4)(5)
0.025
4
]
PV=(2,000)[
1−(1+0.00625)−20
0.00625
]
PV=(2,000)[
1−(1.00625)−20
0.00625
]
PV=(2,000)[
1−0.882840265061485
0.00625
]
PV=(2,000)[
0.117159734938515
0.00625
]
PV=(2,000)(18.74555759016237)
PV=37,491.12
Required: Future Value
Formula to be used: FV=R[
(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)𝑚𝑡−1
𝑟
𝑚
]
Solution: FV=(2,000)[
(1+
0.025
4
)(4)(5)−1
0.025
4
]
FV=(2,000)[
(1+0.00625)20−1
0.00625
]
FV=(2,000)[
(1.00625)20−1
0.00625
]
FV=(2,000)[
1.132707738392917−1
0.00625
]
FV=(2,000)[
0.132707738392917
0.00625
]
FV=(2,000)(21.23323814286672)
FV=42,466.48
Therefore the present value is Php 37,491.12 and the future
value is Php 42, 466.48.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-81-2048.jpg)
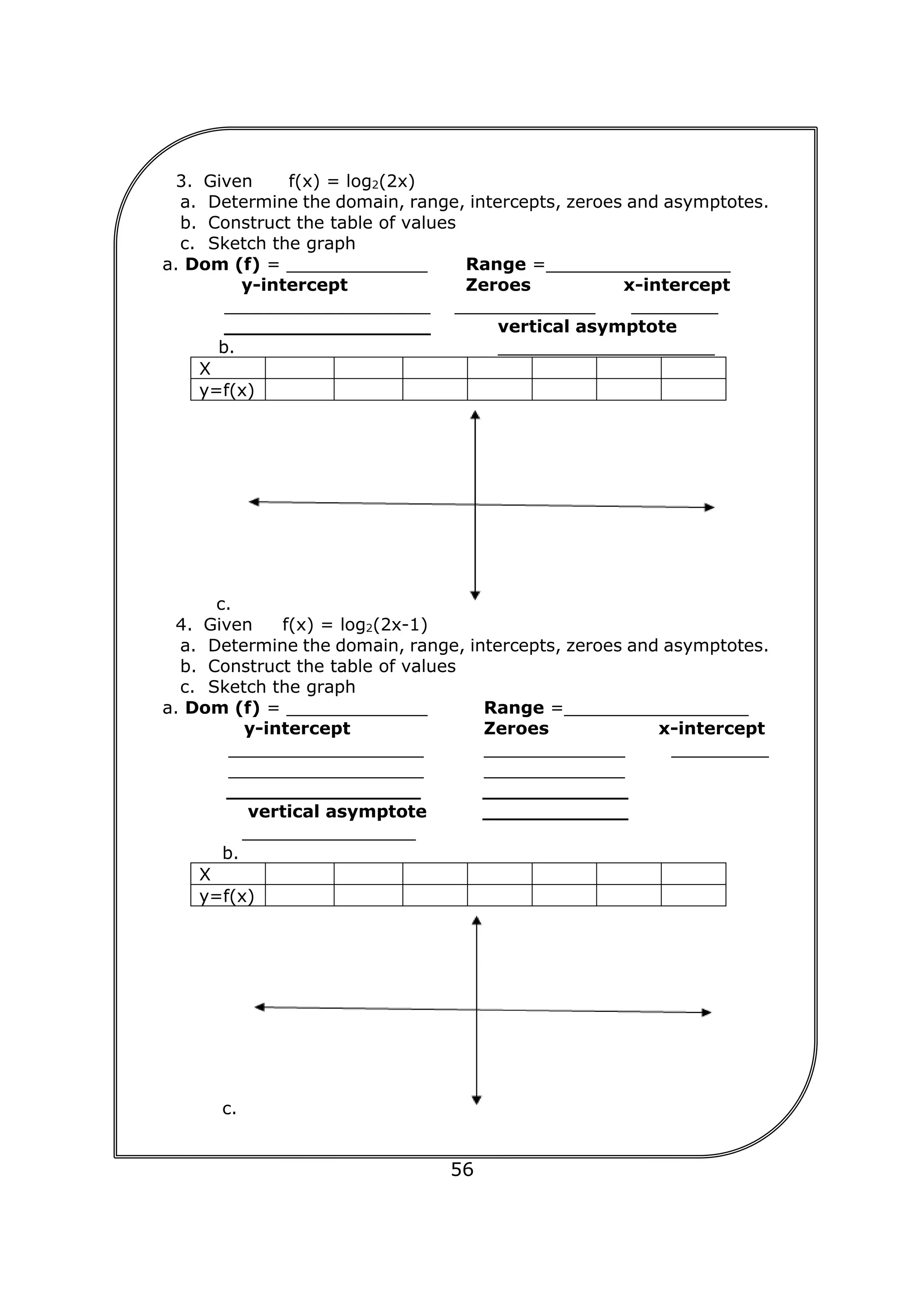
![75
b. Julius, a grade 8 student from Mandaue City, would like to
save Php 5,000 for his moving up ceremony. How much
should he deposit in a savings account every end of the
month for 2.5 years if the interest is at 0.25% compounded
monthly.
Analyse the situation: This situation shows a simple ordinary annuity
Given: FV=5,000 m=12 r=0.0025 t=2.5
Required: R, the periodic payment
Formula to be used: FV=R[
(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)𝑚𝑡−1
𝑟
𝑚
]
Solution: 5,000=R[
(1+
0.0025
12
)(12)(2.5)−1
0.0025
12
]
5,000=R[
(1+0.0002083)30−1
0.0002083
]
5,000=R[
(1.0002083)30−1
0.0002083
]
5,000=R[
1.006267910912696−1
0.0002083
]
5,000=R[
0.006267910912696
0.0002083
]
5,000=R(30.0907869068459)
5000
30.0907869068459
= R
R = 166.16
Therefore Julius needs to save Php 166.16 every end of the month.
c. The buyer of the car pays Php 15,000 every beginning of the
month for 4 years. If money is 6% compounded monthly,
how much is the price of the car?
Analyse the situation: This situation shows a simple annuity due since
the payment interval and interest period are the same (both monthly) and
the payment is always at the beginning of the period. It looks for present
value.
Given: R=15,000 m=12 r=0.06 t=4
Required: Present Value
Formula to be used: PV=R+R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−(𝑚𝑡−1)
𝑟
𝑚
]
Solution: PV=15,000+ (15,000)[
1−(1+
0.06
12
)−((12)(4)−1)
0.06
12
]
PV=15,000+(15,000)[
1−(1.005)−47
0.005
]
PV=15,000+(15,000)[
1−0.791033903141295
0.005
]
PV=15,000+(15,000)[
0.208966096858705
0.005
]
PV=15,000+(15,000)(41.79321937174105)
PV=15,000+626,898.29
PV= 641,898.29
Therefore the price of the car is Php 641,898.29.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-82-2048.jpg)
![Activity 2
76
d. Jason borrowed an amount of money from Landbank. He pays
Php 3,250 each quarter for 4 years. How much money did he
borrow if the interest is 2% compounded semi-annually?
Analyse the situation: This situation shows a general ordinary annuity
since the payment interval and interest period are not the same.
Given: R=3,250 m=2 r=0.02 t=4 n=4
Required: Present Value
Formula to be used: PV=R[
1−(1+𝑗)−𝑛𝑡
𝑗
] where j=(1 +
𝑟
𝑚
)
𝑚
𝑛 − 1
Solution: solve for j first
j=(1 +
0.02
2
)
2
4 − 1
j=(1+0.01)0.5
– 1
j=(1.01)0.5
– 1
j= 1.00499-1
j=0.00499 then solve for PV
PV=(3,250)[
1−(1+𝑗)−𝑛𝑡
𝑗
]
PV=(3,250)[
1−(1+0.00499)−(4)(4)
0.00499
]
PV=(3,250)[
1−(1.00499)−16
0.00499
]
PV=(3,250)[
1−0.923447380412246
0.00499
]
PV=(3,250)[
0.076552619587754
0.00499
]
PV=(3,250)(15.34120633021126)
PV= 49,858.92
Therefore Jason borrowed an amount of Php 49,858.92.
Determine whether the following as simple annuity or general annuity.
1. Quarterly payments of Php 3,000 for 4 years with interest rate of 3%
compounded quarterly.
Answer:_____________________________________
2. Semi-annually payments of Php 2,500 for 8 years with interest rate
of 2% compounded monthly.
Answer:_____________________________________
3. Juana started paying Php 3,000 quarterly in a fund that pays 3%
compounded annually.
Answer:_____________________________________
4. The buyer of the house pays Php 25,000 every beginning of the
month for 5 years with 6% compounded monthly.
Answer:_____________________________________](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-83-2048.jpg)



![80
Given: R=50,000 m=1 r=0.03 t=6 n=4
Formula to be used: PV=R[
1−(1+𝑗)−𝑛𝑡
𝑗
] where j=(1 +
𝑟
𝑚
)
𝑚
𝑛 − 1
solve for j first
j=(1 +
0.03
1
)
1
4 − 1
j=(1.03)0.25
– 1
j= 1.00742-1
j=0.00742 then solve for PV
PV=(50,000)[
1−(1+0.00742)−(4)(6)
0.00742
]
PV=(50,000)[
1−(1.00742)−24
0.00742
]
PV=(50,000)[
1−0.8374258359711481
0.00742
]
PV=(50,000)[
0.162574164028519
0.00742
]
PV=(50,000)(21.91026469387054)
PV= 1,095,513.23
Fair Market Value (FMV)=80,000+1,095,513.23=₱1,175,513.23
Hence, Ms. Ceniza’s offer has a higher market value.
2. Find the future value at the end of year 4 of the cash flow
stream given that the interest rate is 6%.
Lets list the payment in same periodic payment
First 100
Second 100 100
Third 100 100
Fourth 100 100 100
FV1 FV2 FV3
FV = FV1 + FV2 + FV3
Lets solve the FV1
Given: R=100 m=1 r=0.06 t=4
Formula: FV=R[
(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)𝑚𝑡−1
𝑟
𝑚
]
Solution: FV1=(100)[
(1+
0.06
1
)(1)(4)−1
0.06
1
] FV1=(100)[
0.26247696
0.06
]
FV1=(100)[
(1.06)4−1
0.06
] FV1=(100)(4.374616)
FV1=(100) [
1.26247696−1
0.06
] FV1=437.46
Lets solve the FV2
Given: R=100 m=1 r=0.06 t=3
Formula: FV=R[
(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)𝑚𝑡−1
𝑟
𝑚
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-87-2048.jpg)
![81
Solution: FV2=(100)[
(1+
0.06
1
)(1)(3)−1
0.06
1
] FV2=(100)[
0.191016
0.06
]
FV2=(100)[
(1.06)3−1
0.06
] FV2=(100)(3.1836)
FV2=(100) [
1.191016−1
0.06
] FV2=318.36
FV3 = 100
So, FV= 437.46 + 318.36 + 100 = 855.82
Hence the future value at the end of year 4 is 855.82.
Deferred Annuity – an annuity that does not begin until a given
time interval has passed.
Period of Deferral, k – time between the purchase of an annuity
and the start of the payments for ,the deferred annuity.
Formula of the Present Value of Deferred Annuity
PV=R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−(𝑘+𝑝)
𝑟
𝑚
] – R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−𝑚𝑘
𝑟
𝑚
]
where R=periodic payments, r=rate, m=frequency of conversion
k=period of deferral, p=period of actual payments
Examples:
1. Determine the period of defferal and period of actual payments.
a. Monthly payments of ₱10,000 for 8 years that will start 6 months from
now.
Answer: k=5 months or 5 periods, p=96 months or 96 periods
b. Quarterly payments of ₱3,000 for 6 years that will start first quarter
after two years.
Answer: k=8 quarters or 8 periods, p=24 quarters or 24 periods
2. On the 30th
birhtday of Ms. Geronimo, she decided to buy a pension
plan. This plan will allow her claim Php 50,000 quarterly for 10 years
starting first quarter after her 55th
birthday. What one-time payment
should she make on her 30th
birthday, if the interest rate is 10%
compounded quarterly?
Given: R=50,000 m=4 r=0.1 k= 100 quarters p=40 quarters
Formula: PV=R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−(𝑘+𝑝)
𝑟
𝑚
] – R[
1−(1+
𝑟
𝑚
)−𝑘
𝑟
𝑚
]
Solution: PV=(50,000)[
1−(1+
0.1
4
)−(100+40)
0.1
4
] – (50,000)[
1−(1+
0.1
4
)−(100)
0.1
4
]
PV=(50,000)[
1−(1+0.025)−140
0.025
] – (50,000)[
1−(1+0.025)−100
0.025
]
PV=(50,000)[
1−(1.025)−140
0.025
] – (50,000)[
1−(1.025)−100
0.025
]
PV=(50,000)[
1−0.031525272203131
0.025
]–(50,000)[
1−0.084647368388026
0.025
]
PV=(50,000)[
0.968474727796869
0.025
] – (50,000)[
0.915352631611974
0.025
]
PV=(50,000)(38.73898911187)-(50,000)(36.61410526448)
PV=1,936,949.455593739 – 1,830,705.263223948
PV=106,244.19
Therefore, the one-time payment for this pension is
Php 106,244.19.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-88-2048.jpg)



























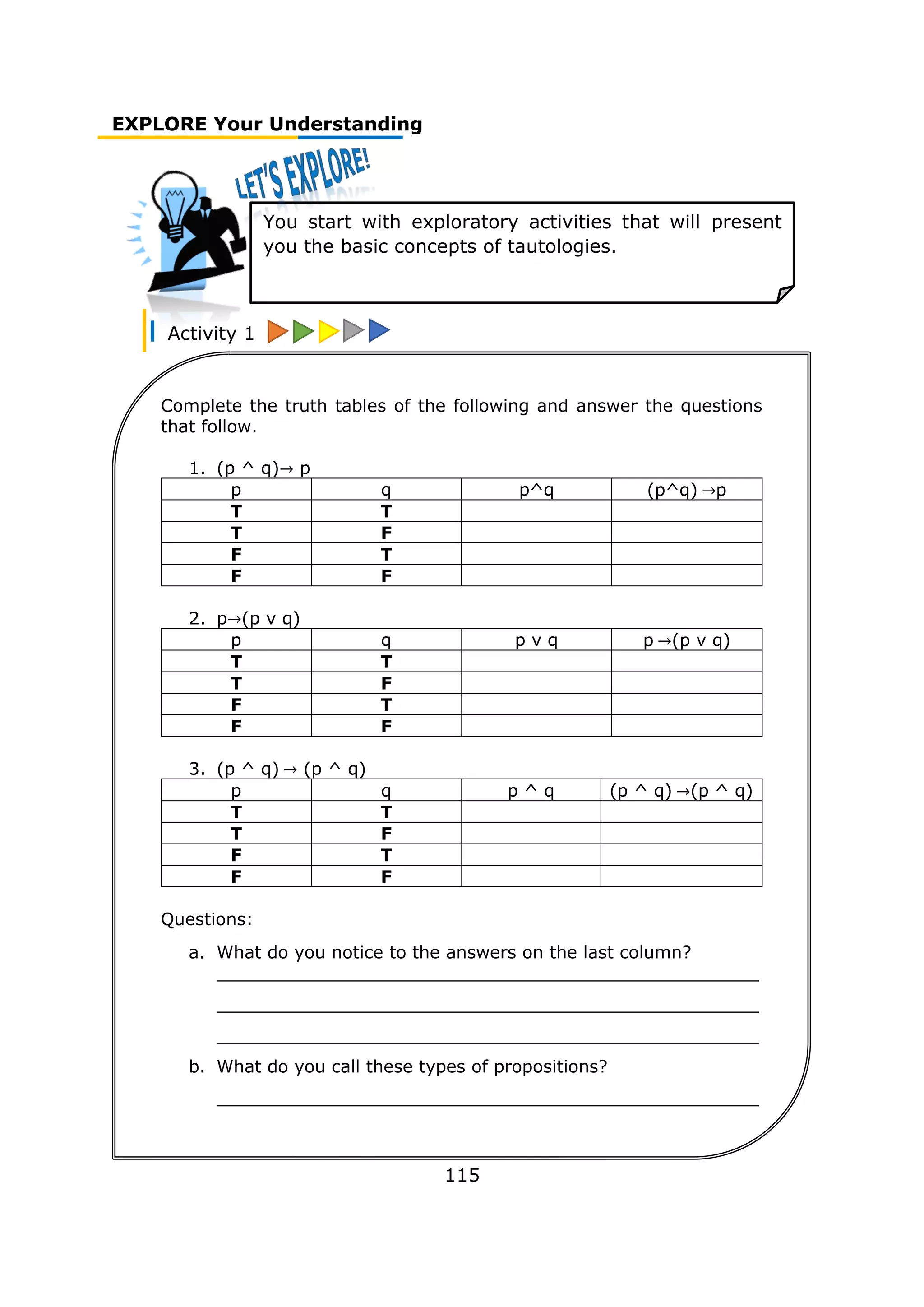
![FIRM UP Your Understanding
116
Now you will step on! Appreciate learning more about the
concepts of tautologies and fallacies. You will meet
interesting activities that will help you.
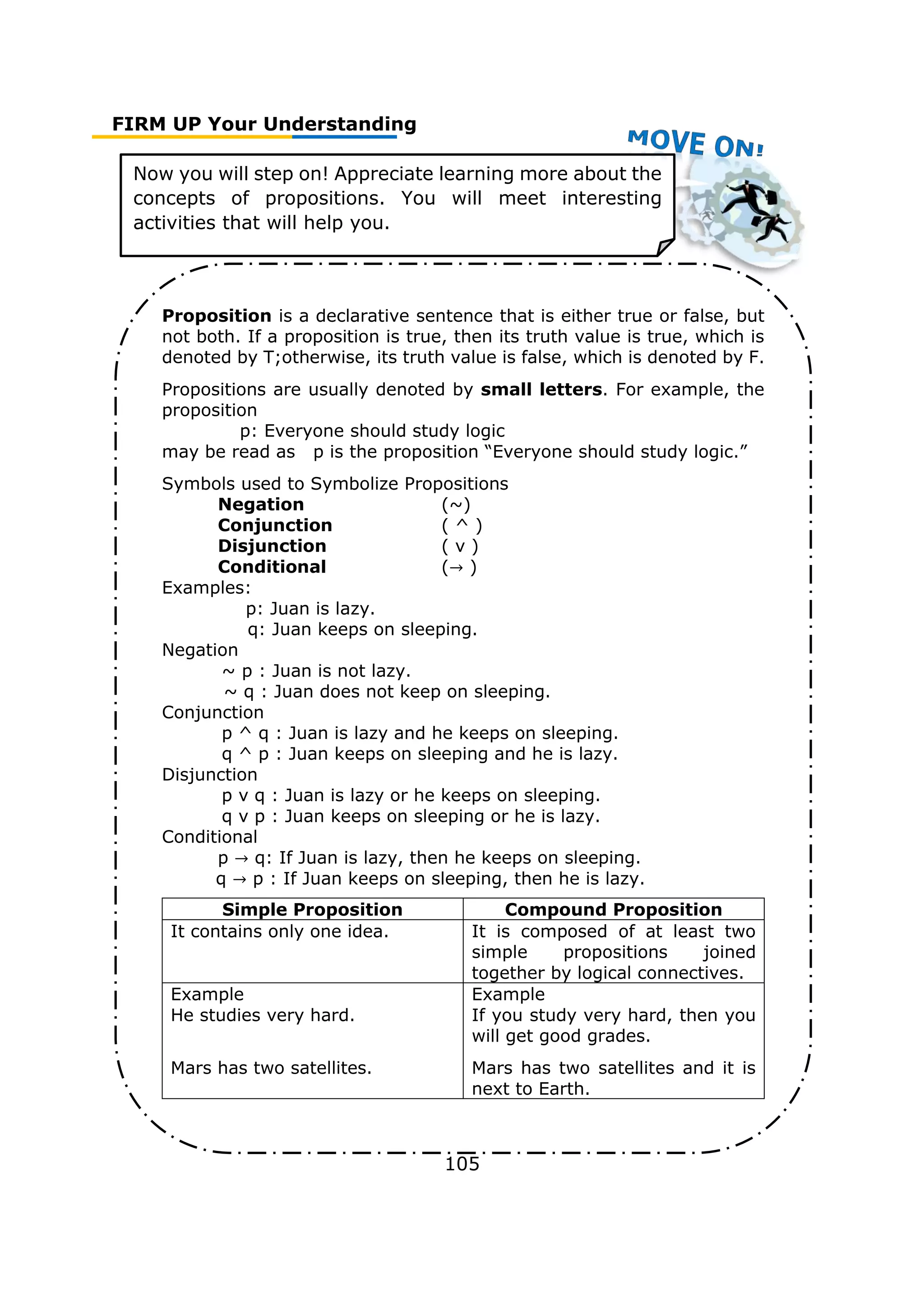
Tautology is a formula or assertion that is true in every possible
interpretation.
A valid argument satisfies the condition; that is, the conclusion q is
true whenever the premises p1, p2, …, pn are all true.
Different Tautologies or valid arguments. Let p,q, and r be propositions
Propositional Form Standard form
Rule of
Simplification
(p^q) → p _p^q_
∴ p
Rule of Addition p→(p v q) __p__
∴ p v q
Rule of
Conjunction
(p^q) →(p^q) p
__q__
∴ p^q
Modus Ponens [(p →q)^p] ) →q p→q
__p__
∴ q
Modus Tollens [(p→q)^(~q)] →(~p) p→q
__~q__
∴ ~p
Law of Syllogism [(p→q)^(q→r)] →(p→r) p→q
__q→r__
∴ p→r
Rule of Disjunctive
Syllogism
[(p v q)^(~p)] →q p v q
__~p__
∴ q
Rule of
Contradiction
[(~p) → ∅]→p _(~p) → ∅_
∴ p
Rule of Proof by
Cases
[(p→r)^(q→r)] →[(pvq) →r] p→r
__q→r__
∴ (p v q)→r
Rule of Simplification
Juan sings and dances with Maria.
Therefore, Juan sang with Maria.
Rule of Addition
Juan sings with Maria.
Therefore, Juan sang or danced with Maria.
Rule of Conjunction
Juan sings with Maria.
Juan dances with Maria.
Therefore, Juan sang and danced with Maria.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-123-2048.jpg)
![117
Modus Ponens
If my alarm sounds, then I will wake up early.
My alarm sounded.
Therefore, I woke up early.
Modus Tollens
If my alarm sounds, then I will wake up early.
I did not woke up early.
Therefore, I my alarm did not sound.
Laws of Syllogism
If my alarm sounds, then I will wake up early.
If will wake up early, then I will be early in school.
Therefore, if my alarm sounds then I will be early in school.
Rules of Disjunctive Syllogism
Juan sings or dances with Maria.
Juan did not sing with Maria.
Therefore, Juan danced with Maria.
Rules of Contradiction
If I will not do it, then no one will do it.
Therefore, I did it.
Rule of Proof by Cases
If my alarm sounds, then I will be early in school.
If I will wake up early, then I will be early in school.
Therefore, If my alarm sounds or I will wake up early then I will
be early in school.
Fallacy is an argument which is not valid. In fallacy, it is possible for
the premises to be true but the conclusion is false. Fallacy is not a
tautology.
Common Fallacies in Logic
Propositional Form Standard form
Fallacy of the
Converse
[(p →q)^q] → p p →q
__q__
∴ p
Fallacy of the
Inverse
[(p→q)^(~p)] →(~q) p →q
__~p__
∴ ~q
Affirming the
Disjunct
[(p vq)^p] →(~q) p v q
__p__
∴ ~q
Fallacy of the
Consequent
(p→q) →(q→p) _p→q_
∴ q→p
Denying a Conjunct [~(p^q)^(~p)] →q ~(p ^ q)
__~p__
∴ q
Improper
Transposition
(p→q) → [(~p) →(~q)] __ p→q __
∴ (~p) →(~q)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genmathqi-210920122820/75/Genmath-qi-124-2048.jpg)