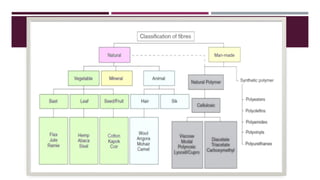
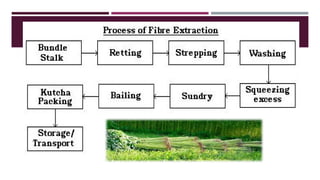
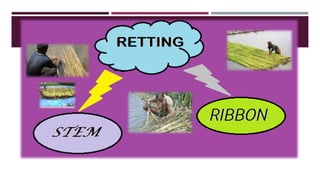
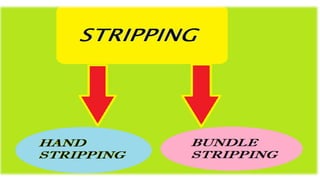
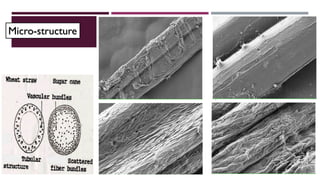
The document discusses fiber extraction processes, highlighting materials like cotton, flax, and jute used for various applications including textiles and cordage. It details the retting process, conditions for effective extraction, and methods for stripping fibers from plants, as well as the processing of sugarcane bagasse into fibers. Additionally, it outlines the recycling uses of these fibers in manufacturing and composites.