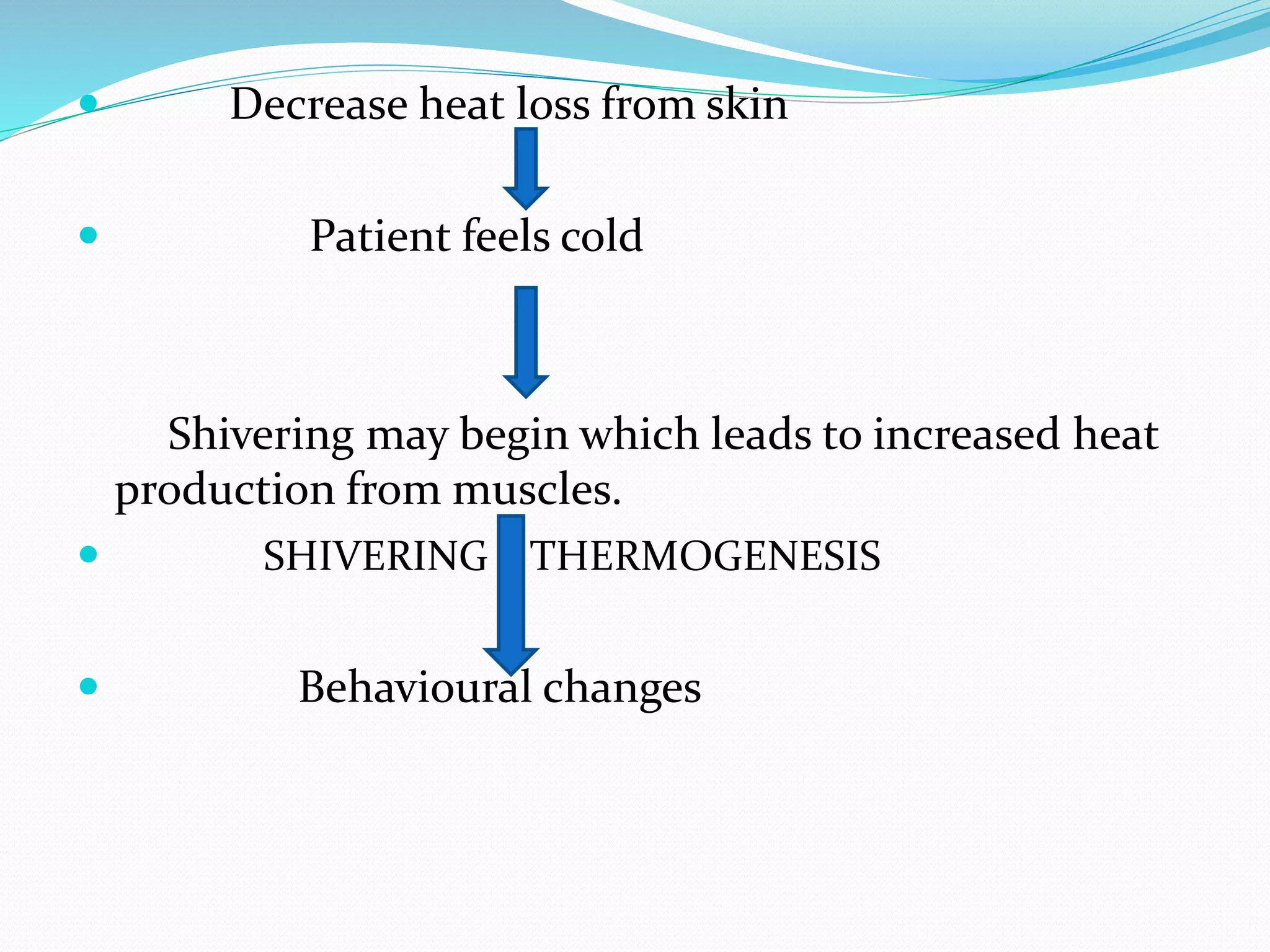
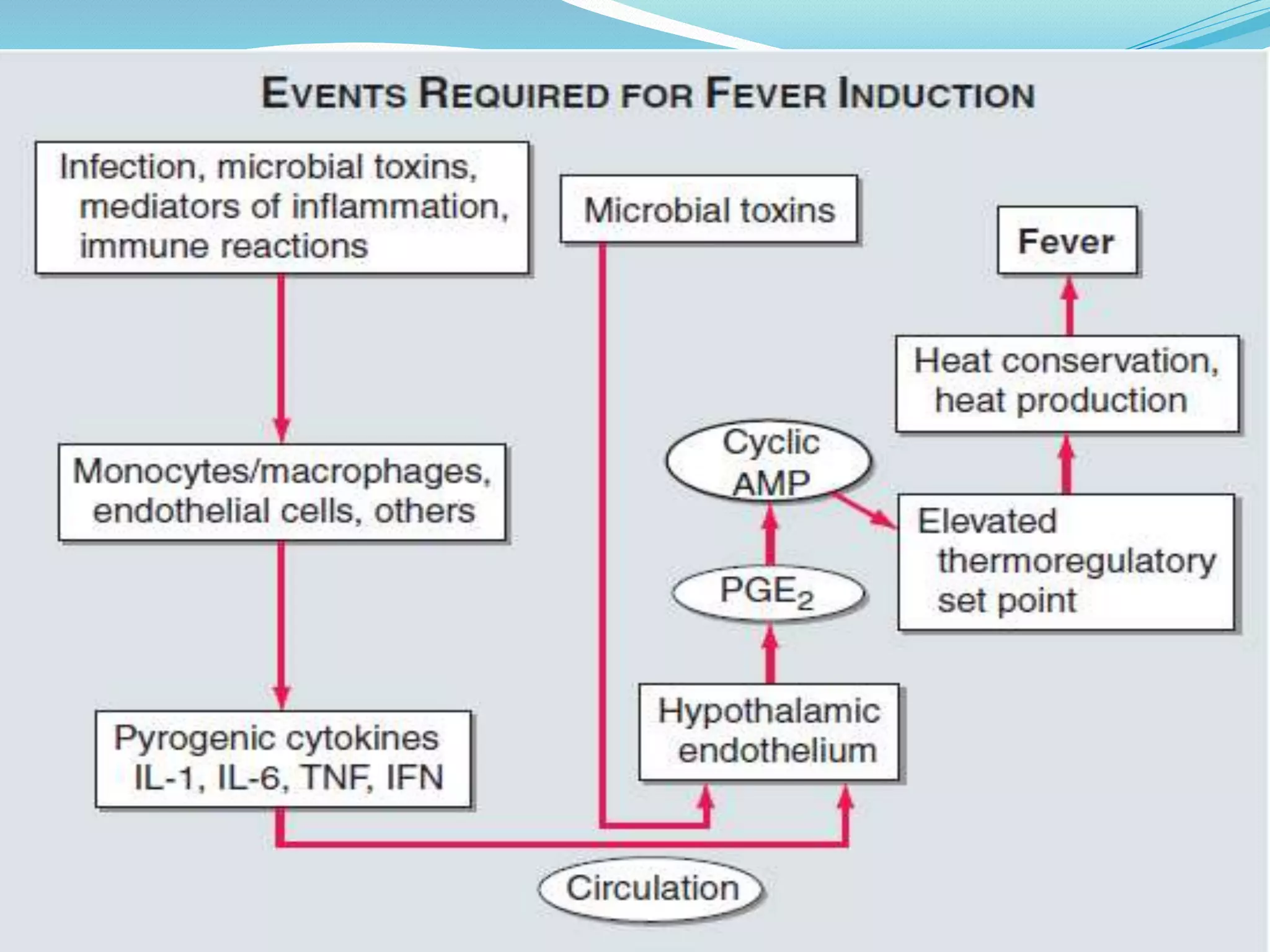
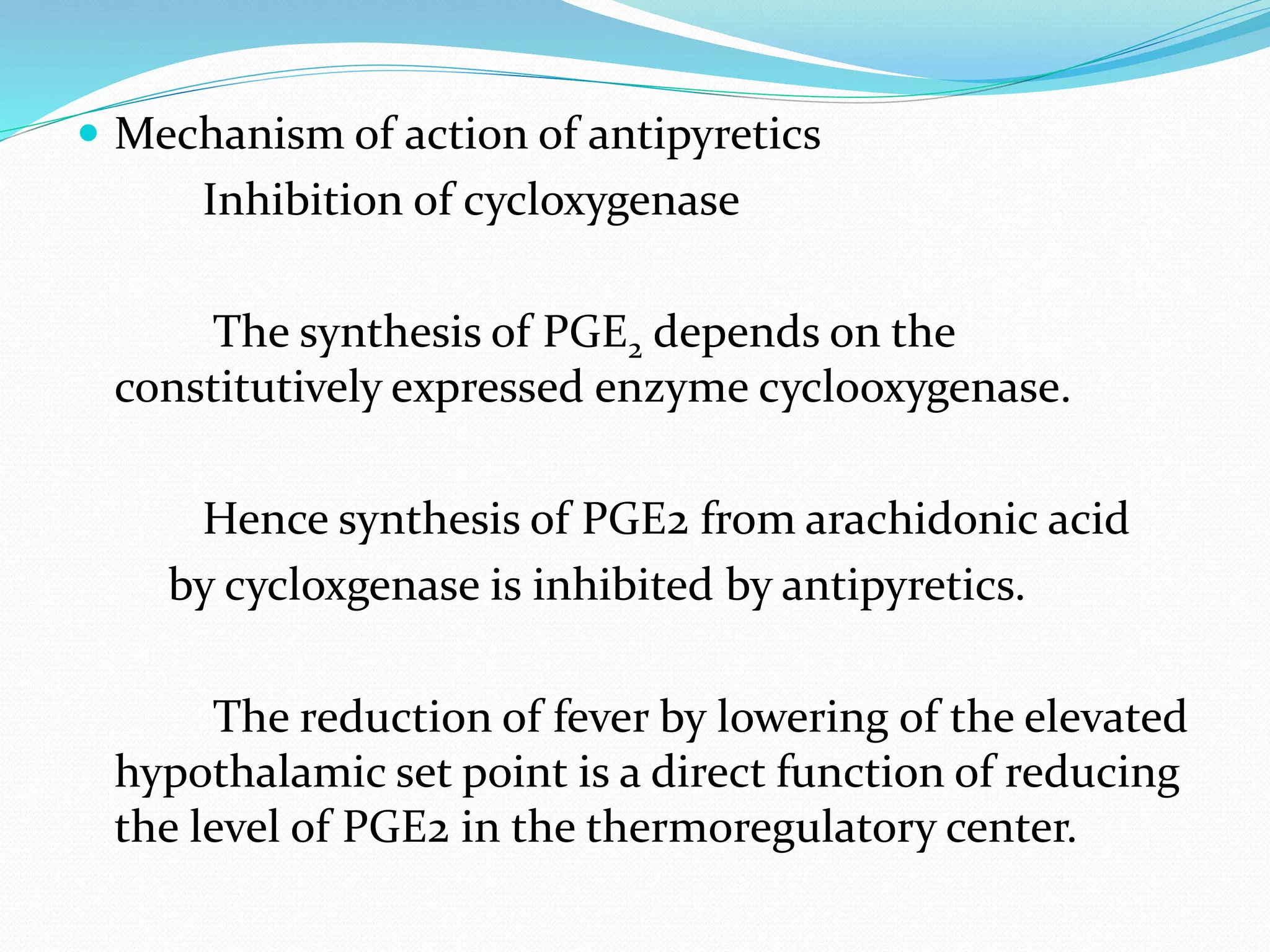
The document defines fever and its measurement, emphasizing the pathophysiological processes that lead to an increased hypothalamic set point and subsequent temperature regulation. It discusses pyrogens, differentiating between exogenous and endogenous, and outlines approaches for patient evaluation and laboratory workups. Furthermore, it addresses treatment options for fever and hyperthermia, highlighting the limitations of antipyretics and the necessary interventions for severe cases.