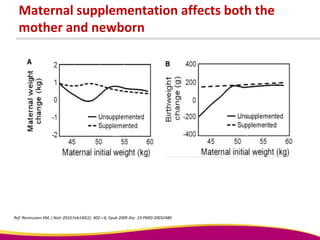
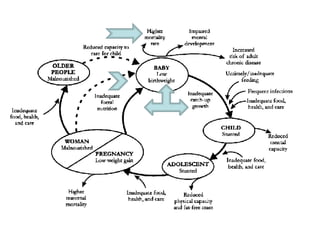
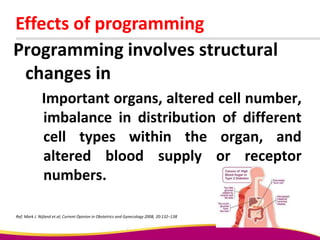
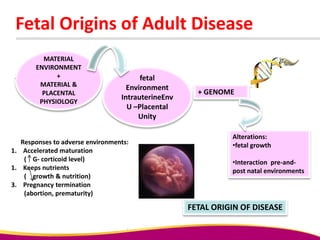
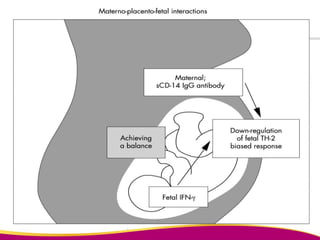
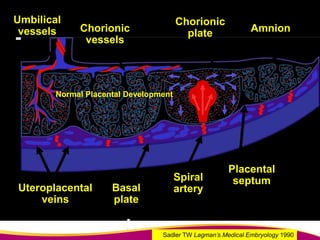
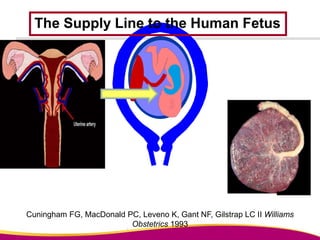
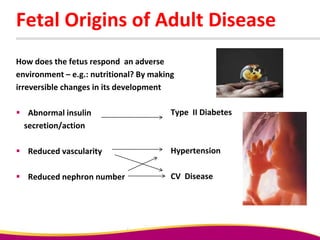
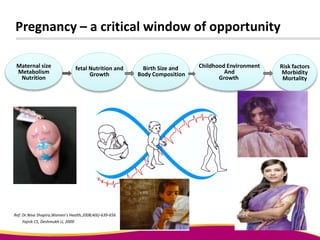
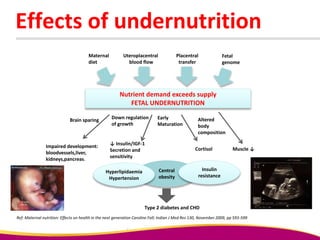
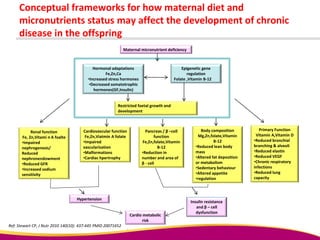
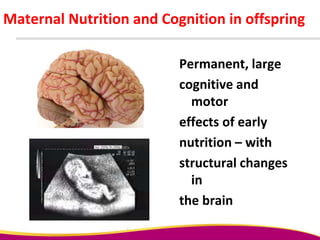
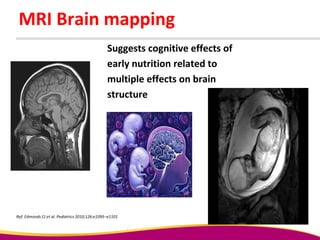
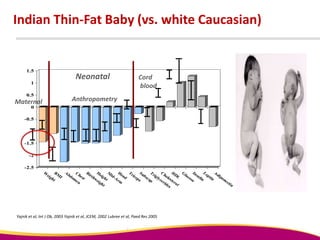
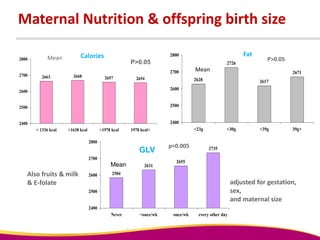
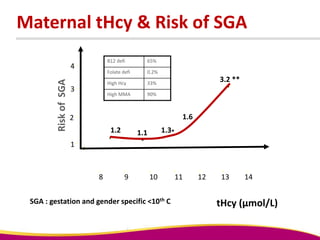
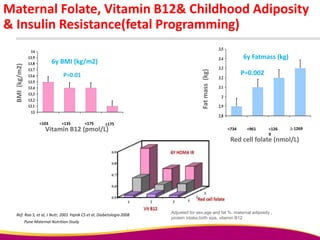
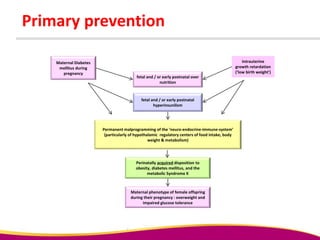
Dr. Narendra Malhotra gave the POGS oration on fetal origins of adult diseases. He has had an illustrious career as an obstetrician and gynecologist in India, holding many leadership positions and publishing extensively. His research has shown that adverse conditions in the womb and early life can program the fetus's development and permanently increase risks for diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease later in adulthood. Maternal nutrition, infections, and other environmental factors during pregnancy can influence the fetus through hormonal and epigenetic changes leading to effects on organs like the pancreas, kidneys and blood vessels that manifest as disease in later life.


















![Recommended total weight gain
Weight gain per
week after 12 weeks
First 12 weeks [88] 0.9 – 1.8 Kg (2-4 lb)
After 12 weeks [88]
BMI < 19.8 12.5 to 18 Kg (28 – 40 lb) o.5 Kg (-1 lb)
BMI of 19.8 to 26.0 11.5 to 16 Kg (25 – 35 lb) 0.4 Kg (- 1 lb)
BMI > 26.0 TO 29.0 7 to 11.5 Kg (15 – 25 lb) 0.3 Kg (0.7 lb)
BMI >29.0 7 to 11.4 Kg ( 15 – 25 lb)
Multiple pregnancy [92]
BMI < 19.8 22.7- 28.1 Kg ( 50 – 62 lb)
BMI of 19.8 to 26.0 18.1 – 24.5 Kg (40 – 54 lb)
BMI > 26.0 TO 29.0 17.2-21.3 Kg (38- 47 lb)
BMI >29.0 13.2 – 17.2 Kg (29-38 lb)
Twin pregnancy[88] 15.9 – 20.4 Kg (34 – 45 lb) 0.7 Kg (3lb)
Twin pregnancy[88] >16.2 Kg at 24 weeks [91]
22.7 Kg (50 lb) overall
Adolescent Pregnancy[93]
≤ 16 years old Upper end of recommendations
Upper end of
recommendations
> 16 – 19 years old Similar to adult women
Similar to adult
women
Recommended weight during pregnancy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fetalprogramming-111222024704-phpapp02/85/Fetal-programming-41-320.jpg)