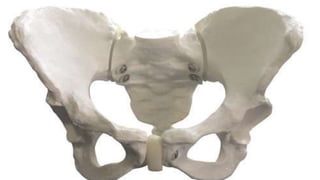
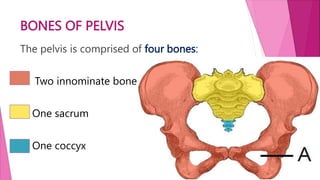
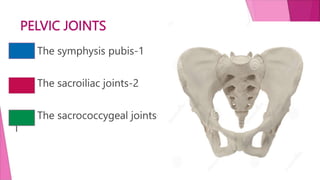
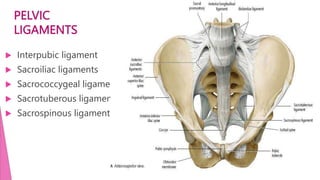
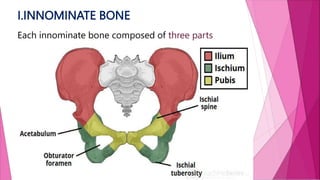
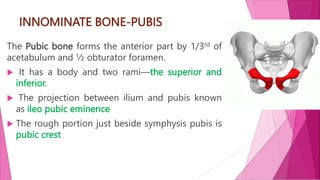
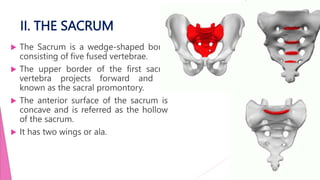
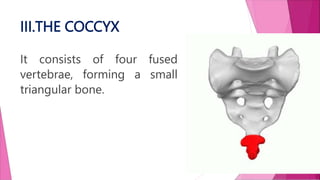
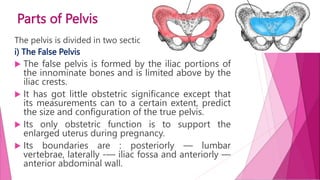
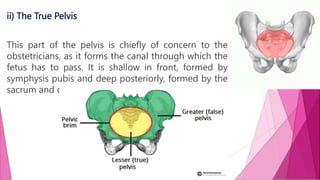
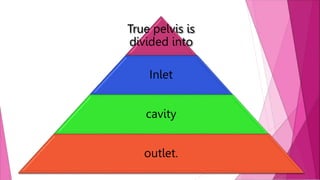
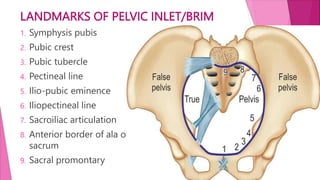
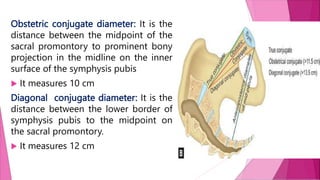
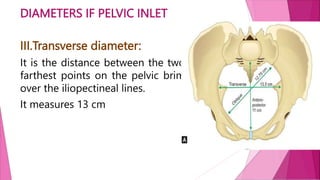
The female pelvis is comprised of four bones - the two innominate bones, sacrum, and coccyx. It has several diameters and landmarks that are important for childbirth. The pelvis can be divided into the false pelvis, pelvic inlet, cavity, and outlet. The inlet is defined by the symphysis pubis, sacral promontory, and iliac bones. Its diameters include the true conjugate, obstetric conjugate, and transverse. The cavity and outlet also have anteroposterior and transverse diameters that are measured. Knowledge of the bones, diameters, and landmarks of the female pelvis is essential for midwives during labor and delivery.