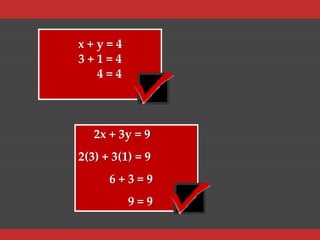
This document appears to be notes from a math class covering systems of inequalities and equations. It includes examples of solving systems of equations by elimination and substitution. It provides step-by-step instructions for setting up and solving systems using both methods. It also shows examples of applying systems of equations to word problems involving tickets sales and math test points.