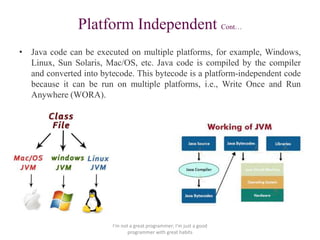
The document discusses the key features of the Java programming language. It describes Java as simple, object-oriented, platform independent, secure, robust, architecture-neutral, portable, interpreted, high-performance, distributed, multi-threaded, and dynamic. Some of its main features include automatic garbage collection, bytecode that runs on any device, secure sandboxes, and support for creating distributed and multi-threaded applications.