- It is easier to design classes for thread safety from the beginning rather than retrofitting them for thread safety later.
- The document discusses features of the Java programming language such as being object-oriented, platform independent, secure, robust, architecture-neutral, portable, high-performance, multi-threaded, and dynamic.
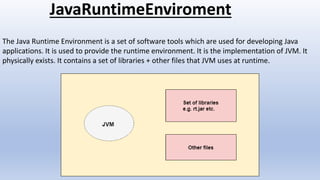
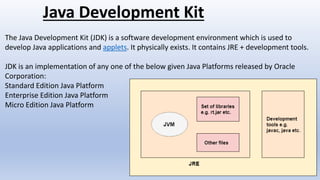
- It also explains key Java concepts like the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and Java Development Kit (JDK).


![What is Java
• Java is a programming language and a platform.
• Java is a high level, robust, object-oriented and secure programming language.
• James Gosling, Mike Sheridan, and Patrick Naughton initiated the Java language project in June
1991. The small team of sun engineers called Green Team.
Example :-
public class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("hello java");
}}
Output : hello java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mypresentation2onjava-191011034204/85/Presentation-on-java-3-320.jpg)