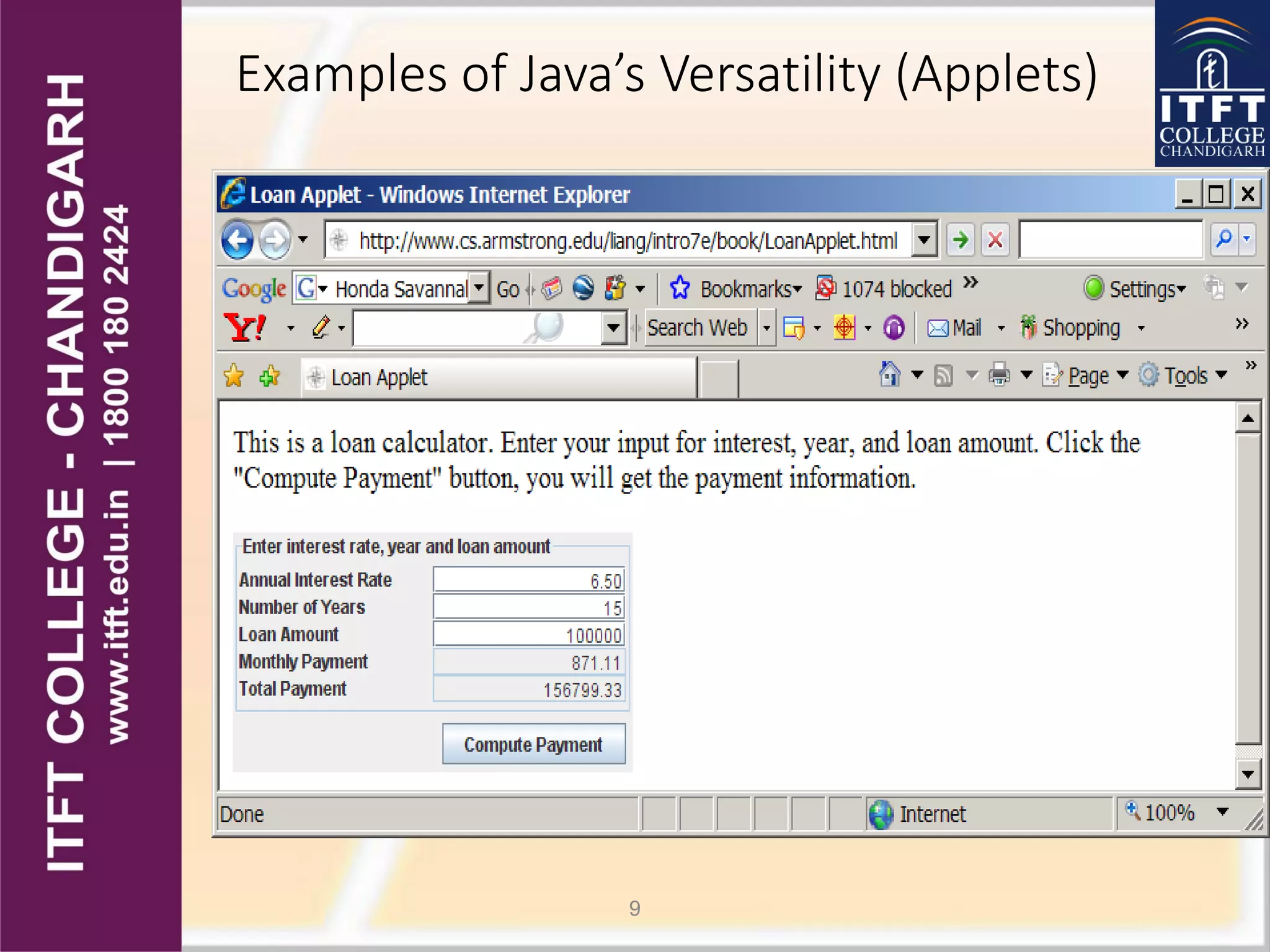
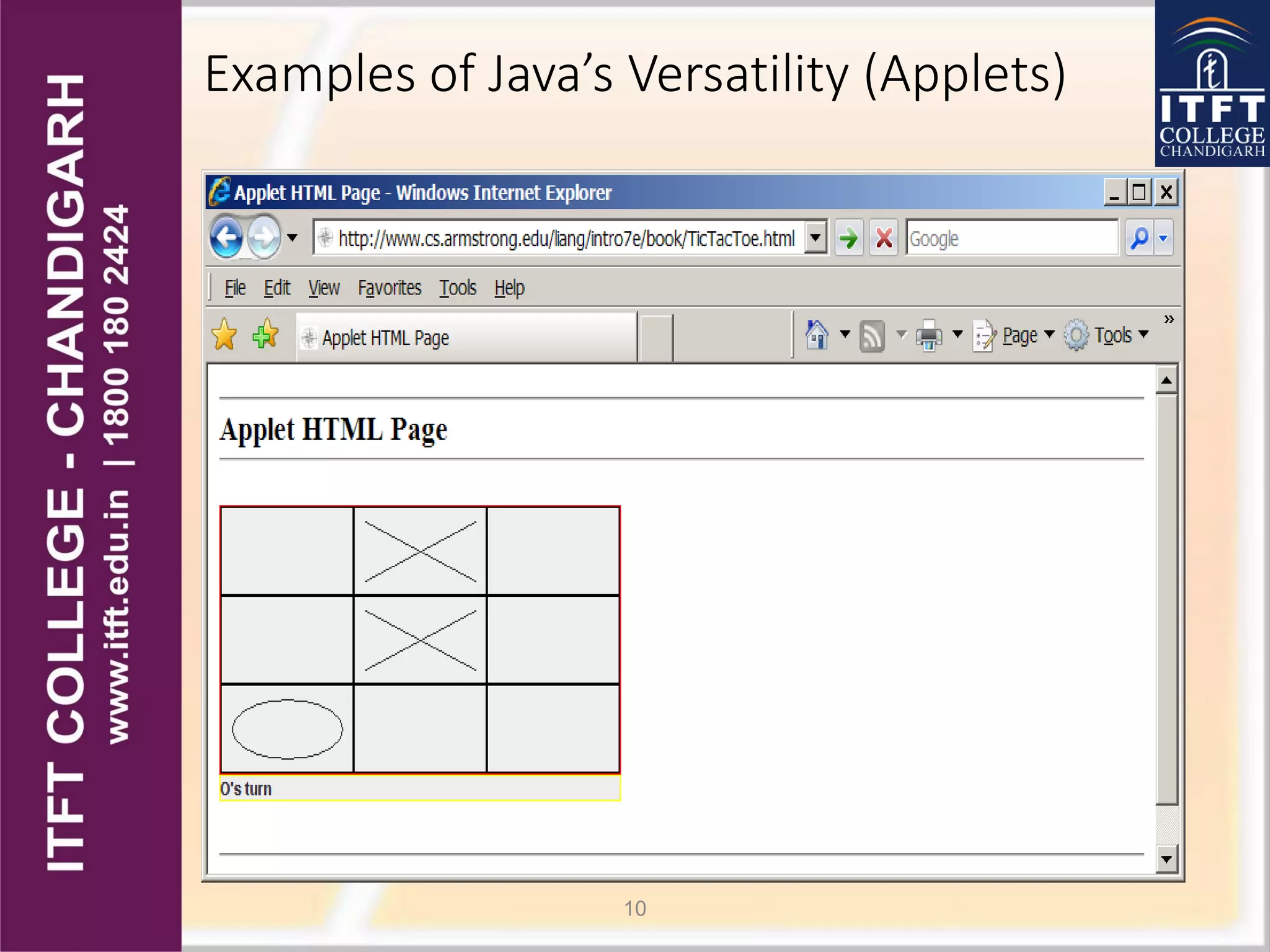
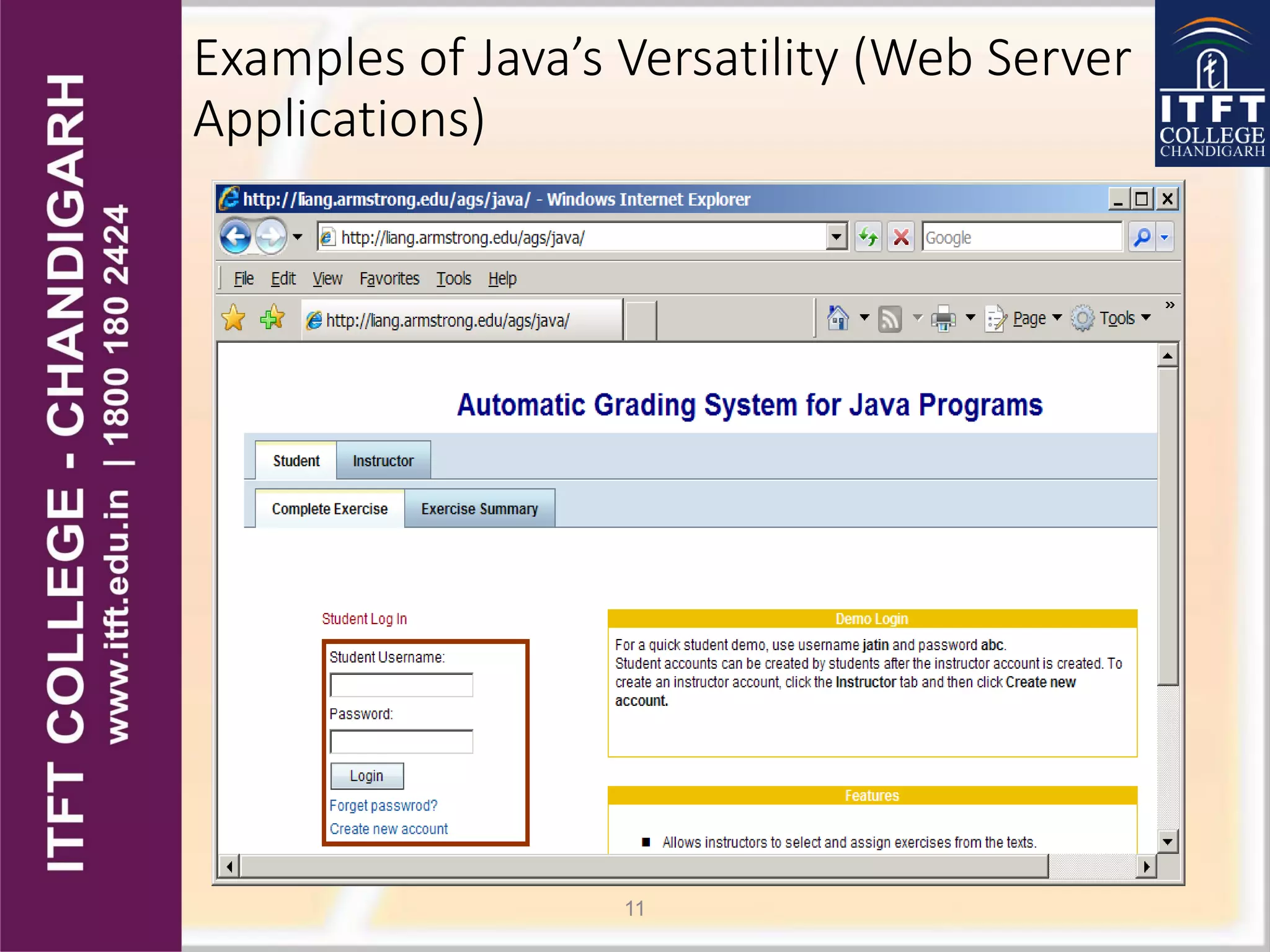
Java was developed by James Gosling in 1991 at Sun Microsystems. It was originally called Oak but found its way into web browsers like Netscape in 1995. There have been many versions released since including Java 1.0 in 1995 up to the current Java 8. Java can be used to create a variety of applications from desktop programs, to web applications, to programs for devices like phones and tablets. It is designed to be portable, secure, robust and easy to use.