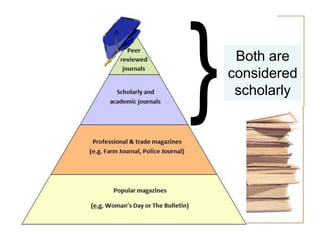
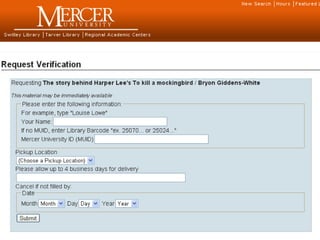
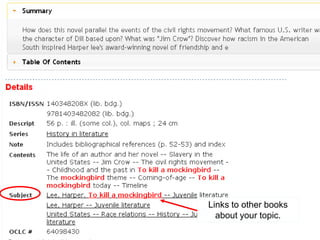
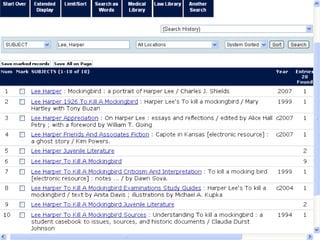
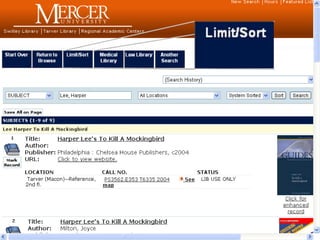
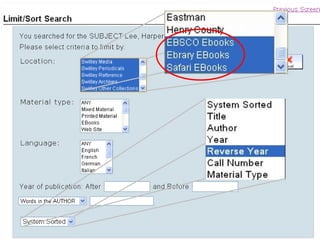
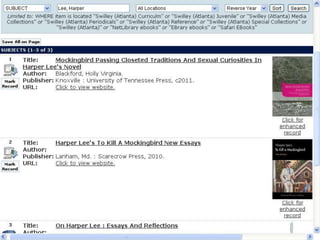
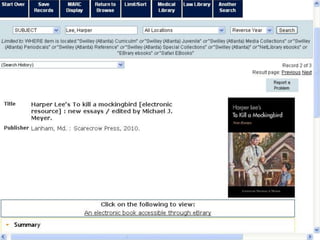
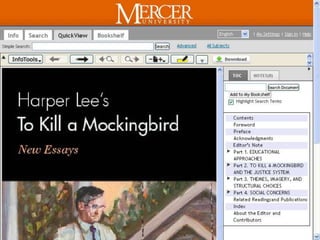
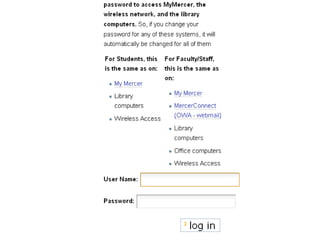
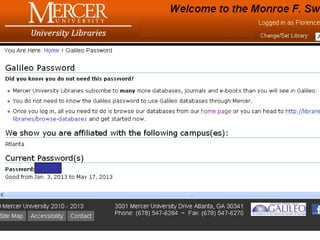
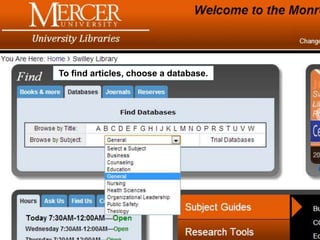
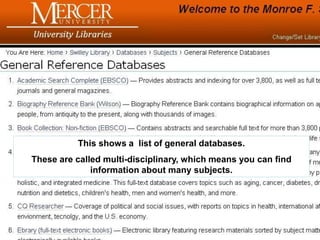
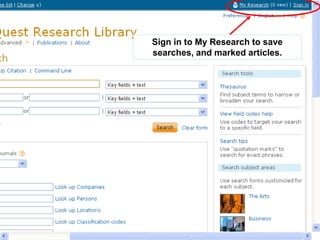
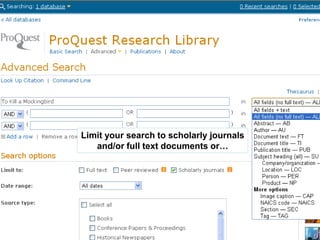
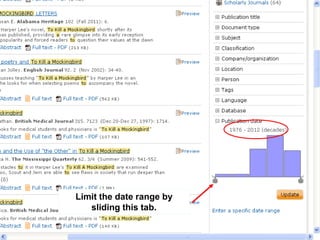
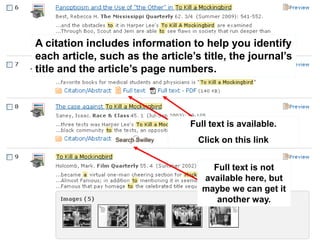
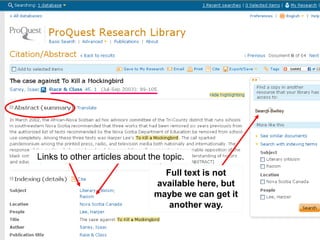
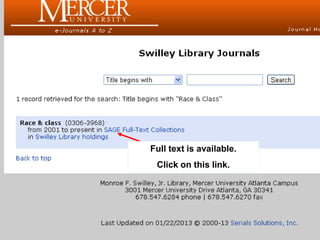
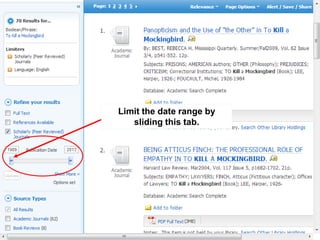
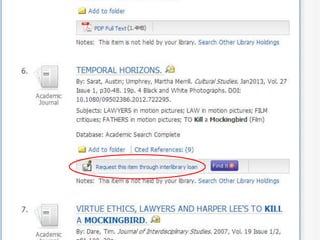
This document provides information and resources for research methods at Mercer University. It introduces Florence Tang as the liaison librarian for the College of Continuing and Professional Studies. It then defines reference librarians and their role in helping students find information. The document outlines steps for background research and developing a topic. It discusses finding books using the library catalog and finding articles using databases. It provides tips for evaluating different sources of information like scholarly journals, popular magazines, and websites. Finally, it discusses interlibrary loan, citing sources, and getting tutoring help.