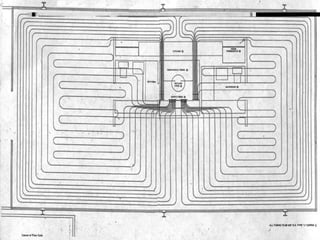
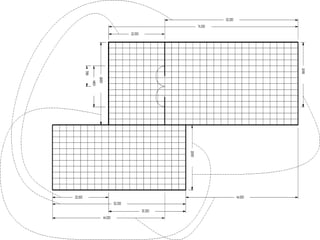
- Farnsworth House was designed and built from 1946 to 1951 by German architect Ludwig Mies van der Rohe.
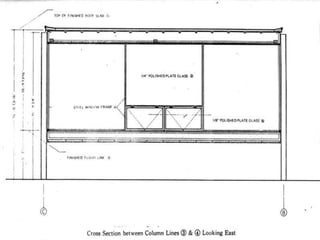
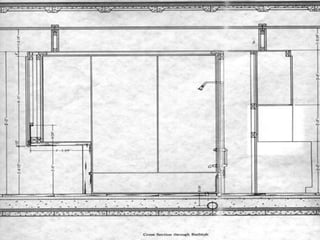
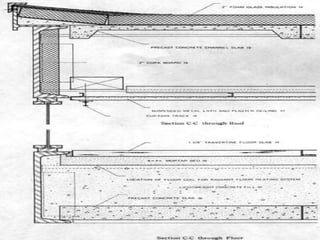
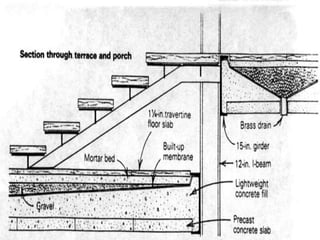
- The house consists of precast concrete floor and roof slabs supported by a carefully crafted steel skeleton frame, with single panes of glass spanning from floor to ceiling.
- Though it proved difficult to live in, Farnsworth House is still regarded as an important accomplishment of the international style for its elegant simplicity.