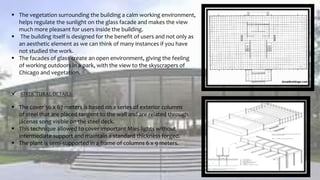
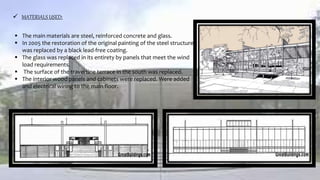
Ludwig Mies van der Rohe was a pioneering German-American architect known for developing the International Style of architecture. Some key aspects of his work included an emphasis on simplicity, open floor plans, and exposing structural elements. Some of his most famous works that exemplified his principles were the Barcelona Pavilion, which featured glass walls and floors, and Crown Hall at IIT, which had a large open space defined by a minimal steel structure. Mies strove to create flexible, universal spaces using modern materials like steel and glass.




![ By 1928 Mies was appointed Director of the GermanSection of the
International Exposition in Barcelona, because the Weimar Republic wished to
present itself asprogressive.
The building was balanced with a pool and asculpture by Georg Kolb. He
became well known for theglass and steel “Skin and Bones” clarity that
BarcelonaPavilion expressed, as well as the belief that space must bemade
universal and flexible. The Barcelona Pavilion housed the first Barcelona chair,
which was designed for the pavilion, originally in whiteleather.
In 1930 he designed the ‘Tugendhat house’ in Brno,Czechoslovakia. The
building is a luxurious two-story plan, which can be entered from the street
and the upper level.
The individual spaces built, could be shut off using draperies on ceiling tracks.
Thisdesign, inspired Van der Rohe to design some of his mostfamous pieces of
furniture, including the Brno Chair, theTugendhat chair, and the X table.
In 1930, Gropius recommended Mies van der Rohe assuccessor to Hannes
Meyer who had taken over WalterGropius as director of the Dessau Bauhaus.
Mies focused thecurriculum on architecture and interior design, with
moreintensity than for other subjects.
When the Dessau Bauhaus was closed by the Nazis, Mies van der Rohe
moved it to Berlinin 1933, but on August 10, after 15 years of operation,
theschool was closed by the Nazi regime, because it didn’t suit
thenationalistic taste of German leaders. Same year, Mies’s work was on
display in The Modern Architecture-International exibhit.
. It was at thisexhibition that the term “International Style” .
FANSWORTH HOUSE [1951]
SEAGRAM BUILDING [1958]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessismore1finalll-220504054132/85/less-is-more-mies-van-de-rohe-5-320.jpg)