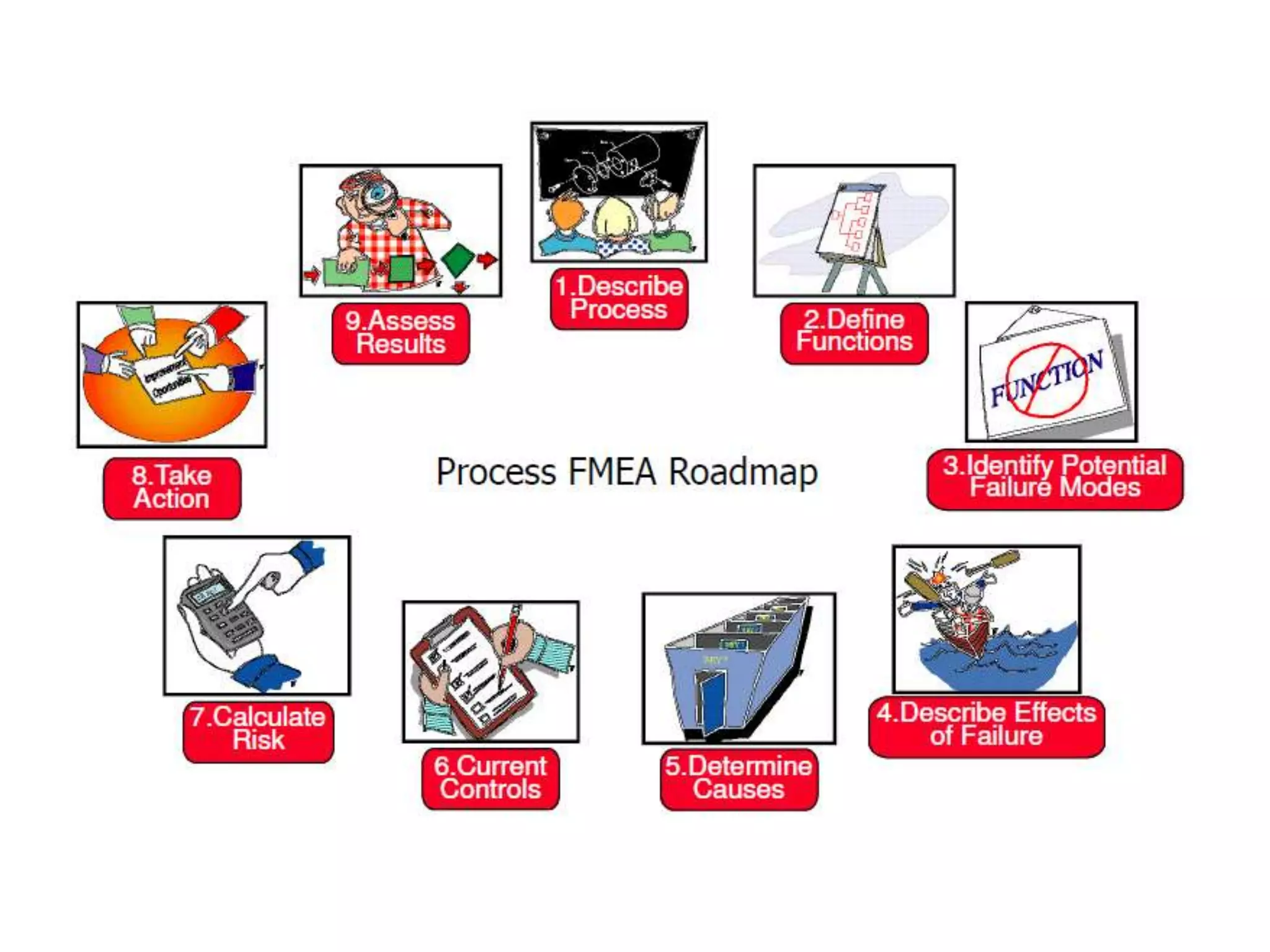
FMEA is a systematic method for identifying and preventing potential problems or failures in a design, product or process. It was developed in the 1960s for the aerospace industry. The key purposes of FMEA are to identify potential failure modes and their causes, eliminate or reduce risks, and document the analysis. FMEA is applied in both design processes and operational processes to improve quality by minimizing failures. Common mistakes include applying FMEA too late, having the wrong team members, and overdependence on numerical ratings.