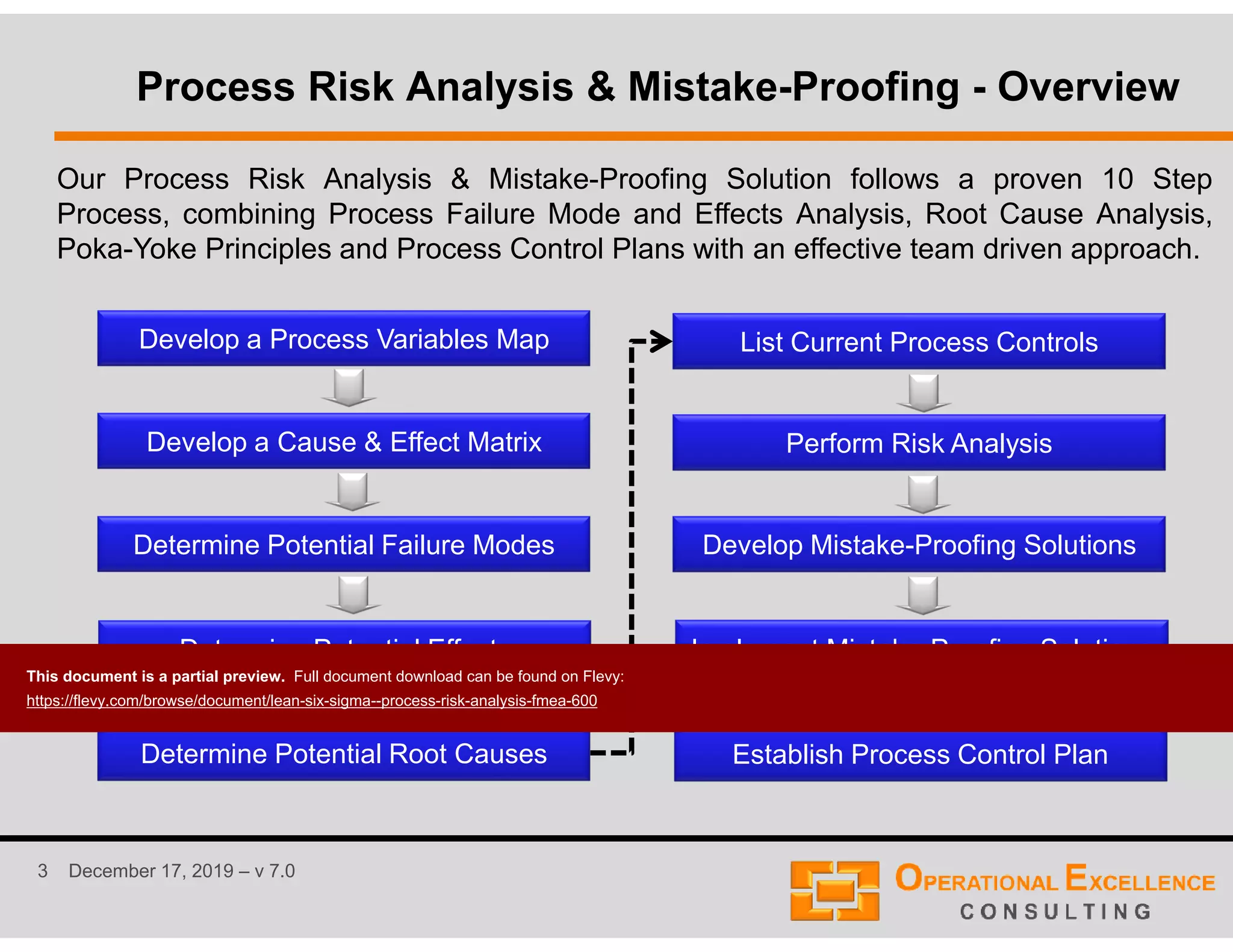
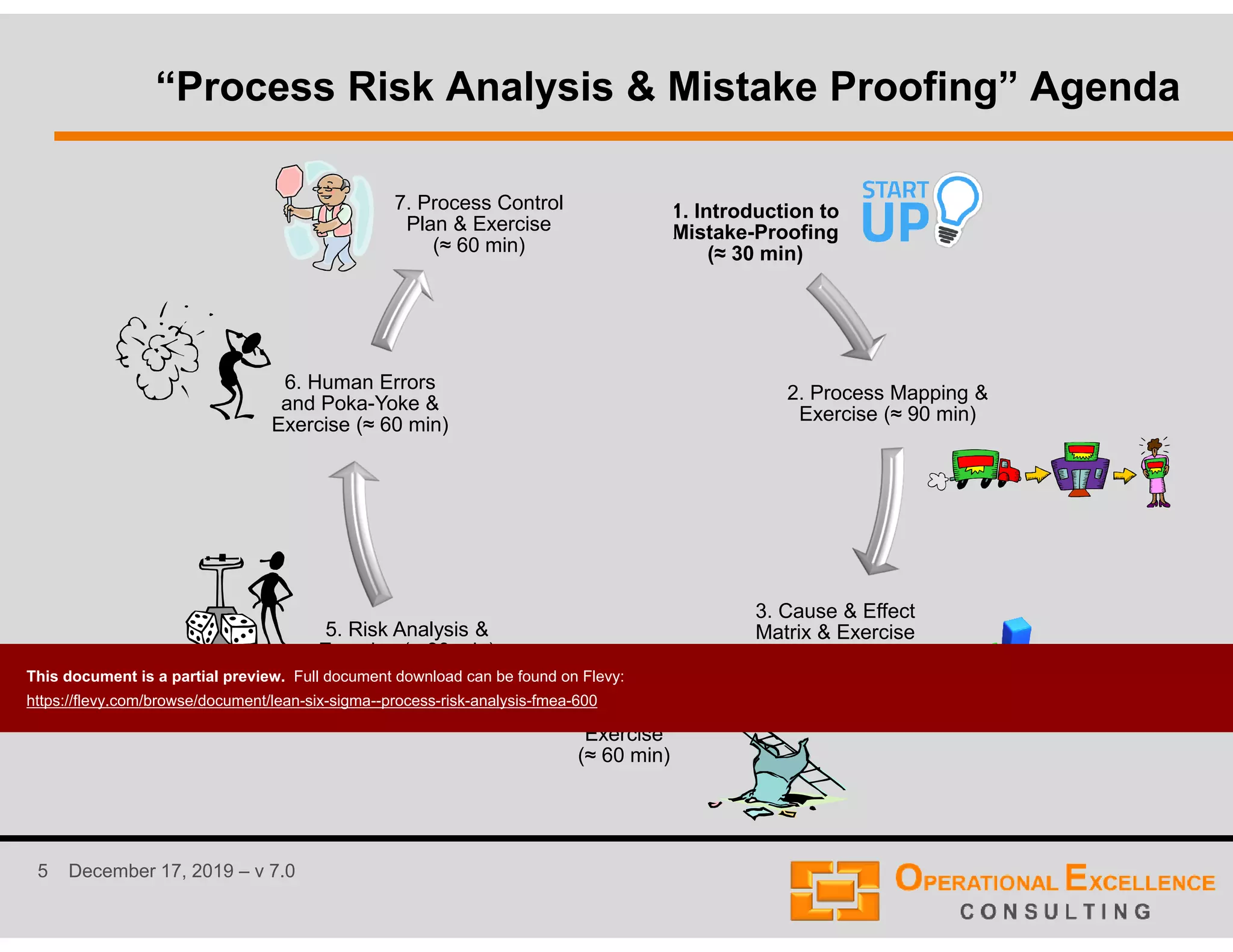
The document outlines a 10-step process risk analysis and mistake-proofing solution that incorporates principles such as failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), root cause analysis, and poka-yoke. It emphasizes the importance of a team-driven approach with multi-disciplinary involvement to identify and mitigate potential risks while enhancing process control. Additionally, the document details various methodologies and categorizations involved in analyzing and mapping processes for improved efficiency and quality.