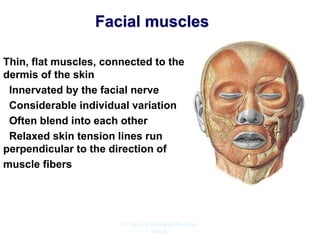
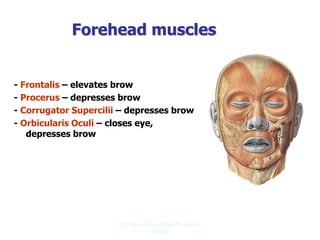
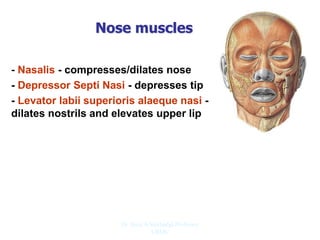
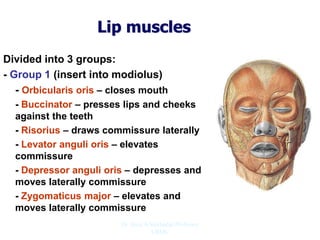
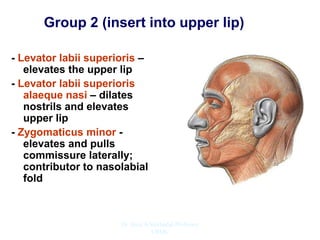
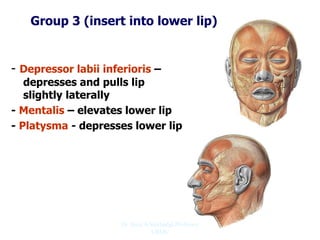
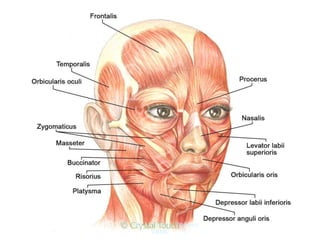
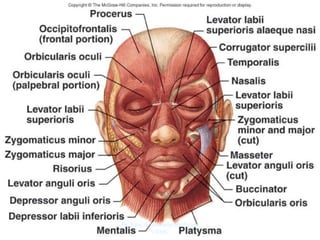
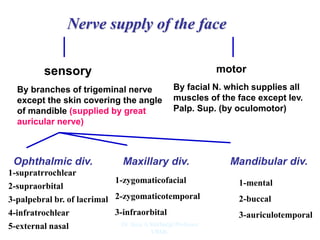
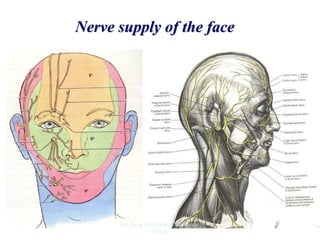
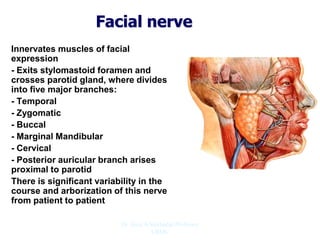
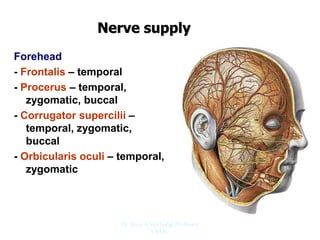
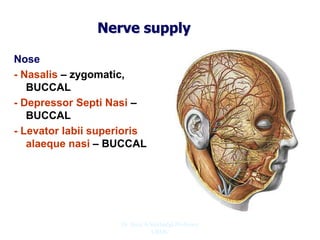
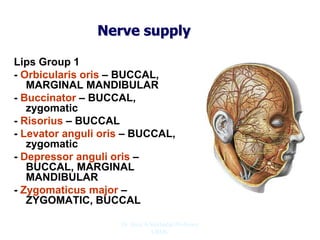
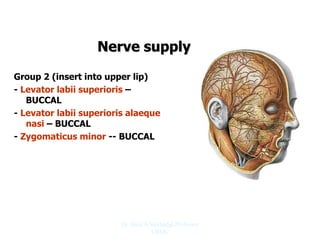
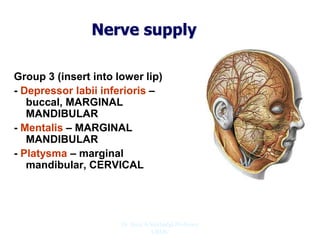
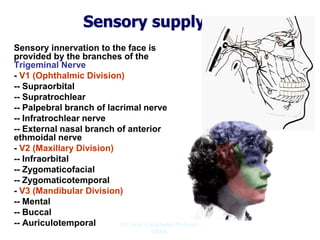
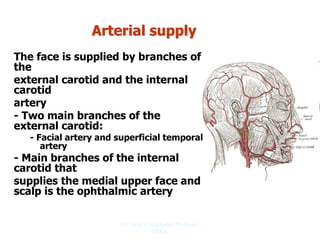
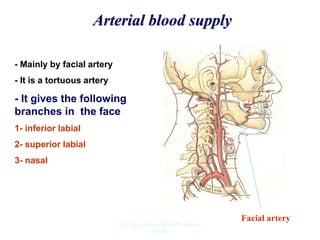
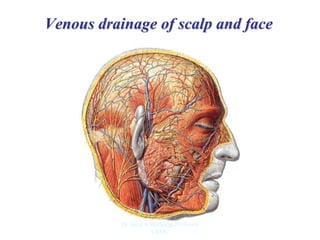
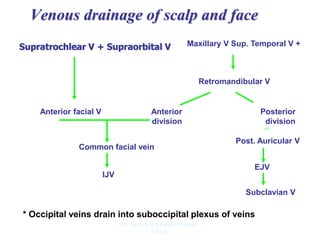
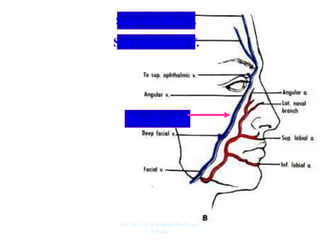
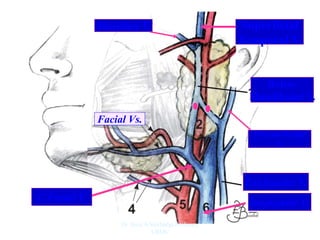
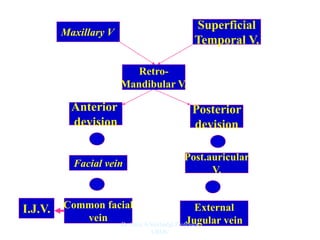
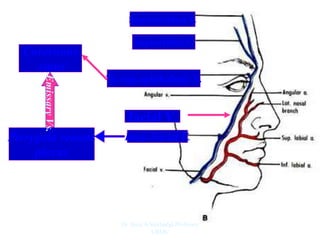
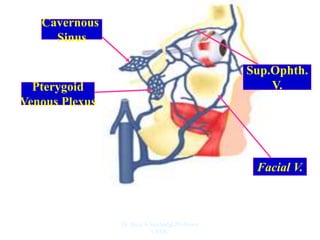
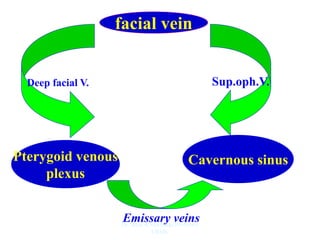
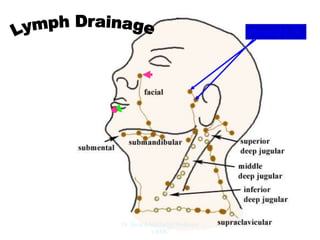
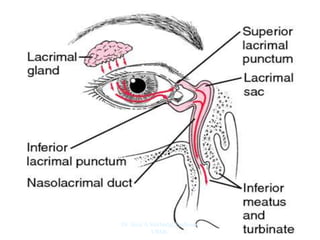
The document outlines the anatomy of the face, including layers such as skin, superficial fascia, and muscles, highlighting the vascular nature of facial skin and the absence of deep fascia to allow for facial expression. It details the nerve supply, arterial supply, and venous drainage of the face, emphasizing the role of the facial nerve in innervating facial muscles and the importance of the trigeminal nerve in sensory supply. Additionally, it covers the anatomy of the lacrimal apparatus, including the lacrimal gland and passages involved in tear drainage.