The document discusses methods to handle selfishness in replica allocation within mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) to improve data accessibility and minimize network partitioning. It proposes a selfish node detection algorithm that evaluates nodes based on a credit risk score and suggests a novel replication allocation technique that reduces traffic overhead. The proposed system demonstrates improvements in performance, particularly in reducing query delay compared to existing methods.

![Handling Selfishness in Replica Allocation over a Mobile Ad Hoc Network for improving data accessibility
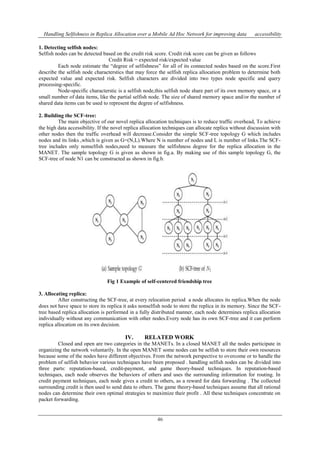
Data replication techniques that address both query delay and data accessibility in a MANET and it
demonstrates a trade-off and proposes techniques to balance it. Dynamic Connectivity based Grouping (DCG)
introduces the cooperative caching based data access methods, including cache path , cache data, and hybrid.
V. RESULT
In this module, the performance of the proposed method is analyzed. Based on the analyzed results X-graphs
are plotted. Delay is the basic parameters considered here and X-graph is plotted for this parameters.
In this graph we are comparing existing system with proposed system. By observing this graph we
conclude that the delay proposed system is better than existing system.
VI. CONCLUSION
The problem in the existing system is selfish nodes from the replica allocation perspective this problem
is referred as selfish replica allocation to overcome this problem two techniques has been used selfish node
detection method and novel replica allocation technique. Every node in the MANET calculates the credit risk
information to measure the degree of selfishness to detect the selfish nodes, by these selfish nodes can be
detected and are not used in transferring the packets from one node to the other node.
REFERENCES
[1]. Jae-Ho Choi, Kyu-Sun Shim, SangKeun Lee, and Kun-Lung Wu,”Handling Selfishness in Replica
Allocation over a Mobile Ad Hoc Network”,IEEE Trans. Mobile computing ,vol 11,no.2,Feb 2012.
[2]. L. Anderegg and S. Eidenbenz, “Ad Hoc-VCG: A Truthful and Cost-Efficient Routing Protocol for
Mobile Ad Hoc Networks with Selfish Agents,” Proc. ACM MobiCom, pp. 245-259, 2003.
[3]. P. Padmanabhan, L. Gruenwald, A. Vallur, and M. Atiquzzaman, “A Survey of Data Replication
Techniques for Mobile Ad Hoc Network Databases,” The Int’l J. Very Large Data Bases, vol. 17, no.
5, pp. 1143-1164, 2008.
[4]. T. Hara and S.K. Madria, “Data Replication for Improving Data Accessibility in Ad Hoc Networks,”
IEEE Trans. Mobile Computing, vol. 5, no. 11, pp. 1515-1532, Nov. 2006.
[5]. W. Wang, X.-Y. Li, and Y. Wang, “Truthful Multicast Routing in Selfish Wireless Networks,” Proc.
47
ACM MobiCom, pp. 245-259,2004.
[6]. S.-Y. Wu and Y.-T. Chang, “A User-Centered Approach to Active Replica Management in Mobile
Environments,” IEEE Trans. Mobile Computing, vol. 5, no. 11, pp. 1606-1619, Nov. 2006.
[7]. J. Zhai, Q. Li, and X. Li, “Data Caching in Selfish Manets,” Proc. Int’l Conf. Computer Network and
Mobile Computing, pp. 208-217, 2005.
[8]. D. Hales, “From Selfish Nodes to Cooperative Networks -Emergent Link-Based Incentives in Peer-to-
Peer Networks,” Proc. IEEE Int’l Conf. Peer-to-Peer Computing, pp. 151-158, 2004.
[9]. T. Hara and S.K. Madria, “Consistency Management Strategies for Data Replication in Mobile Ad Hoc
Networks,” IEEE Trans. Mobile Computing, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 950-967, July 2009.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f1074547-141101052038-conversion-gate01/85/International-Journal-of-Engineering-Research-and-Development-3-320.jpg)