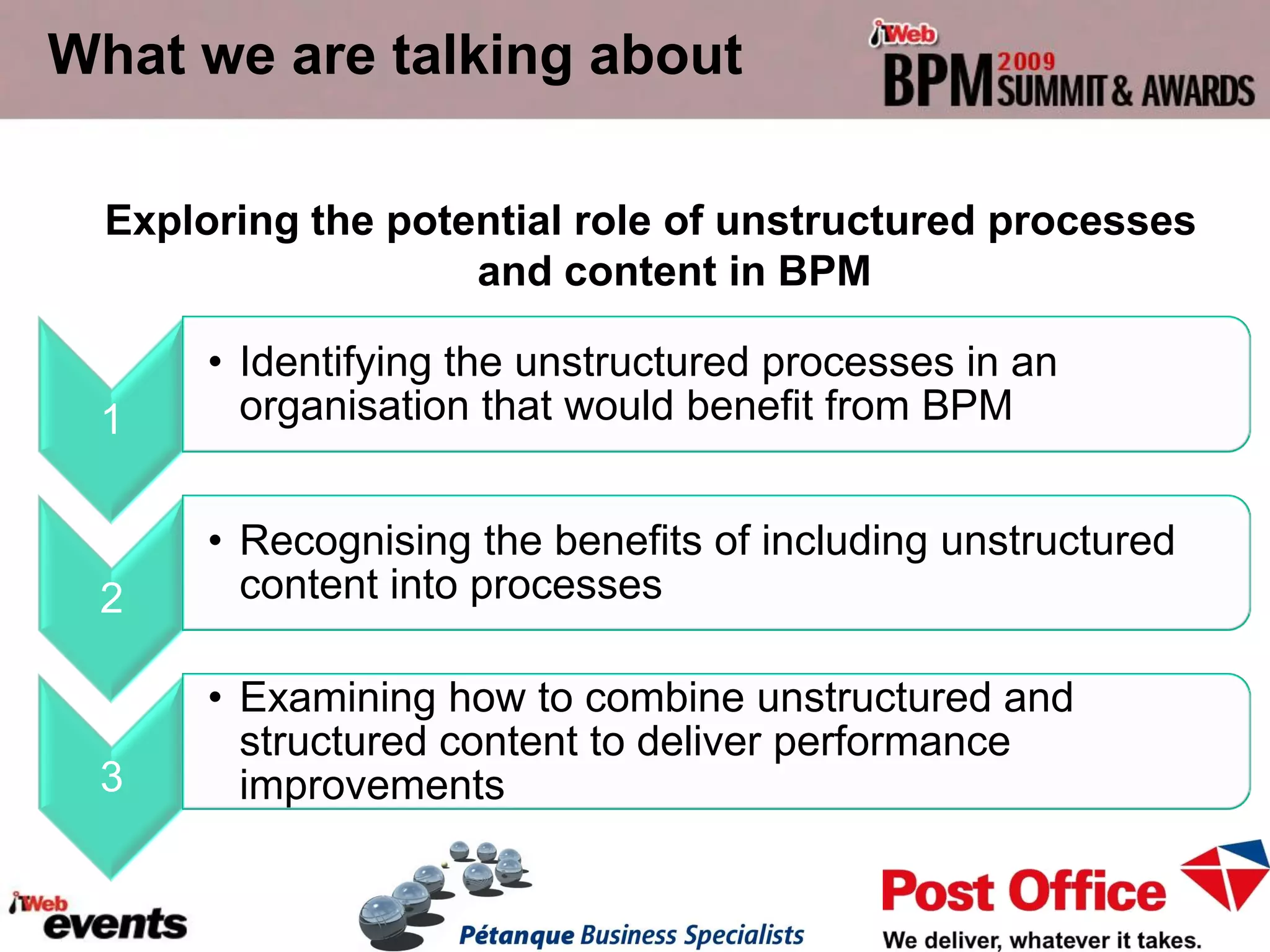
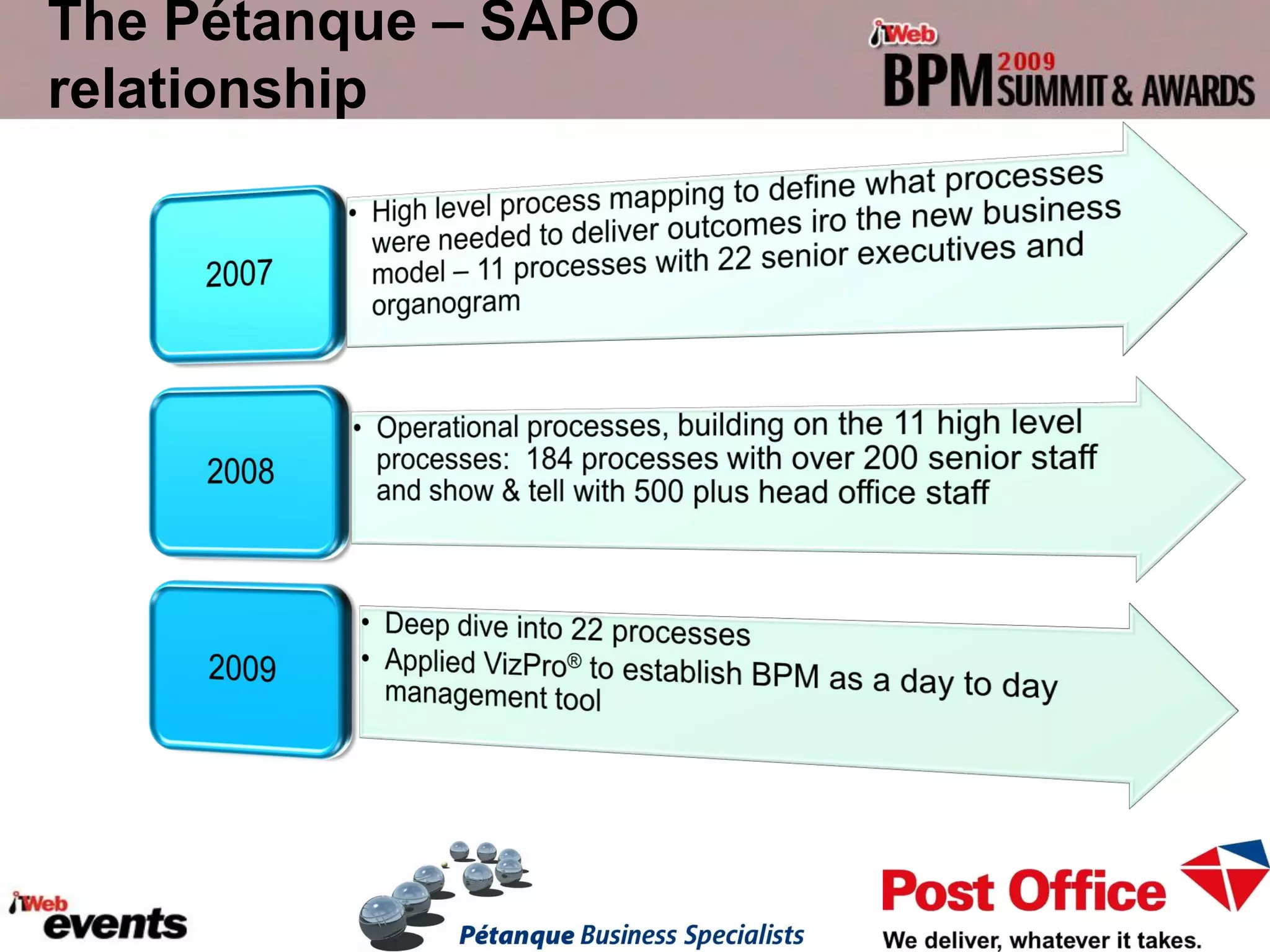
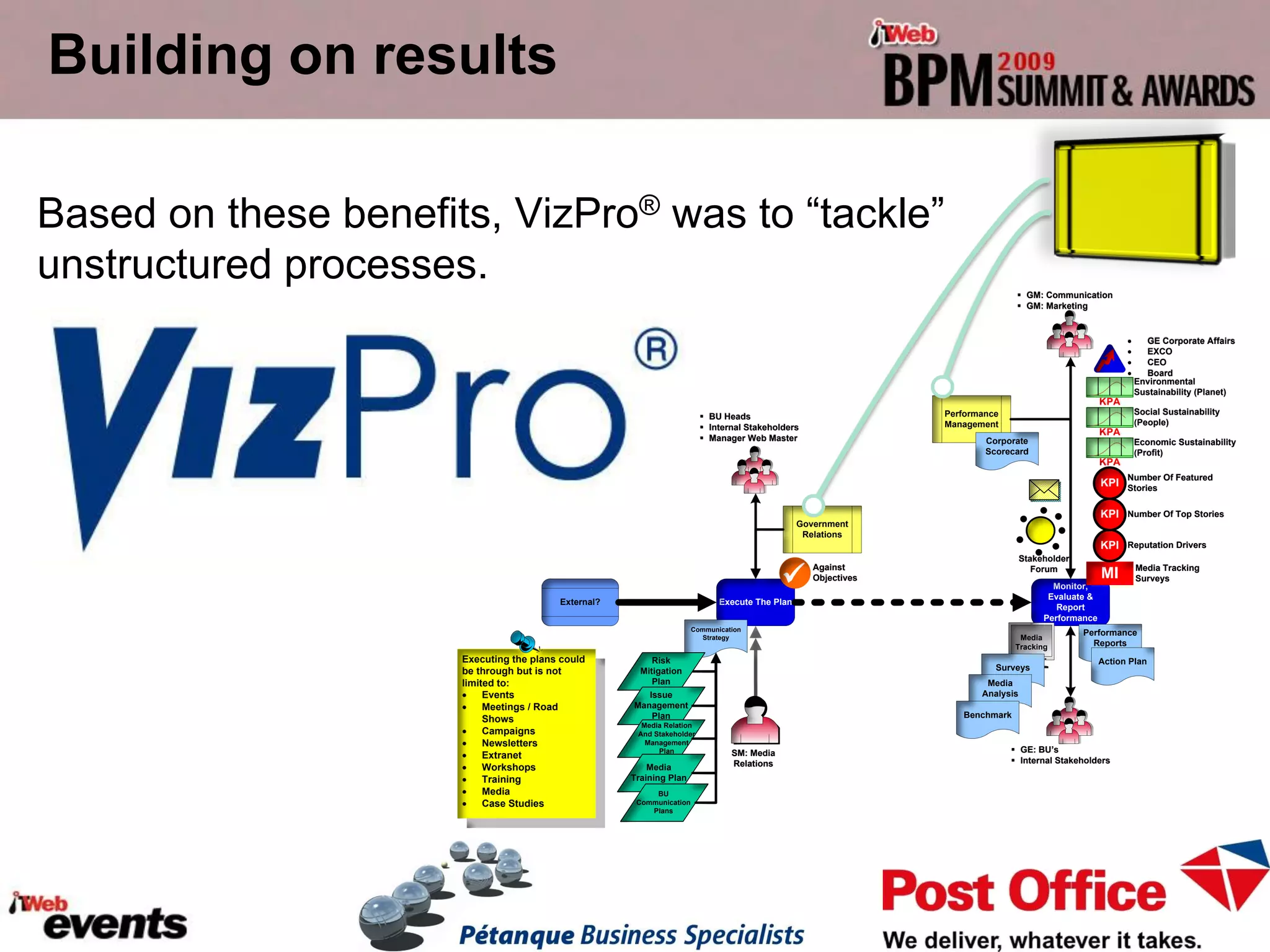
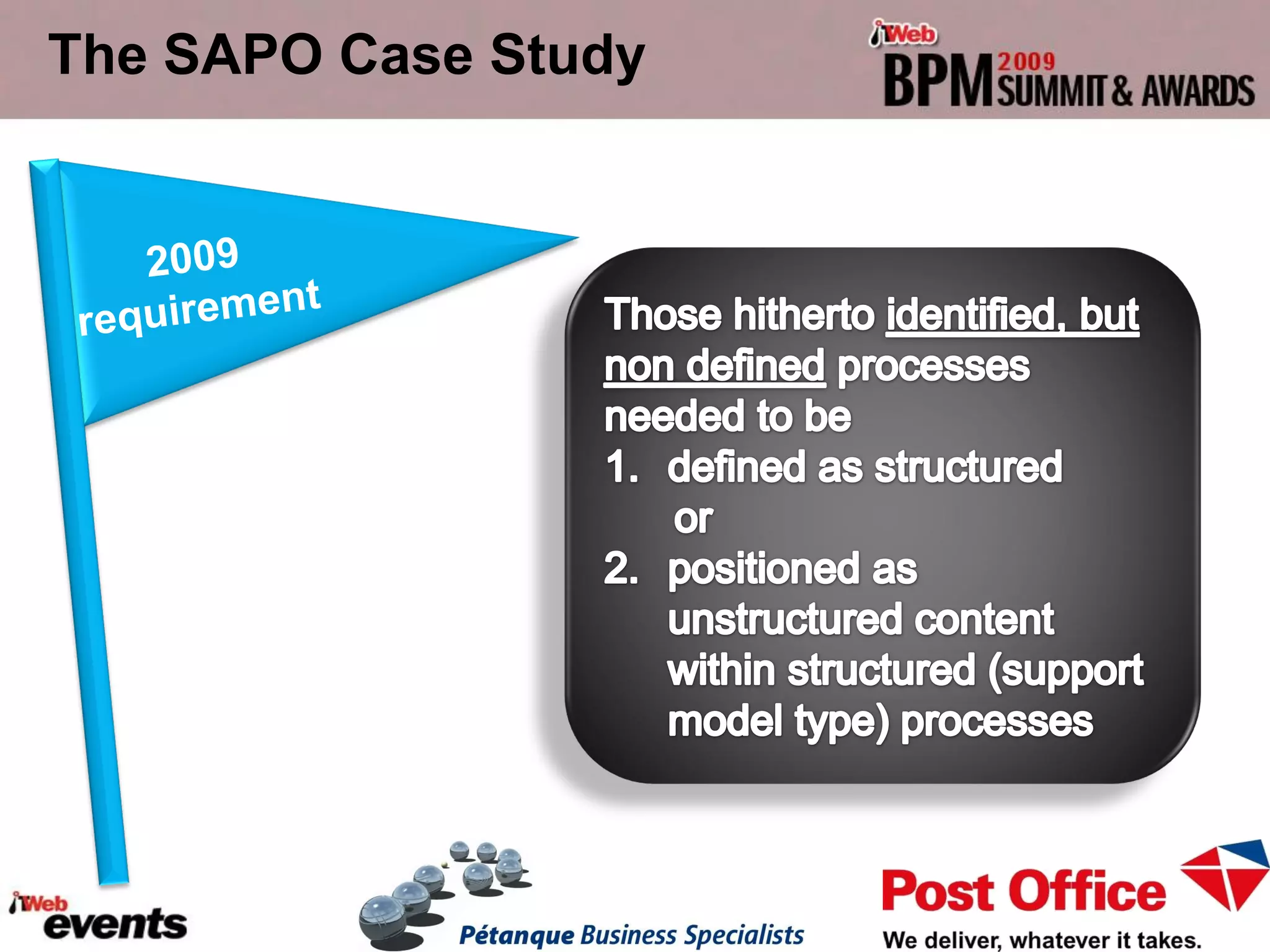
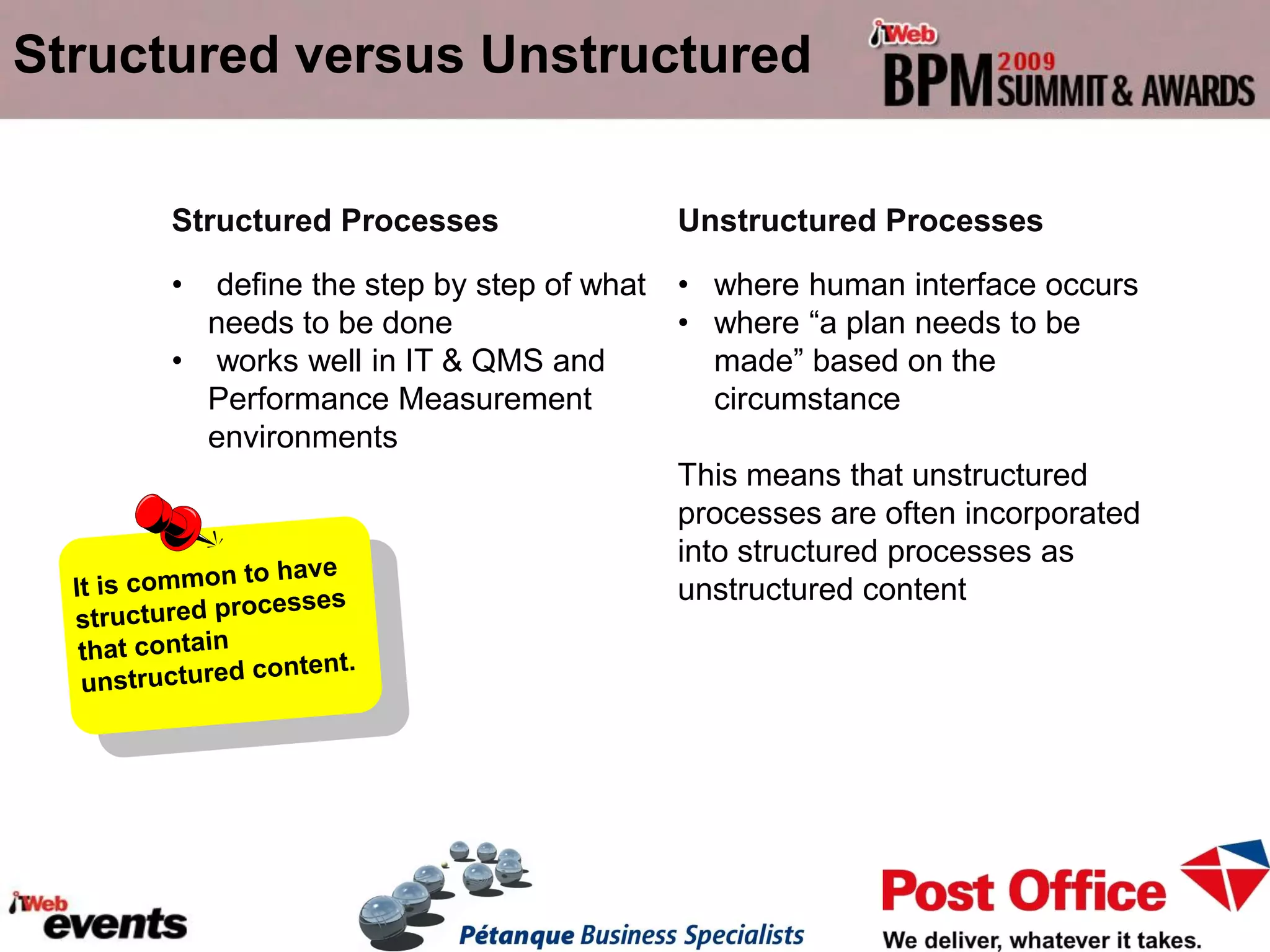
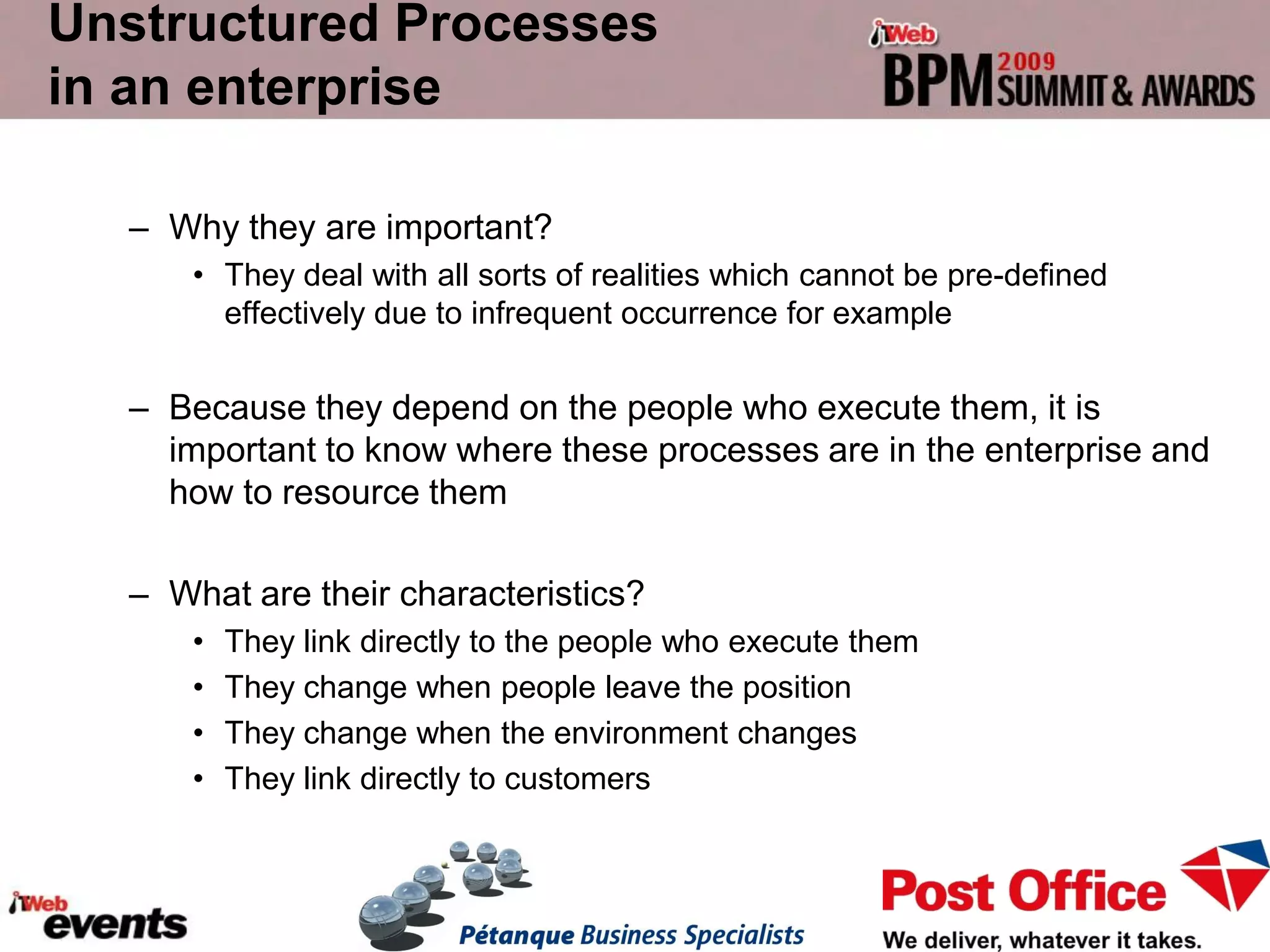
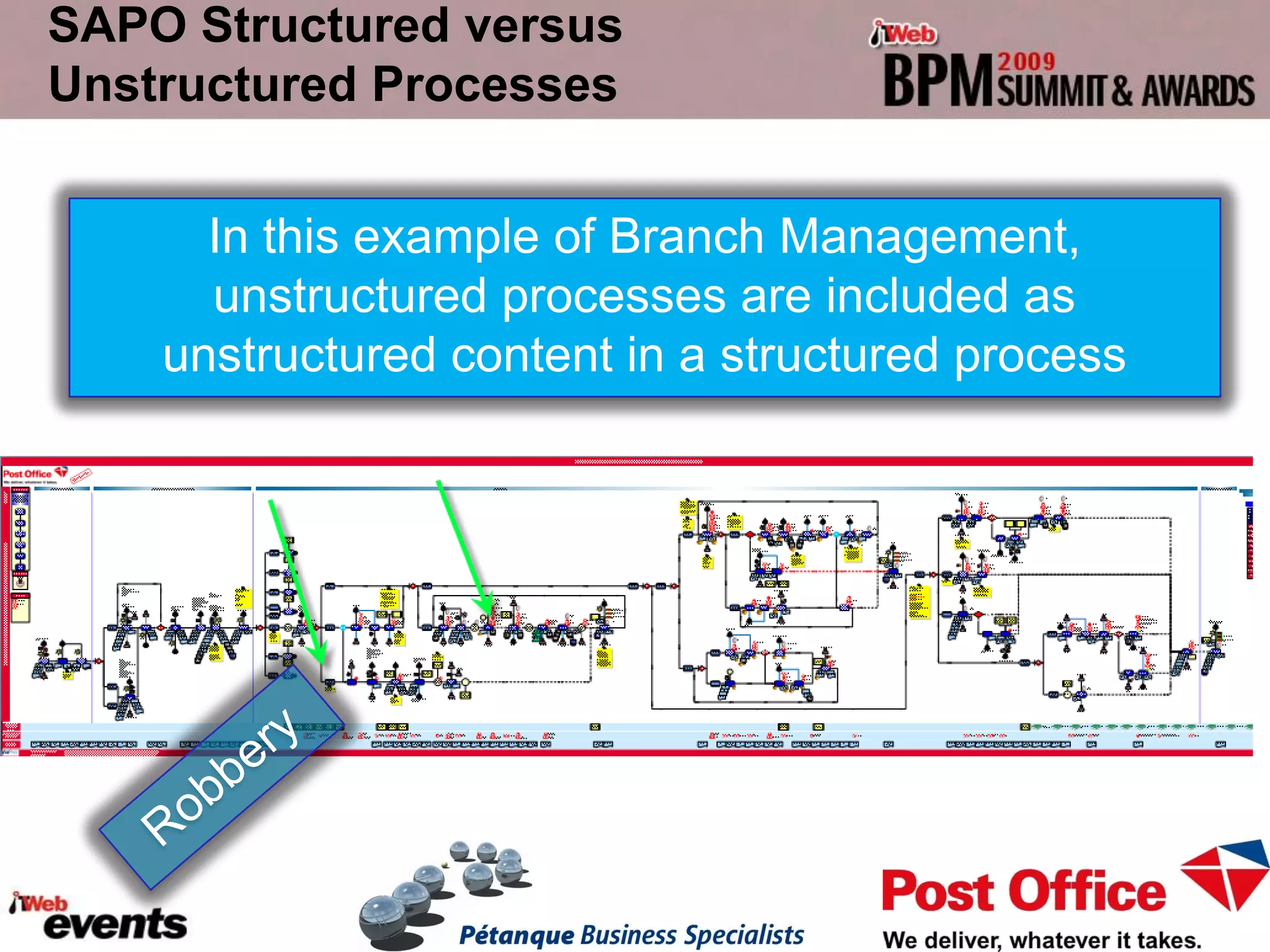
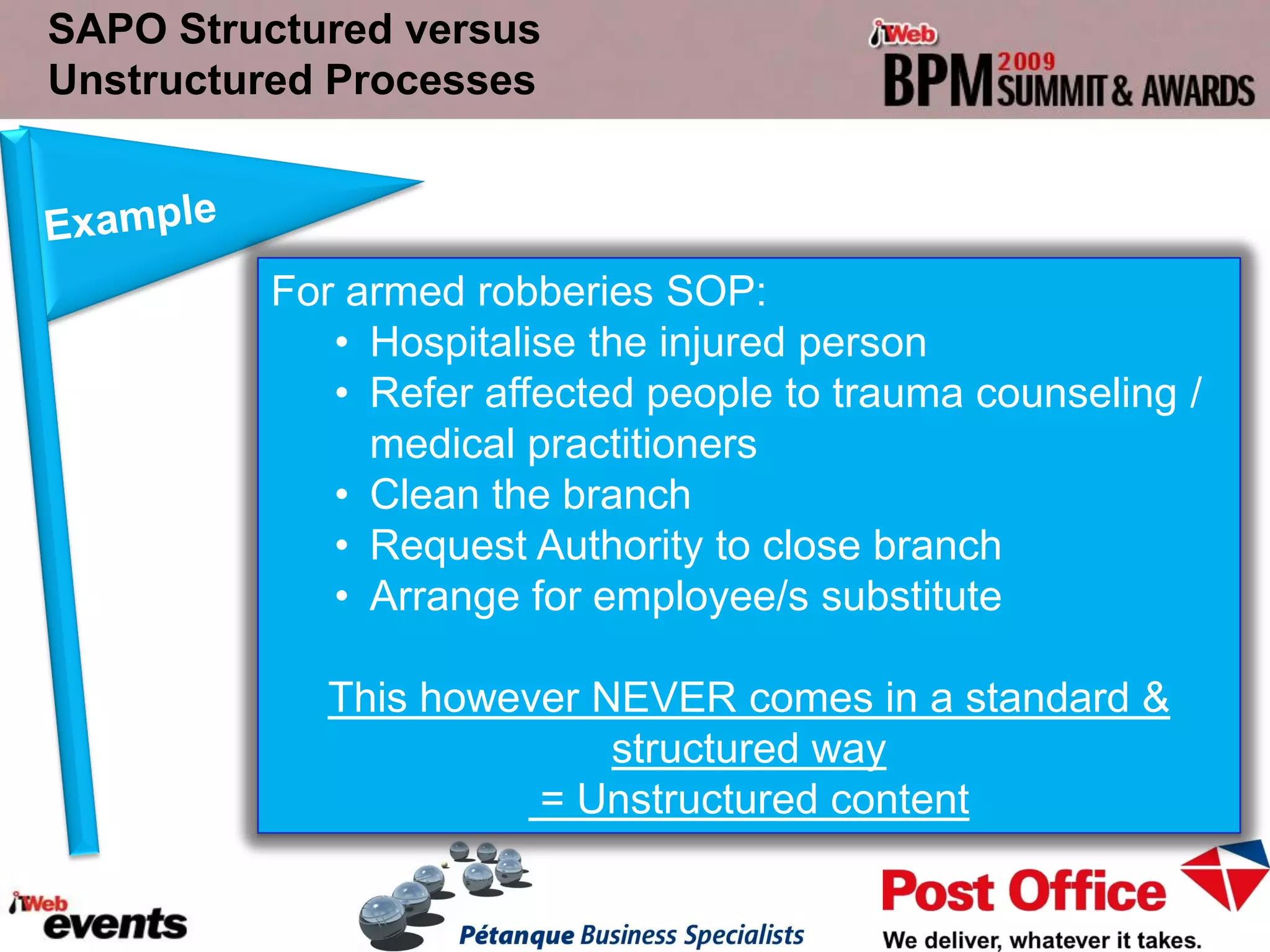
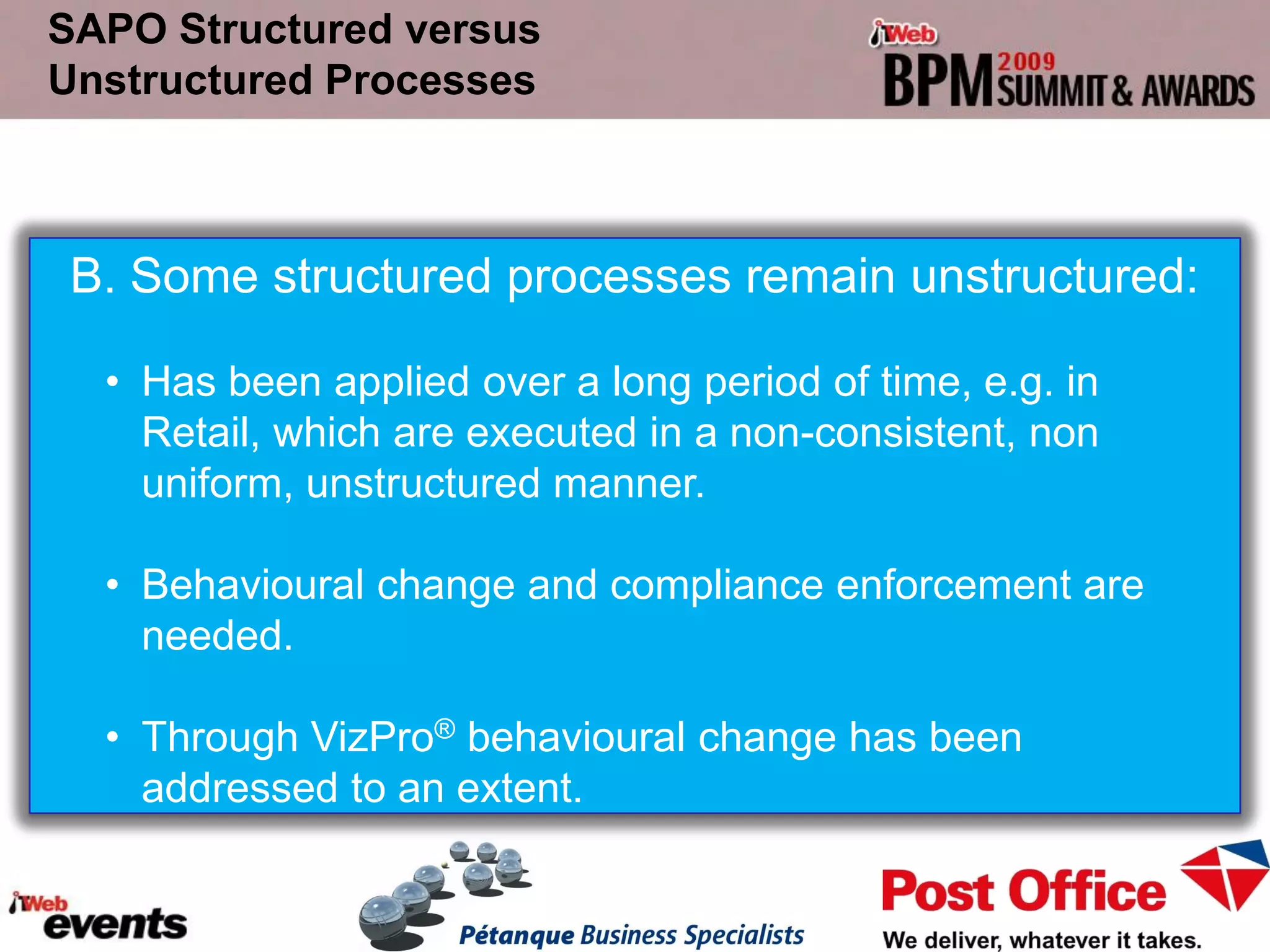
The document discusses exploring the potential role of unstructured processes and content in business process management (BPM). It identifies unstructured processes that could benefit from BPM, recognizes the benefits of including unstructured content in processes, and examines how to combine unstructured and structured content to drive performance improvements. The case study of SAPO aims to define, link, and manage processes to achieve strategic goals using both structured and unstructured elements. Unstructured processes are important because they deal with realities that cannot be pre-defined and depend on human execution.